Uses of Succinylcholine: It is used to calm muscles during surgery. It is used to calm muscles while on a breathing machine.
How does succinylcholine (Anectine) work?
Succinylcholine (Anectine) is a neuromuscular blocker. It works by blocking your brain from sending certain signals to your muscles. This causes your muscles to relax. Succinylcholine (Anectine) is given along with general anesthesia to help relax and keep your body still during surgery.
What does succinylcholine do to muscles?
Succinylcholine binds at the sites meant for acetylcholine. It causes a muscle contraction, and makes it impossible for the muscles to contract again for a period of time, causing profound muscle relaxation, or muscle paralysis. |.
How long does succinylcholine take to kick in?
Its rapid onset and offset, with effects beginning within 60 seconds of intravenous administration and lasting between four to six minutes, make succinylcholine particularly useful in the setting of short medical procedures requiring brief periods of muscle relaxation. 9
How is succinylcholine detected in the blood?
The fourth characteristic of succinylcholine is good news for assassins: sux is almost impossible to detect because its metabolites are all naturally occurring molecules. here’s how it works. Most molecules of succinylcholine break down in blood into succinylmonocholine and choline, thanks to a circulating enzyme called pseudocholinesterase.

How does succinylcholine relax muscle?
Mechanism of action. Succinylcholine is an ultra-short-acting depolarizing muscle relaxant, which binds to motor endplate cholinergic receptors to produce depolarization. Since the depolarization is sustained, the electrical activity of the motor endplate is lost, leading to paralysis.
How does succinylcholine affect muscle contraction?
Succinylcholine, commonly used in anesthesia, paralyzes normal skeletal muscles by blocking transmission at the myoneural junction, but in denervated muscle, it produces sustained muscle contractions lasting several minutes.
Which receptors are targeted by succinylcholine?
Succinylcholine binds to nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction and opening the ligand-gated channels in the same way as acetylcholine, resulting in depolarization and inhibition of neuromuscular transmission.
How does succinylcholine increase potassium?
Systemic succinylcholine, in contrast to acetylcholine released locally, can depolarize all of the up-regulated AChRs leading to massive efflux of intracellular potassium into the circulation, resulting in hyperkalemia.
What does succinylcholine do to pulse?
Succinylcholine caused a transient (63-600 s) dose-related positive chronotropic effect. The heart rate was increased to 14.4 +/- 2.1% (mean +/- SE) above the control value after the administration of 1,000 micrograms of succinylcholine.
Why does succinylcholine cause muscle pain?
The plasma potassium increases to a higher level in patients who develop succinylcholine pains than in those who do not [25]. During the fasciculations produced by succinylcholine, muscle fibre damage gives rise to both the hyperkalaemia and the subsequent muscle pains [32].
What type of inhibitor is succinylcholine?
Succinylcholine is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker, meaning it causes a prolonged period of membrane depolarization in order to exert its therapeutic effects.
What kind of inhibitor is succinylcholine?
Sodium Potassium Chloride Symporter Inhibitor. Myorelaxant Agent.
What type of muscle relaxant is succinylcholine?
Succinylcholine is a depolarizing muscle relaxant that has been used for rapid sequence induction and for procedures requiring only a brief duration of muscle relaxation since the late 1950s. The drug, however, has serious side effects and a significant number of contraindications.
How long does potassium stay elevated after succinylcholine?
The expected increase of 0.5 mEq/dL is associated with the normal efflux of K+ of the activated nAChR channel. The slight increase is generally benign, occurs within 5 minutes of administration, and in one randomized study, resolved to 90% of initial level within 12 minutes after discontinuance of succinylcholine.
What is the antidote for succinylcholine?
There is no antidote for succinylcholine toxicity; however, treating physicians focused on stabilizing the physiology, which resulted in the survival of this patient.
How long does succinylcholine increase potassium?
Succinylcholine causes for a transient elevation in potassium by 0.5 – 1.0 mEq in the first 3-5 minutes following administration. This is not of grave concern for most patients as their potassium level is likely normal with hopefully normal kidney function.
Does succinylcholine cause rigidity?
