What does MRI stand for?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. An MRI scanner is a large tube that contains powerful magnets. You lie inside the tube during the scan.
What are the types of MRI?
- Profound Medical
- Insightech
- EpiSonica
- Kona Medical
- Mirabilis Medical
- SonaCare Medical
- EDAPTMS
- Theraclion
- Alpinion Medical Systems
- Beijing Yuande Bio-Medical Engineering
What is spatial resolution?
Spatial resolution refers to the ability of an imaging modality to differentiate two adjacent structures as being distinct from one another. Other related terms include definition or visibility of detail. Spatial resolution is expressed in line pairs per mm (lp mm). The absence of spatial resolution in an image may be referred to as blur.
What is spatial resolution in ultrasound?
Ultrasound Physics. Spatial Resolution. Spatial Resolution: Spatial resolution of any imaging system is defined as its ability to distinguish two points as separate in space. Spatial resolution is measured in units of distance such as mm. The higher the spatial resolution, the smaller the distance which can be distinguished.

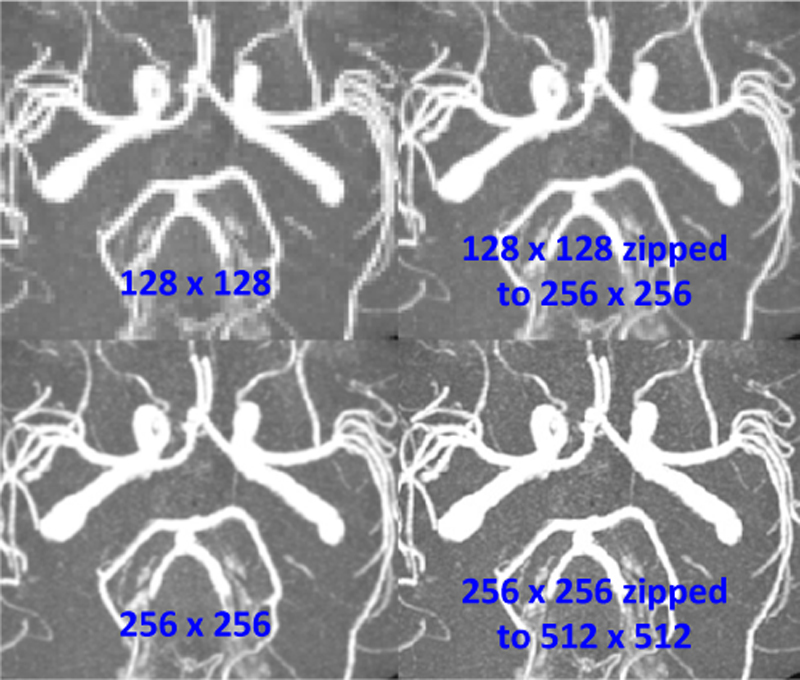
How do I increase the resolution of an MRI image?
Several approaches can be used to increase the over- all resolution of MRI scans. Hardware improvements directly increase the resolution of the acquired images. For example, increasing the number of coil receiver channels or increasing the main magnetic field going through the MRI core, B0 increases the MRI signal.
How do you increase spatial resolution?
Another way to enhance spatial resolution is to improve the sampling of detector units by deflecting the focal spot on the x-ray tube anode along longitudinal and fan angle direction (2–4).
What increases spatial resolution in radiography?
CT spatial resolution can be improved by up to a factor of about 2 by reducing the re- construction FOV (zoom).
What parameters affect spatial resolution in MRI?
In MRI, spatial resolution is defined by the size of the imaging voxels. Since voxels are three-dimensional rectangular solids, the resolution is frequently different in the three different directions. The size of the voxel and therefore the resolution depends on matrix size, the field-of-view, and the slice thickness.
What is the spatial resolution of MRI?
Spatial resolution The resolution of CT is superior to the resolution of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is typically 1–2 mm for most sequences and more than adequate for most clinical applications of CT.
What does spatial resolution depend on?
The spatial resolution that can be achieved by a spectrometer depends on the angular distribution of radiation emitted from the surface, the angular response of the spectrometer, and the altitude of the orbit.
