What are the consequences of social class?
Consequences of Social Class A. Social class affects aspects of family life such as mate selection, divorce patterns, and childrearing practices.1. Children of the capitalist class are under great pressure to select the right mate, and they have a narrower field of potential partners.2.
How do social structures impact on health?
- Health behaviors reflect interplay between people and contextual factors.
- “Social determinants” include societal institutions, ideologies, and inequalities.
- Health behaviors contribute to and reflect embodiment and other biosocial processes.
- Recent work engages health lifestyles, agency, and multilevel life course dynamics.
What are the social factors affecting health?
- socioeconomic status, which includes education, income, and occupation
- the neighborhood and physical environment, such as housing, the built environment, and environmental and toxic exposures
- the food environment, which involves such factors as food insecurity and food access
- health care, including access to affordable, quality care
How do social ties affect our health?
- A Protective Influence. Having extended family who are active on the internet also tends to improve mental health over time.
- Awareness of Social Ties. “Much research ignores how social media has changed our relationships.” said Hampton. ...
- Social Media Impacts on Psychological Distress. ...
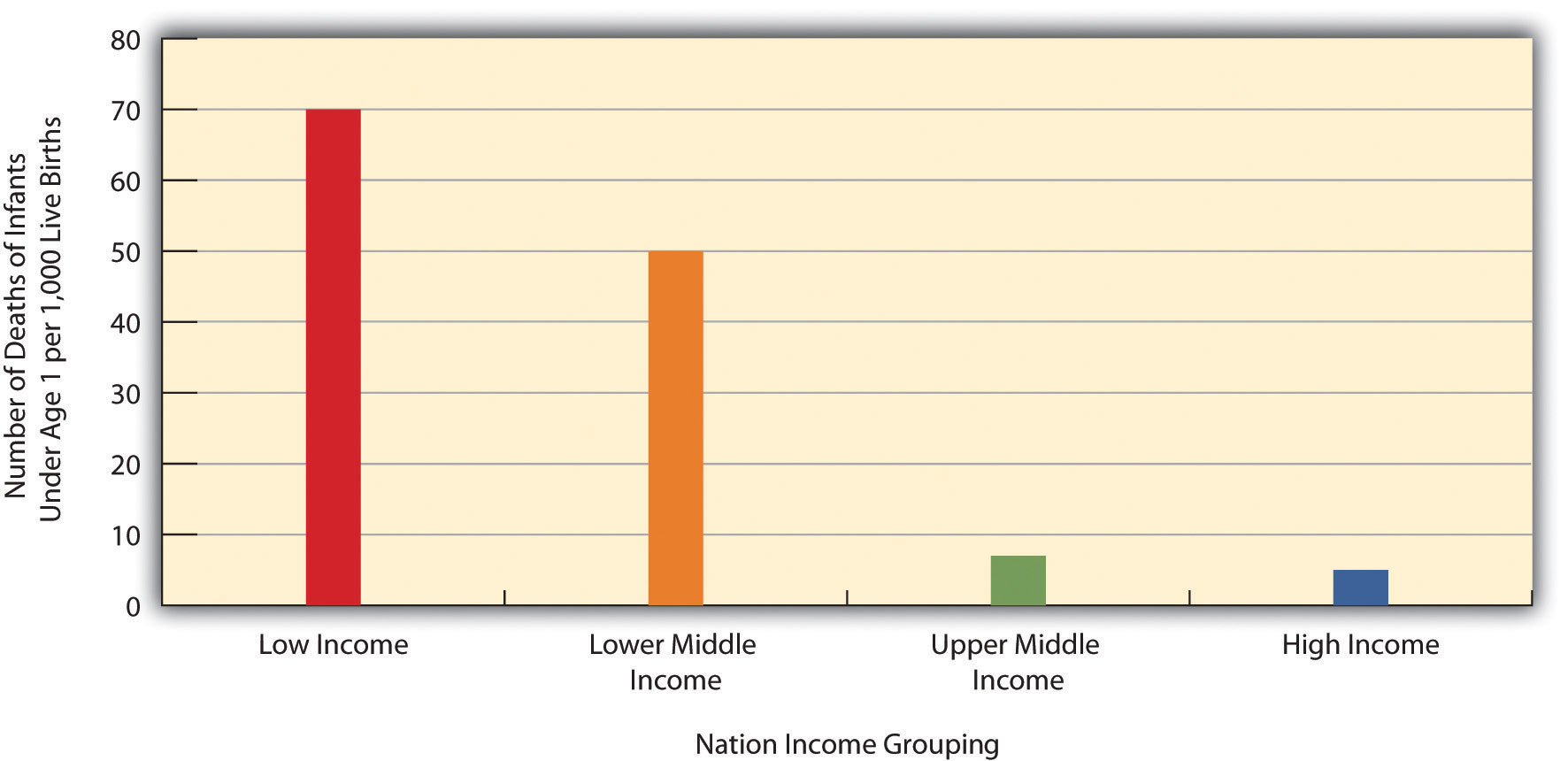
Why is poverty important for health?