Masseter muscle rigidity following administration of succinylcholine for induction of general anesthesia is considered an early warning sign for the possibility of an episode of dreaded complication i.e., malignant hyperthermia.
How does succinylcholine cause flaccid paralysis?
Muscle relaxation occurs when calcium ATPases on the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SERCA) remove calcium from the myoplasm and pump it back into the SR [9]. Because it is a depolarizing NMBA, SCH first induces muscle fasiculations followed by flaccid muscle paralysis.
How is succinylcholine an agonist?
Comment: Succinylcholine (sux) is a short-acting depolarizing neuromuscular blocker. It acts as an acetylcholine agonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions, resulting in persistent depolarization of the motor end plate.
Is succinylcholine an inverse agonist?
Succinylcholine (suxamethonium) is a highly potent agonist at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is a direct cholinergic agonist in that it binds to the same binding site as the endogenous transmitter acetylcholine and activates the receptor in the same manner as acetylcholine.
What Do I Need to Tell My Doctor Before I Take Succinylcholine?
1. If you have an allergy to succinylcholine or any other part of succinylcholine. 2. If you are allergic to any drugs like this one, any other dru...
What Are Some Things I Need to Know Or Do While I Take Succinylcholine?
1. Tell all of your health care providers that you take succinylcholine. This includes your doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and dentists. 2. Very bad...
How Is This Medicine (Succinylcholine) Best Taken?
Use succinylcholine as ordered by your doctor. Read all information given to you. Follow all instructions closely. 1. It is given as a shot into a...
What Are Some Side Effects That I Need to Call My Doctor About Right away?
WARNING/CAUTION: Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug. Tell your doctor o...
What Are Some Other Side Effects of Succinylcholine?
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help i...
How Do I Store and/or Throw Out Succinylcholine?
1. If you need to store succinylcholine at home, talk with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist about how to store it.
How Does Succinylcholine Work?
Before understanding how succinylcholine makes muscles relaxed , it is important to have a basic understanding of how a muscle contraction is initiated.
What is succinylcholine?
Succinylcholine is a "Depolarizing Neuromuscular Blocker". Succinylcholine is usually given intravenously and binds to the same receptors as acetylcholine. In doing so, the end effect of succinylcholine is to block acetylcholine from being able to bind or act. The effect of this binding is that sux causes the same subsequent reactions ...
What is the chemical that crosses the nerve to the muscle?
This point of contact is known as the neuromuscular junction. At the neuromuscular junction, the nerve releases a chemical called acetylcholine (Ach for short). Ach crosses from the nerve to the muscle side of the connection and triggers further electrochemical changes that culminate in muscle contraction. Succinylcholine is a "Depolarizing ...
What happens when succinylcholine is present?
When succinylcholine is present, it binds to the receptors (4) and blocks them so that acetylcholine cannot bind there.
How long does succinylcholine block last?
Duration of Action: the block with succinylcholine starts to wear off in 3 minutes and is completely gone by 15 minutes.
Why is it important to take a muscle relaxer?
Once a patient is unconscious, and certainly once a muscle relaxant starts to work, breathing and oxygen delivery is impaired. The anesthesiologist becomes responsible for assuring these vital functions for the patient.
Why are neuromuscular blockers called non-depolarizers?
Other commonly used muscle relaxants or neuromuscular blockers are called "non-depolarizers" because they bind and block the receptor without activating it , and thus there are no depolarizations or contractions.
What is the purpose of a nerve stimulator in a continuous infusion of succinylcholine chlor?
If a continuous infusion of succinylcholine chloride is necessary, a nerve stimulator should be used to monitor the effects of the neuromuscular blockade to a train of 4 in conjunction with continuous cardiac monitoring and end-tidal carbon dioxide measurements.
What is succinylcholine chloride?
Continuing Education Activity. Succinylcholine chloride is a short-acting depolarizing neuromuscular blockade that is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a provision to other sedatives or hypnotics. It is a correlate of acetylcholine (ACh); hence, it disrupts all cholinergic receptors of the parasympathetic ...
What is the purpose of reviewing interprofessional team strategies for improving care coordination and communication?
Review interprofessional team strategies for improving care coordination and communication to advance the use of succinylcholine where it is indicated and improve patient outcomes.
