
In agglutination tests, an antigen reacts with its corresponding antibody, resulting in visible clumping of bacterial cells. With latex agglutination tests, latex particles are coated with antibodies that agglutinate specific antigens and form a more easily visible precipitate.
What does agglutination mean in blood type testing?
What does agglutination mean in blood type testing? Agglutination (biology) Agglutination is the process that occurs if an antigen is mixed with its corresponding antibody called isoagglutinin . This term is commonly used in blood grouping .
How to perform a saline agglutination test?
SLIDE AGGLUTINATION TEST
- Collect a blood sample in a EDTA tube
- Place one drop of the blood onto a microscope slide followed by either 1-2 drops of saline for a dog or 3-4 drops for cat.
- Rock the slide backwards and forwards several times
- First observe with the naked eye, this is to examine for any macro-agglutination (See the slide on the right in the picture).
What is the difference between agglutination and hemolysis?
What is the difference between agglutination and hemolysis? This process is called agglutination. The clumps of erythrocytes block small blood vessels throughout the body, depriving tissues of oxygen and nutrients. As the erythrocyte clumps are degraded, in a process called hemolysis, their hemoglobin is released into the bloodstream.
What is an Ig lab test?
This test measures the amount of immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, in your blood. Antibodies are proteins made by the immune system to fight disease-causing substances, like viruses and bacteria. Your body makes different types of immunoglobulins to fight different types of these substances. An immunoglobulins test usually measures three specific types of immunoglobulins.
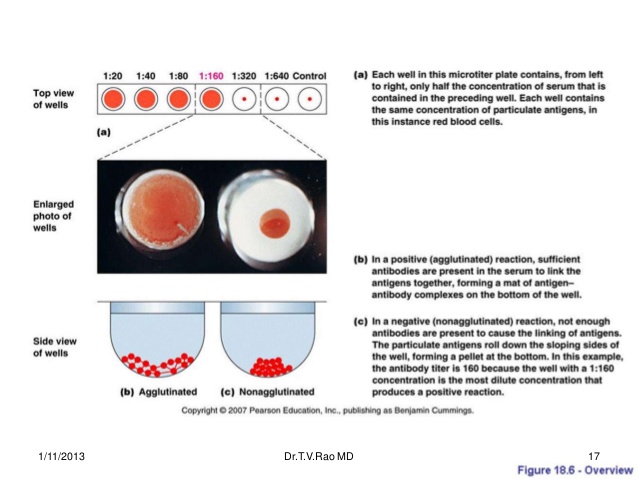
How does a blood agglutination test work?
The sample is sent to a lab, where it is mixed with latex beads coated with a specific antibody or antigen. If the suspected substance is present, the latex beads will clump together (agglutinate). Latex agglutination results take about 15 minutes to an hour.
How do you read an agglutination test?
The results are read directly from the slide. The subject is blood group A if agglutination occurred with the Anti-A test serum; group B if agglutination occurred with the Anti-B test serum; group AB if agglutination occurred with both test serums, and O if there was no agglutination in either case.
What are the steps in agglutination?
The process of agglutination involves two steps. First step is sensitization and second is lattice formation. It is attachment of specific antibody to corresponding antigen. pH, temperature and time of incubation influence the reaction.
What does it mean if agglutination occurs in a test?
The agglutination indicates that the blood has reacted with a certain antibody and is therefore not compatible with blood containing that kind of antibody. If the blood does not agglutinate, it indicates that the blood does not have the antigens binding the special antibody in the reagent.
What does positive agglutination look like?
In the presence of agglutination, the red blood cells will remain clumped: this indicates a positive test .
What causes the agglutination?
Agglutination is caused by the formation of antibody-antigen complexes and occurs at room temperatures. Auto-agglutination is produced as a result of a complex formed between the patient's own RBC antigens and antibodies, mediated by cold-reacting antibodies.
Which blood causes agglutination?
Agglutination occurred when the RBC antigens were bound by the antibodies in the serum. He called the antigens A and B, and depending upon which antigen the RBC expressed, blood either belonged to blood group A or blood group B.
How do you read a titer?
The USDA considers a titer of ≥1:4 to be positive. A result of <1:2 is equivalent to a negative @ 1:4 or 1:8 result. A titer of >1:128 may indicate recent infection. A titer of ≥1:320 may indicate recent infection.
How is agglutination observed?
Agglutination occurs when an insoluble or particle antigen interacts with an antibody. A positive reaction can be detected macroscopically in a short time. However, the antigen-antibody complex may be seen with the naked eye if the complex size is large. Both IgG or IgM could be involved in the agglutination reaction.
How do you read an antibody screen?
If the antibody screen is positive, in most cases the next step would be to perform antibody identification. If the screen is negative, there is a very high likelihood that no significant antibodies are present (though some rare antibodies against low-incidence RBC antigens could still be present).
What is the agglutination test?