Does mAs affect spatial resolution?
The first experiment showed that, when the film density is kept constant, the higher the kVp, the lower the resolution and image contrast percentage; also, the higher the mAs, the higher the resolution and image contrast percentage.
How does focal spot affect spatial resolution?
The limiting spatial resolution is essentially the same (i.e., ~3 lp/mm) that was achieved using the small focal spot. This example shows that for contact radiography, the size of the focal spot has negligible effect on the spatial resolution performance.
What is spatial resolution in imaging?
In terms of digital images, spatial resolution refers to the number of pixels utilized in construction of the image. Images having higher spatial resolution are composed with a greater number of pixels than those of lower spatial resolution.
What determines the resolution of an MRI machine?
MR images have a fixed resolution that is determined by factors such as scan time, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), physical properties of the scanner (3 Tesla vs. 7 Tesla), and the sampling rate.
How does slice thickness affect spatial resolution in MRI?
The results showed that thinning slices led to increased signal detection but to decreased SNR because of higher contrast in the partial volume effect. In addition, increasing matrix size and slice thickness for high-resolution imaging led to a decrease in signal detection.
What is the meaning of spatial resolution?
In other words, the spatial resolution is defined as the measurement of a small object, which is resolved by the sensor, or the ground area imaged for the instantaneous field of view (IFOV) of the sensor, or the linear dimension on the ground represented by each pixel.
What are the six factors that control spatial resolution?
Factors affecting CT spatial resolutionfield of view. as the FOV increases so do the pixel size; resulting in a decrease.pixel size. the smaller the pixel size the higher the spatial resolution.focal spot size. ... magnification. ... motion of the patient.pitch. ... kernel. ... slice thickness.More items...•
What is good spatial resolution?
Typical spatial resolution in images acquired with clinical scanners is around 6–7 mm.
What is a high spatial resolution?
Spatial resolution is the detail in pixels of an image. High spatial resolution means more detail and a smaller grid cell size. Whereas, lower spatial resolution means less detail and larger pixel size. Typically, drones capture images with one of the highest spatial resolutions.
What is the spatial resolution of 1080p?
List of Video ResolutionsResolution TypeCommon NamePixel SizeSD (Standard Definition)480p640 x 480HD (High Definition)720p1280 x 720Full HD (FHD)1080p1920 x 1080QHD (Quad HD)1440p2560 x 14403 more rows•Nov 27, 2020
How to determine MRI resolution?
Resolution is the ability of human eyes to distinguish one structure from other. In MRI the resolution is determined by the number of pixels in a specified FOV. The higher the image resolution, the better the small pathologies can be diagnosed. Resolution is directly proportional to the number of pixels (The higher the number of pixels the greater the resolution). Pixel size can be calculated by dividing the field of view by the matrix size (e.g.FOV 320, Matrix 320x320, Pixel size =320/320=1mm). There are two resolution parameters used in MRI for the production of a two dimensional image i.e. basic resolution and phase resolution.
What is the basic resolution of an image?
Basic resolution is the number of pixels in the readout direction. Basic resolution also determines the size of the image matrix. Basic resolution is inversely proposal to the size of the pixel and (the lower the resolution the higher the pixel size).
How to make a picture smoother?
Increase FOV. Increasing FOV increase the pixel size and SNR therefore the image will become smoother.
What does decreasing phase resolution do to a photo?
Decreasing phase resolution will reduce the image quality and scan time. Reducing phase resolution will increase the pixel size therefore the SNR will increase considerably.
What is the SNR of a photo?
Signal to noise ratio (SNR) is inversely proportional to the basic resolution. In other words SNR is directly proportional to the pixel size. Increasing the base resolution will reduce the pixel size therefore the SNR of the image will be reduced.
What is phase resolution?
Phase resolution is the number of pixels in the phase direction. Phase resolution normally expressed as a percentage value of the basic resolution. Decreasing phase resolution will increase the pixel size in one direction and result in a rectangular pixel shape.
How to reduce scan time?
Reduce the base resolution by one or two steps. Reducing base resolution will reduce the scan time.
What happens when you increase the resolution of a picture?