A healthy body depends largely on eating a healthy, balanced diet; studies have shown that poverty overwhelmingly results in the financial inability to meet daily nutritional needs. Because people in a low socio-economic class less able to buy healthy food, they are lacking many vitamins and other nutrients provided by a balanced diet.
Why do low income people have high stress levels?
Low income earners experience high stress levels due to low socio-economic conditions which often contributes to unhealthy habits such as smoking and infrequent exercise. Smoking is one of the most noticeable habitual differences between the upper and lower socio-economic classes. Another example of how class differences in lifestyle affect health can be realized through the differences in the amounts of physical activity or exercise. People of a lower social class are less likely to exercise regularly. This disparity may be attributed to a number of reasons: fear of crime may hinder outdoor activities, lack of leisure time, or lack of employers positively enforcing exercise.
How can we improve access to healthcare?
Access to healthcare in remote locations can also be increased through permanent doctor/dentist residency or increased doctor travel to these areas.
Why are underclass women less likely to get screening tests?
A study on breast and cervical cancer argues that underclass women are less likely to receive screening tests, possibly because they do not have enough time, or may not have adequate transportation to get to appointments.
Can low income people get health insurance?
Low-income jobs rarely provide comprehensive health insurance and many must depend on social assistance to afford prescription drugs. High-income persons on the other hand, are able to afford medications or have good employer health insurance. Consequently, without an proper insurance plan, cancer patients experience poorer outcomes while do not receive proper dental care which puts http://pulseandsignal.com/upscale-dating-services/. Developing puerto rican men dating increases one’s chance of developing a number of diseases and conditions including perfectly matched dating colorado springs.
Is socioeconomic status related to health?
The connection between health and socio-economic status is even more evident when examining the increased risk of heart disease and other adverse health conditions of the poor due to behaviors and lifestyle .
Is access to healthcare a socioeconomic indicator?
Access to healthcare is one of the primary indicators of health in every country. Even here in Canada, with our universal healthcare system, access to healthcare remains tied to socio-economic status and as one’s economic status increases so does their health status. Keep in mind, it is widely accepted that low-income and low-education are linked to low socio-economic class.
How do social and cultural variables affect health?
In short, the influence of social and cultural variables on health involves dimensions of bothtime(critical stages in the life course and the effects of cumulative exposure) as well asplace(multiple levels of exposure). The contexts in which social and cultural variables operate to influence health outcomes are called, generically, thesocial and cultural environment.
How is socioeconomic health related to SES?
An association between SES and health has been recognized for centuries (Antonovsky, 1967). Socioeconomic differences in health are large, persistent, and widespread across different societies and for a diverse range of health outcomes. In the social sciences, SES has been measured by three different indicators, taken either separately or in combination: educational attainment, income, and occupational status. Although these measures are moderately correlated, each captures distinctive aspects of social position, and each potentially is related to health and health behaviors through distinct mechanisms.
What are the factors that determine health?
Health is determined by several factors including genetic inheritance, personal behaviors, access to quality health care, and the general external environment (such as the quality of air, water, and housing conditions). In addition, a growing body of research has documented associations between social and cultural factors and health (Berkman and Kawachi, 2000; Marmot and Wilkinson, 2006). For some types of social variables, such as socioeconomic status (SES) or poverty, robust evidence of their links to health has existed since the beginning of official record keeping. For other kinds of variables—such as social networks and social support or job stress—evidence of their links to health has accumulated over the past 30 years. The purpose of this chapter is to provide an overview of the social variables that have been researched as inputs to health (the so-called social determinants of health), as well as to describe approaches to their measurement and the empirical evidence linking each variable to health outcomes.
What are the variables that are used in health research?
Variables other than household income also may be useful for health research—such as assets including inherited wealth, savings, or ownership of homes or motor vehicles (Berkman and Macintyre, 1997). Whileincomerepresents theflow of resourcesover a defined period,wealthcaptures the stock of assets (minus liabilities) at a given point in time, and thus indicateseconomic reserves. Measuring wealth is particularly salient for studies that involve subjects towards the end of the life course, a time when many individuals have retired and depend on their savings. In the Panel Study of Income Dynamics, for example, only a weak association was seen between post-tax family income and mortality among post-retirement-age subjects, while measures of wealth continued to indicate a strong association with mortality risk (Duncan et al., 2002).
What is the relationship between income and health?