What is the therapeutic index of succinylcholine chloride?
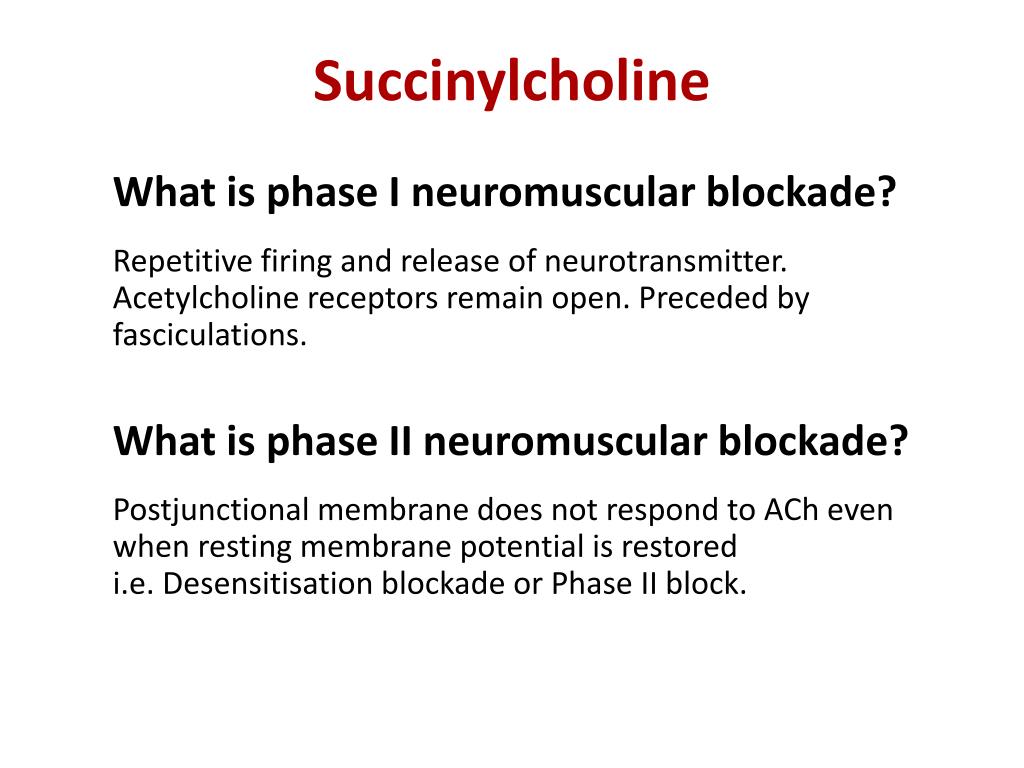
The therapeutic index is the measurement range of drug safety among the average age groups. The range for adults is 0.3 to 1 mg/kg, with a recommended dose of 0.6 mg/kg administered intravenously. Patients who have received succinylcholine chloride should be on continuous cardiac monitoring in conjunction with end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring. Pulse oximetry also requires monitoring. If a continuous infusion of succinylcholine chloride is necessary, a nerve stimulator should be used to monitor the effects of the neuromuscular blockade to a train of 4 in conjunction with continuous cardiac monitoring and end-tidal carbon dioxide measurements. The use of a nerve stimulator will indicate whether the patient is exhibiting a phase-I neuromuscular block or it has converted to a phase-II neuromuscular block.
What is the primary treatment for succinylcholine toxicity?
Primary treatment and intervention for succinylcholine toxicity is airway maintenance and respiratory support sufficient for the patient to maintain adequate oxygenation until the drug is metabolized, and the patient can maintain adequate oxygenation and ventilation without mechanical support.
How long does succinylcholine stay in your system?
The mechanism of action is apparent within 60 seconds of intravenous administration and continues up to 360 seconds or 6 minutes. Succinylcholine's pharmacological and chemical composition makes it neuromuscular receptor site-specific. Thus succinylcholine is ineffective on the smooth and cardiac muscles of the body.
What is the Creative Commons 4.0 license?
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, a link is provided to the Creative Commons license, and any changes made are indicated.
How long does succinylcholine blockade last?