The agglutination test using formalin-preserved whole tachyzoites is available commercially (bioMérieux, Marcy-l'Etoile, France) and detects IgG antibody. The test is very sensitive to IgM antibody, and “natural” IgM antibody causes nonspecific agglutination in sera that yield negative results when tested in the DT and the IFA test. This problem is avoided by including 2-mercaptoethanol in the test. The method is accurate, simple to perform, inexpensive, and excellent for screening purposes.307 This method, that is, with mercaptoethanol, should not be used for the measurement of IgM antibodies.
What is the purpose of agglutination reactions?
Antibodies that cause this reaction are referred to as agglutinins. Agglutination assays can be used to determine concentrations of specific antibodies in a patient's immune sera. A constant amount of a suspended particulate antigen is added to a series of tubes containing a twofold dilution of patient's immune serum, and the titer of antibody in the serum is the reciprocal of the highest serum dilution showing agglutination of the particulate antigen. Agglutination reactions are routinely used for identification and serotyping of a wide range of bacterial foodborne pathogens.
How to test for brucellosis?
STAT has been used extensively for many years in the diagnosis and surveillance of brucellosis. STAT is performed by mixing whole bacterial cell antigens with serum and incubating the mixture. A bacterial suspension of B. abortus strain 99 or B. abortus strain 1119-3 in phenol saline (NaCl 0.85% [w/v] and phenol at 0.50% [v/v]) constitutes the test antigen; formaldehyde must not be used. Since the test is performed at neutral pH, it primarily detects IgM isotype. Even though STAT is sensitive, as it detects IgG (particularly IgG1) less efficiently, the test is considered less specific ( Corbel & Hendry, 1985; Nielsen et al., 1984; OIE, 2018 ).
What is the most useful test for rapid screening?
The macroscopic slide agglutination test is the most useful test for rapid screening.18,19 Twelve serotypes of killed Leptospira (including strains responsible for most infections in the US) are included in this test. The microscopic agglutination test uses live organisms and is the gold standard for detecting antibodies to Leptospira.
How long does it take for antibodies to show up in a blood test?
Generally, agglutination test results are not positive until after the first week of infection; antibody levels peak 3 to 4 weeks after the onset of symptoms and can persist for years, although concentrations may decline over time. Demonstration of at least a fourfold rise in antibodies between acute and convalescent serum samples tested together is most definitive. Newer serologic tests may become useful and include indirect hemagglutination tests, passive microcapsule agglutination test, and enzyme immunoassays. 20–24
How is MAT titre determined?
The MAT titre of a patient is determined by the incubation of different serum dilutions with a panel of leptospires. The agglutination reaction is visualised by dark field microscopy, and the end-point is considered as the serum dilution that promotes 50% of agglutination. However, cross-reaction of the patients’ antibodies with different serovars may produce paradoxical reactions [9]. These reactions are common; however, they become less pronounced with the maturation of the immune response, which increases the test specificity [89].
What is AC/HS test?
When two different compounds (i.e., acetone and formalin) are used to fix parasites for use in the agglutination test, a “differential” agglutination test (AC/HS test) results because the different antigenic preparations vary in their ability to recognize sera obtained during the acute and chronic stages of the infection. 308 This test has proved useful in helping differentiate acute from chronic infections and is best used in combination with a battery of other tests. When the AC/HS yields a “nonacute” pattern, the infection has been present for at least 12 months from the time of serum sampling. 309
What is the agglutination test?
Particle Agglutination Test: This test includes latex particles, treated red blood cells and whole bacterial cells. Depending on amount and avidity of the antigens the visibility of agglutination may vary but inevitably shows up given that the suspected infection is there.
What is the purpose of a latex agglutination test?
On of these types makes is possible to perform a Latex Agglutination Test, the one that makes it easier to mark some Antigens and/or Antibodies in the organism.
How long does it take to get results from a latex agglutination test?
The latex agglutination test protocol is really quick and it shows its results in 15 minutes to an hour. If your medical facility is ready to perform the protocol right away, all you’ll need to do is to wait for 15 minutes to an hour to get your results. In another way, your doctor will set you an appointment in a few days to give you ...
Is a latex agglutination test scarier than blood?
Latex Agglutination Test Procedure. For you, the latex agglutination test procedure is nothing scarier than the usual giving of the example of your blood, saliva or urine in the medical facility. Your part is pretty simple. You give the needed example and then you just have to wait for the results.
Is a particulate antigen test reliable?
If the particulate antigen shows the agglutination, then the result is positive. The results of the test are extremely reliable.
Can you run your saliva through your practitioner?
But as it was said, all you do during the procedure is simply providing the example of your saliva, urine or blood, which may be performed during pregnancy many times anyway. So no reason to be bothered, but running it through your practitioner is always the greatest choice.
What is the process of agglutination?
Agglutination is the process that occurs when an antigen is mixed with its corresponding antibody called agglutinin and is commonly used in blood grouping. Latex agglutination testing, also called latex fixation, is a diagnostic study that is widely used as a laboratory method to identify certain antibodies and antigens.
What is the Latex Agglutination Test?
Latex agglutination tests can be taken by collecting a sample containing the specific antigen, or antibody, which is later mixed with an antibody, or antigen, which is coated on latex beads in serial dilutions with normal saline. If the suspected substance is present, the latex beads will clump together. This clumping is called agglutination.