An alternative possibility is that the relationship between income and health is explained by a third variable—such as inherited ability—that is associated with both socioeconomic mobility and the adoption of health maintenance behaviors.
How is health determined?
Health is determined by several factors including genetic inheritance, personal behaviors, access to quality health care, and the general external environment (such as the quality of air, water, and housing conditions). In addition, a growing body of research has documented associations between social and cultural factors and health ...
What are the two social variables?
Two social variables are of particular interest in characterizing social relationships: social networks and social support . Social networksare defined as the web of person-centered social ties (Berkman and Glass, 2000). Its assessment includes the structural aspects of social relationships, such as size (the number of network members), density (the extent to which members are connected to one another), boundedness (the degree to which ties are based on group structures such as work and neighborhood), and homogeneity (the extent to which individuals are similar to one another). Its assessment also may extend to aspects including frequency of contact, extent of reciprocity, and duration. Social supportrefers to the various types of assistance that people receive from their social networks and can be further differentiated into three types: instrumental, emotional, and informational support. Instrumental supportrefers to the tangible resources (such as cash loans, labor in kind) that people receive from their social networks, whileemotional supportincludes less tangible (but equally important) forms of assistance that make people feel cared for and loved (such as sharing confidences, talking over problems). Informational supportrefers to the social support that people receive in the form of valuable information, such as advice about healthy diets or tips about a new cancer screening test.
What did psychologists convey about poverty?
Psychologists conveyed poverty's mental health effects on the disadvantaged and chronically ill.
How many older people live below poverty?
Nearly three-fourths of older adults live below the poverty level, she said. Moreover, nearly 40 percent of people in rural areas of the United States are living in poverty. "That is a huge correlation," Stamm said. "Clearly, rural and poverty go together.".
Does poverty cause mental health problems?
The constraints of poverty can cause a cycle of poor mental and physical health, according to psychologists who presented research at APA's 2003 Annual Convention on the impact of poverty on people's well-being.
Does poverty affect HIV?
Specifically, they found that poverty was related to depression and anxiety in the participants, which in turn negatively affected their HIV prognosis. Dove said psychologists need to better address this social class factor and how it can potentially influence mental health.
How does culture affect health?
And each of these cultures has its own health beliefs and treatment methods. And your culture influences how you think and your health issues. For instance, some people believe that it’s best to have a family dentist, while other opt for home remedy and traditional methods for dental health care. Your cultural beliefs affect how you decide in choosing health care providers, treatment, and medicine to take.
Why is health considered a cultural concept?
Technically, health is considered a cultural concept because our health is regarded by our experiences in life, as per the cultural class we belong to.
What is culture in the social system?
By definition, culture is the literacy and characteristics of a particular group of people, mostly with their own beliefs and faith regarding religion, cuisine, language, social habits, and many more. Hence, people can describe it as developing a group identity brought up by a unique social system.
What is culture shared among?
culture is shared among a group of people who falls under the same name and understanding
Do poor people have access to healthcare?
Sadly, the cultures’ access to health resources within the community is usually restricted. Most poor communities have limited access to healthcare needs for adults and children.
Can a patient depend on his cultural beliefs to comply with treatment and medication?
Sometimes, a patient will also depend on his cultural beliefs to comply with the treatment and medication. While this is usually his discretion, his family and even his extended family would interfere with his decisions.
Why is social stress a major cause of illness?
Social stress is a major cause of illness. Poorer persons experience more stress and have less control over that stress. Stress amplifies the myriad health risks embedded in every day aspects of lower class life.
How does social capital affect health?
Among other things, individuals with higher social capital typically have better access through their networks to high-quality information.
Why do African Americans have higher mortality rates than whites?
At all income levels, African Americans have higher mortality and morbidity rates than do whites. One explanation for this is racism. (Racial Discrimination is highly stressful and affects both physical and mental health.
Why are Hispanics so poor?
Hispanic Americans experience an array of diseases linked to poverty and despair, including fatal accidents, diabetes, and chronic liver disease. Hispanic Americans are 2.5 times more likely than non-Hispanic whites to live in poverty and, except for Cubans, are half as likely to have completed college. Cultural and language barriers as well as discrimination can make it difficult for Hispanics to take advantage of health care resources even when they can afford them.
What is the effect of lack of access to health care on the poor?
Lack of access to health care also fosters illness and disability amon the poor.
What are the environmental conditions that place poor people at risk of illness and death?
Environmental conditions place poor people at risk of illness and death. Chemical, air, and noise pollution all occur more often in poor neighborhoods than in wealthier neighborhoods.
How does racial discrimination affect communities?
Racial discrimination keeps members of minority groups in segregated communities and enables industrialists, with the tacit approval of government bureaucrats and politicians, to place environmental hazards in those communities without worrying that residents will have the political power or financial resources to resist.