Succinylcholine's neuromuscular blockade takes effect within 60 seconds of intravenous administration and lasts between four to six minutes. 2 Similar to acetylcholine, it binds to cholinergic receptors of the motor endplate to induce membrane depolarization and, eventually, muscle paralysis, which may be maintained for as long as an adequate concentration of succinylcholine remains at the receptor site. 8 Succinylcholine has no direct action on smooth or cardiac muscle, nor does it appear to act on pre-synaptic or ganglionic acetylcholine receptors. 5 The paralysis induced by succinylcholine has been described as "progressive", first involving the muscles of the face and glottis, then the intercostals and diaphragm, then followed by other skeletal muscles. 8
What is the role of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor?
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the...
What is succinylcholine used for?
Succinylcholine is a depolarizing skeletal muscle relaxant used adjunctly to anesthesia and for skeletal muscle relaxation during intubation, mechanical ventilation, and surgical procedures.
How is succinylcholine metabolized?
Metabolism. Succinylcholine is rapidly metabolized by plasma cholinesterase in the bloodstream to succinylmonocholine, which is then further hydrolyzed (albeit more slowly) to succinic acid and choline. 8. Hover over products below to view reaction partners. Succinylcholine.
What is the name of the compound that is a quaternary ammonium salt?
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl cholines. These are acylated derivatives of choline. Choline or 2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula (CH3)3N+ (CH2)2OH.
How much of a dose of a drug is excreted in the urine?
Approximately 10% of an administered dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. 8
Does succinylcholine cause cardiac arrest?
Succinylcholine has no effect on consciousness or pain threshold, and must therefore be used in conjunction with adequate anesthesia. 9 There have been rare reports of the development of acute rhabdomyolysis with hyperkalemia - resulting in ventricular dysrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and death - after the intravenous administration of succinylcholine to apparently healthy pediatric patients who were subsequently found to have undiagnosed skeletal myopathy (most frequently Duchenne's muscular dystrophy). 9 Infants or children experiencing seemingly idiopathic cardiac arrest soon after the administration of succinylcholine should therefore be treated immediately for hyperkalemia. Given that patients may not present with any apparent risk factors, the use of succinylcholine in pediatric patients should be restricted to emergency intubation or other situations in which a suitable alternative is unavailable. 9
How should I use this drug? TOP
This medicine is for injection into a vein or muscle. It is given by a health care professional in a hospital or clinic setting.
Where should I store this drug? TOP
This drug is given in a hospital or clinic and will not be stored at home.
What happens when acetylcholine binds to the AChR?
When acetylcholine binds to the AChR on muscle, the channel opening is of a very short duration because of the rapid transmitter degradation by acetylcholinesterase in the perijunctional area. In contrast, the depolarizing relaxants decamethonium and succinylcholine have a biphasic action—an initial contraction followed by relaxation. This is because both drugs are not susceptible to hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase and are therefore not eliminated from the junctional cleft easily. Depolarization of the endplate by the relaxant causes the adjacent voltage-gated sodium channels to open, causing a wave of depolarization to sweep along the muscle. If the depolarizing relaxant is not removed from the cleft, the sodium channels adjacent to the endplate remain in the inactivated state, resulting in muscle paralysis or relaxation. 10 Jonsson et al. now demonstrate that in addition to this sodium channel–dependent mechanism, the receptor itself, after initial depolarization, becomes desensitized to further depolarization. This observation is consistent with in vivo studies and clinical observations: Even long after complete recovery of twitch and train-of-four from succinylcholine-induced paralysis, the neuromuscular junction can often behave in a more sensitive (desensitized) fashion when depolarizing or nondepolarizing relaxant is subsequently administered. 5
Why is succinylcholine used?