How do I prepare for a cold agglutinin test?
You don’t need any special preparation for a cold agglutinin test. Your doctor will arrange for you to give a small blood sample at your local clinic or hospital.
What is cold agglutinin news?
Cold Agglutinin Disease News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider ...
What is the titer of a test?
Test results are generally available as a titer — the dilution at which clumping occurred. They appear as 1:64, for example. The larger the second number, the more cold agglutinins are present. A titer value greater than 1:512 is usually found in patients with CAD, with rare cases reportedly having a value as low as 1:64.
What happens when a blood test results become available?
When the test results become available, your doctor will discuss them with you as well as any treatments you may need.
Can cold agglutinin cause CAD?
Most people have very low levels of cold agglutinins, but infections can sometimes cause levels to rise. Some people develop CAD as an autoimmune disease, though the reasons for this are not clear. The cold agglutinin test measures the levels of cold agglutinins in a patient’s blood.
What is agglutination?
Agglutination is the visible expression of the aggregation of antigens and antibodies. Agglutination reactions apply to particulate test antigens that have been conjugated to a carrier. The carrier could be artificial (such as latex or charcoal particles) or biological (such as red blood cells). These conjugated particles are reacted with patient serum presumably containing antibodies. The endpoint of the test is the observation of clumps resulting from that antigen-antibody complex formation. The quality of the result is determined by the time of incubation with the antibody source, amount and avidity of the antigen conjugated to the carrier, and conditions of the test environment (e.g., pH and protein concentration). Various methods of agglutination are used in diagnostic immunology and these include latex agglutination, flocculation tests, direct bacterial agglutination, and hemagglutination.
How does agglutination differ from precipitation?
Agglutination differs from precipitation reaction in that since agglutination reaction takes place at the surface of the particle involved, the antigen must be exposed and be able to bind with the antibody to produce visible clumps. In agglutination reactions, serial dilutions of the antibody solution are made and a constant amount ...
What is the reaction where a particulate antigen combines with its antibody?
Agglutination is an antigen-antibody reaction in which a particulate antigen combines with its antibody in the presence of electrolytes at a specified temperature and pH resulting in the formation of visible clumping of particles. It occurs optimally when antigens and antibodies react in equivalent proportions.
Why are clumps more visible?
Because cells are so much larger than a soluble antigen, the result is more visible when the cells aggregate into clumps. When particulate antigens react with specific antibody, antigen-antibody complex forms visible clumping under optimum PH and temperature. Such a reaction is called agglutination. Antibodies that produce such reactions are called ...
When antibodies and antigens react in equal proportions, the reaction occurs?
This reaction is analogous to the precipitation reaction in that antibodies act as a bridge to form a lattice network of antibodies and the cells that carry the antigen on their surface.
What is the titer of the antiserum?
The titer of the antiserum is recorded as the reciprocal of the highest dilution that causes clumping. Since the cells have many antigenic determinants on their surface, the phenomenon of antibody excess is rarely encountered.
Is aglutination test sensitive?
Agglutination tests are easy to perform and in some cases are the most sensitive tests currently available. These tests have a wide range of applications in the clinical diagnosis of non- infectious immune disorders and infectious diseases. Agglutination reactions have a wide variety of applications in the detection of both antigens and antibodies in serum and other body fluids. They are very sensitive and the result of the test can be read visually with ease.
Which dilution of serum (Ab) prevents hemagglutination?
HAI Titer: The highest dilution of serum (Ab) that prevents hemagglutination is called the HAI titer of the serum.
What is the phenomenon of hemagglutination?
But, if the serum of a person infected with measles virus is mixed with RBC and measles virus, there won’t be any agglutination of RBC. This phenomenon is known as hemagglutination inhibition. This arises because antibodies present in the serum ...
What happens if a patient's serum does not contain antibodies?
If the patient’s serum do not contain antibodies against surface proteins of test virus, there will be presence of hemagglutination as surface molecules are free to hemaaglutinate RBCs (negative result).
Why does hemagglutination inhibit RBCs?
This arises because antibodies present in the serum of that infected person react with the measles viruses and neutralize them (positive result); as the hemagglutinins are occupied, they cant bind and agglutinate RBCs. If the patient’s serum do not contain antibodies against surface proteins ...
What is the basis of the HAI assay?
Hemagglutination and hemagglutination inhibition test. The basis of the HAI assay is that antibodies to that particular virus ( for example; measles virus- see image) will prevent attachment of the virus to RBC. Therefore hemagglutination is inhibited when antibodies are present. HAI Titer: The highest dilution of serum (Ab) ...
How to detect influenza virus?
Although influenza viruses can be detected by hemadsorption test, typing of the isolate is done most efficiently by hemagglutination inhibition (HAI).
What is the reaction of viral hemagglutinins with red blood cells?
The reaction of viral hemagglutinins with red blood cells results in a lattice of agglutinated cells that settle irregularly in a tube or microtiter well, a process known as hemagglutination. Unagglutinated cells settle in a compact button. Contents. 1 Principle. 2 Materials and Reagents.
