Risk pooling can have a positive impact on the economy by helping to reduce the financial burden of health care on individuals and families. This, in turn, can free up money that can be spent on other goods and services, which can boost economic growth.
How does the pooling of risks offer protection?
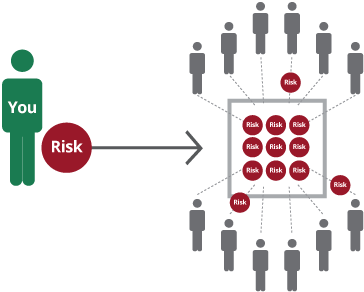
What is risk pooling? together allows the higher costs of the less healthy to be offset by the relatively lower costs of the healthy, either in a plan overall or within a premium rating category. In general, the larger the risk pool, the more predictable and stable the premiums can be.
Why is risk pooling important?
Pooling ensures that the risk related to financing health interventions is borne by all the members of the pool and not by each contributor individually. Risk pooling is required because of the large uncertainty in the magnitude and timing of an individual's health care expenditure needs.
What is risk pooling in economics?
Definition of 'risk pooling' Risk pooling is the practice of sharing all risks among a group of insurance companies. With risk pooling arrangements, instead of participants transferring risk to someone else, each company reduces their own risk.
How insurance companies use risk pooling to generate a profit for their businesses?
The essential insurance model involves pooling risk from individual payers and redistributing it across a larger portfolio. Most insurance companies generate revenue in two ways: Charging premiums in exchange for insurance coverage, then reinvesting those premiums into other interest-generating assets.
What are two benefits of pooling?
There are several benefits to using multinational pooling for companies both large and small....They include:Economies of scale and purchasing power.Global experience rating.Financial cost savings.Improved underwriting terms and conditions.Annual reporting.Management tool and information base.
What is the main purpose of pooling?
The main purpose of pooling is to reduce the size of feature maps, which in turn makes computation faster because the number of training parameters is reduced. The pooling operation summarizes the features present in a region, the size of which is determined by the pooling filter.
What is risk pooling example?
A “Risk pool” is a form of risk management that is mostly practiced by insurance companies, which come together to form a pool to provide protection to insurance companies against catastrophic risks such as floods or earthquakes.
What does pooling mean in finance?
Finance. Pooling is the grouping together of assets, and related strategies for minimizing risk. For example: Asset-backed securities (ABS) is a security whose income payments are backed by a specified pool of underlying assets.
How does risk pooling being connected to your life?
In Insurance Terms, risk pooling is the sharing of common financial risks evenly among a large number of people. So, the Capital Markets or here, Insurance companies, take that risk from you in exchange for a regular payment called premium. The company believes the premium is enough to cover the risk.
What are the benefits of pooling in insurance?
Not insuring is risky, so pooling with others helps spread the risk. Typically, insurers combine groups with favorable experience together with groups with adverse experience. The result is the high and low risk help offset each other. This moderates premiums for all groups.
How the insurer uses pooling for their own benefit?
Insurance pooling is a practice wherein a group of small firms join together to secure better insurance rates and coverage plans by virtue of their increased buying power as a bloc. This practice is primarily used for securing health and disability insurance coverage.
What is the number one reason risk pooling is valuable to the insurance industry?
Risk pooling allows a large number of people to be insured for a small amount of money. Risk pooling transfers risk from an individual to a group.
What is the number one reason risk pooling is valuable to the insurance industry?
Risk pooling allows a large number of people to be insured for a small amount of money. Risk pooling transfers risk from an individual to a group.
What could be an advantage of order pooling for a supplier?
Pooling allows you to pay for the long-haul portion of the shipment one time — often at a more competitive rate since truckload and intermodal get more cost-effective as distance increases.
What are the principles of risk pooling?
Risk-pooling systems are most effective when their participants adhere to several principles: (1) participants should agree that the pool is for needs that arise unpredictably, not for routine, predictable needs; (2) giving to those in need should not create an obligation for them to repay; (3) participants should not ...
Is pooling necessary?
Pooling mainly helps in extracting sharp and smooth features. It is also done to reduce variance and computations.
Why is risk pooling important?
Risk pooling is essential to the concept of insurance. The earliest known insurance policies were written some 5,000 years ago, to protect shippers against the loss of their cargo and crews at sea. Any one of them would be devastated by the loss of a ship. But by pooling their resources, these ancient businessmen were able to spread the risks more evenly among their numbers, so each paid a relatively small amount. Under the Babylonians, those receiving a loan to fund a shipment would pay an additional amount in exchange for a rider cancelling the loan if a shipment should be lost at sea.
Why did the insurance industry grow?
The insurance industry grew enormously, as individuals and businesses sought to protect themselves from economic catastrophe by transferring their risks to an insurance pool. We still have commercial shipping insurance – just as we did in the ancient world – and we also insure against such diverse risks as fires, floods, theft, auto accidents, kidnap and ransom schemes, defaults on the part of our debtors, lawsuits and judgments, dying too early and even against the risk of living too long.
What is premium insurance?
The premium is the cost of pooling one's own risk with that of others via an insurance company and includes the insured's share of expected claims costs, administrative expenses, sales and marketing expenses, and a profit for the insurer. If a premium payer is affected by a covered risk, the insurance company, and not the insured, takes the hit.
What happens if premiums are higher than expected?
If claims are higher than expected, however, the insurance company may have to raise rates on policy holders across the board.
What is the job of an actuary?
A class of professional experts in finance and probability, called actuaries, work for insurance companies to attempt to predict the probability and severity of risk. They also take lapse rates and interest rates or other expected rates of return on investment assets into account, with the goal of setting acceptable premiums.
Do capital markets take risk?
The capital markets, meanwhile, are generally happy to take on risk from individuals and corporations – in exchange for a premium they believe is sufficient to cover the risk.
Is a negative event a risk?
If a negative event can be predicted in a certain case, it's not a risk, but certainty – and certainties are not insurable (with the possible exception of death, which is insurable because its timing is uncertain). Furthermore, if a risk is too frequent, it cannot meaningfully be transferred to an insurance company, ...

History of Risk Pooling
- Risk pooling is essential to the concept of insurance. The earliest known insurance policies were written some 5,000 years ago, to protect shippers against the loss of their cargo and crews at sea. Any one of them would be devastated by the loss of a ship. But by pooling their resources, these ancient businessmen were able to spread the risks more ...
Modern Insurance Policies
- The insurance industry grew enormously, as individuals and businesses sought to protect themselves from economic catastrophe by transferring their risks to an insurance pool. We still have commercial shipping insurance – just as we did in the ancient world – and we also insure against such diverse risks as fires, floods, theft, auto accidents, kidnap and ransom schemes, de…
Risk and Premium
- A class of professional experts in finance and probability, called actuaries, work for insurance companies to attempt to predict the probability and severity of risk. They also take lapse rates and interest rates or other expected rates of return on investment assets into account, with the goal of setting acceptable premiums. The premium is the cost of pooling one's own risk with tha…
Insurable vs. Uninsurable Risks
- Not every negative economic event is insurable. For risk pooling to be effective, the risk should be unforeseen and infrequent. If a negative event can be predicted in a certain case, it's not a risk, but certainty – and certainties are not insurable (with the possible exception of death, which is insurable because its timing is uncertain). Furthermore, if a risk is too frequent, it cannot meanin…