EVEN 50 yr after its introduction, succinylcholine continues to be used, because it still has the fastest onset of effect of the clinically available muscle relaxants. 1 After the initial description of the neuromuscular blocking properties of succinylcholine by Daniel Bovet, 2 S. Thesleff 3 at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm was one of the pioneers who introduced the drug into clinical practice to induce neuromuscular paralysis in humans. (Bovet was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology and Medicine in 1957 for his discovery of synthetic compounds that act on the vascular system and skeletal muscle.) Despite half a century of use, several pharmacologic properties of succinylcholine remained essentially unexplained. These include the lack of fade with single-dose treatment, the development of phase II block with larger doses of the drug, and cardiovascular side effects, particularly the bradycardia and cardiac arrest commonly observed after second or third injections of succinylcholine. 4,5 Because of the chemical nature of succinylcholine, it was assumed that the cardiovascular side effects were related to the nonneuromuscular actions of succinylcholine on other acetylcholine receptors (AChRs), including the heart, autonomic ganglia, and adrenal medulla. In this issue of Anesthesiology, a report by Jonsson et al. , also from the Karolinska Institute, provides biophysical insight into some of the mechanisms of action and side effects of succinylcholine. 6
What receptors are expressed in the neuromuscular junction of the newborn and adult rat?
Garcia N, Santafe MM, Salon I, Lanuza MA, Tomas J: Expression of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1-, M2-, M3- and M4-type) in the neuromuscular junction of the newborn and adult rat. Histol Histopathol 2005; 20:733–43
Does succinylcholine cause bradycardia?
We are still left without a conclusive mechanism of the (more common) succinylcholine-induced bradycardia, which is usually attributed to agonist actions on the muscarinic AChRs of the heart. 5 The authors did note, however, that succinylcholine dose-dependently inhibited ganglionic AChRs.
What is Bovet D?
Bovet D: Some aspects of the relationship between chemical structure and curare-like activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1951; 54:407–37
Does succinylcholine inhibit presynaptic 32 AChRs?
The finding that high doses of succinylcholine inhibited presynaptic α3β2 AChRs ( i.e. , the compound behaved like a nondepolarizing relaxant) may help to explain how high or repeated doses of succinylcholine result in a nondepolarizing type of block (phase II block) characterized by fade and posttetanic potentiation. However, the study did not include direct comparisons of the effects of nondepolarizing compounds on α3β2. Therefore, it is not possible to make conclusive statements as to the similarity between effects of succinylcholine and nondeporalarizing muscle relaxants on these prejunctional receptors.
How effective is Sux?
Sux is highly effective. In IV form, 100 mg of sux will depolarize every muscle in the body of a 70kg man in about 20 seconds. And the patient will not be able to take another breath for at least 5 minutes. So without assisted ventilation, he is toast.
What is a sux?
Sux is a rapidly acting depolarizer that can be given intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM).
What enzyme breaks down succinylcholine?
Most molecules of succinylcholine break down in blood into succinylmonocholine and choline, thanks to a circulating enzyme called pseudocholinesterase. The process is so efficient that only a small fraction of sux molecules that were given actually reach neuromuscular junctions in the first place.
What happens when you give succinylcholine?
When succinylcholine is given, seconds later the patient fasciculates, and all muscles in his body become depolarized. In essence, sux makes every muscle twitch to the point that it becomes unresponsive to any subsequent stimulation: you can’t breathe, you can’t even blink. Sux is highly effective.
What poison was used in the Dubai killing?
Succinylcholine, A Perfect Poison, Makes Appearance in the Dubai Killing. According to Dubai authorities, and as reported by ABC News, Hamas operative Mahmoud al-Mabhouh was given a shot of succinylcholine prior to other grossly things done to his body on the fateful (for him) day of January 19, 2010. And since your humble correspondent is an ...
Is succinylcholine easy to inject?
The IM dose of sux is not much different, but takes a little longer to set in. So there you have it: succinylcholine is an easy to inject poison, it is highly effective, and is guaranteed-to-work quick.
What is the metabolite of SUX?
The muscle relaxant succinylcholine (SUX) evokes respiratory paralysis, and numerous cases of fatal SUX intoxication have been reported. Detection of SUX and its metabolite succinylmonocholine (SMC) is difficult, both due to their (bis-) quaternary structure and the extreme hydrolytic susceptibility …
Does paraoxon enhance the stability of urine?
Paraoxon did not enhance the stability of either target substance in urine, stabilization of urine samples is nonetheless recommended. In summary, SMC was proven to be the most promising target analyte in SUX analysis, with urine being the proposed matrix of choice for forensic applications.