This means that more spatial data is collect than signal data. If we increase the resolution, we will be measuring more spatial frequencies than signal frequencies. This will produce an image with a less signal to noise ratio. This means when we increase our resolution, we will decrease the signal to noise ratio.
What is image resolution?
Image resolution is defined as the amount of detail seen in our image. Detail is the ability to distinguish between adjacent structures. It is important to know that when creating an image, we are looking at a matrix or a grid of tiny squares called pixels or cubes of data called voxel's. The smaller these pixels/voxel's are, the better we will distinguish between adjacent structures. Therefore, by changing our parameters to create smaller pixels/voxel's of data, we will increase our image resolution.
What would happen if we changed the thickness of a slice to 78mm?
If we changed our slice thickness to .78mm, we would have a isotropic voxel or a perfect cube of data.
How are pixels created?
Pixels are created by the phase and frequency values selected by the technologist. This will represent a 2D image.
How to find the size of a pixel?
We can calculate the size of our pixel by taking the field of view (FOV) and dividing it by the frequency/phase value.
What to do if scan time is too long?
If it is too long, we should start over reducing the resolution slightly to save signal and therefore reduce the need to implement other time costing signal improving methods such as the NEX/averages and changing the bandwidth.
Can we increase the number of excitations?
We can increase the number of excitation (NEX) / averages. This will increase our scan time by give us considerable signal.
What are the two types of image resolution?
Two types of image resolution are generally distinguished and tested: high-contrast and low-contrast. High-contrast resolution is the ability to detect finely spaced lines or holes with whose signals differ considerably from background. Low-contrast resolution is the ability to detect and discern objects with only subtle differences in signal intensity. Again, organizations like the American College of Radiology (ACR) and American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) publish detailed procedures for measuring these properties.
What is low contrast resolution?
Low-contrast resolution refers to the ability to identify small objects with only slightly different relaxation times from background. The ACR phantom uses a series of disks with small holes arranged as a circle of 10 spokes. A score is assigned based on the number of complete spokes identified.
What is the high contrast portion of a MR phantom?
The high-contrast portion of MR phantoms contains closely spaced lines, edges, or holes containing material with strong differences in signal intensity from background.
Why is SNR dropping on MRI?
The reason being the centre of the anatomy is too far from the receiver coils. The user must manipulate the scanning parameters to improve SNR while scanning patients with a high BMI.
What causes MRI to make noise?
Noise in MRI is from two main sources: 1. Molecular movement - charged particles in the human body create electromagnetic noise. 2. Electrical resistance - resistance from the receiver coils, data cables and the electronic components of the measurement system. Noise produced in the MRI image depends on: 1.
How to reduce SNR in a T2 sequence?
This can be either reduced by increasing the slice gap or choosing the interleave option (which scans odd number slices together then even numbered slices together). It should be noted that increasing the slice gap beyond certain limits, usually above 50%, can cause misregistration.
How to get the best SNR for MRI?
In order to achieve maximum SNR, the RF coils should be as close as possible to the anatomy being imaged. This the main reason that most MRI systems have dedicated coils for each body part. SNR also depends on the number of transmitter and receiver elements within the RF coils. The higher the number of transmitter and receiver elements, the better the SNR eg. a 32-channel (receiver element) body coil will produce better SNR compared to a 4-channel body coil.
What is SNR in MRI?
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a standard used to describe the performance of an MRI system. An MRI image is not created by pure MRI signals but from a combination of MRI signals and unavoidable background noise.
How does field strength affect SNR?
Increasing the field strength will increase the longitudinal magnetisation by aligning more protons to the axis of the main magnetic field. This results in an overall increase in the amount of signal produced which will improve SNR.
How does high transmitter bandwidth help with scan times?
High transmitter bandwidth can be used effectively to reduce scan times in claustrophobic and moving patients. This option will significantly reduce the minimum TR and TE values allowing the user to reduce the TR and TE values manually, reducing scan time. The main disadvantage of this method is shortening the TEs and TRs usually results in more noise and increases the potential for peripheral stimulation. The diagrams below show how to choose these options and the results of the manipulations.
