Is it possible to convert fructose into glucose?
While the body can't convert fructose directly to glucose, it is possible to make glucose from fructose through a longer, indirect pathway. Cells require a constant supply of energy to keep them running and able to engage in cellular processes.
Can fructose be broken down into glucose?
This may explain why added sugars like high-fructose corn syrup are linked to various health issues. Glucose and fructose are absorbed directly into your bloodstream, while sucrose must be broken down first. Glucose is used for energy or stored as glycogen. Fructose is converted to glucose or stored as fat.
Does fructose increase insulin levels?
Unlike glucose, fructose does not increase blood sugar or insulin levels. However, some studies have found a connection between consumption of fructose and diabetes, which may be caused by a reduction in insulin sensitivity. Fructose is found in a number of natural food sources and even contributes to the sugar content in fruit.
Is fructose better than sucrose?
This energy content is actually common to all carbohydrates -- including starches, which are chemically related to sugars, but don't taste sweet. Because fructose tastes much sweeter than sucrose, it's possible to obtain a similar sweetness effect from fewer grams, and fewer calories,f of fructose than of sucrose.
See more

How long does it take to convert fructose to glucose?
The mean conversion rate from fructose to glucose was 41% ± 10.5 (mean ± SD) in 3–6 hours after ingestion. The conversion amount from fructose to glycogen remains to be further clarified. A small percentage of ingested fructose (<1%) appears to be directly converted to plasma TG.
How is fructose metabolized by the body?
Unlike glucose, which is used by cells as an energy source, fructose is metabolized by the liver, where it promotes the synthesis of fat. In fact, some experts believe our bodies are not designed to handle this excess fructose.
Does the liver turn fructose into glucose?
Fructose is transported to your liver to be converted to glucose or fat, while glucose can be burned for energy as is anywhere in your body.
Is all fructose converted to glucose?
29% - 54% of fructose is converted in liver to glucose, and about a quarter of fructose is converted to lactate. 15% - 18% is converted to glycogen. Glucose and lactate are then used normally as energy to fuel cells all over the body.
How long does it take to get fructose out of your system?
The metabolic effects of high-fructose corn syrup can be reversed in as little as nine days when sugar intake is limited. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, the metabolic effects of HFCS can be reversed in as little as nine days when sugar intake is limited.
Does fructose require insulin to be metabolized?
Fructose stimulates only modest insulin secretion and does not require the presence of insulin to enter cells (2). Avidly taken up by hepatic cells, fructose is rapidly converted to fructose-1-phosphate and bypasses the early, rate-limiting steps of glucose metabolism.
Can eating too much fruit damage your liver?
When large quantities of fructose reach the liver, the liver uses excess fructose to create fat, a process called lipogenesis. Eventually, people who consume too much fructose can develop nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a condition in which too much fat is stored in the liver cells.
Which fruit is not good for liver?
Consuming large amounts of fructose-rich fruits like raisins, dry fruits can result in inflammation and fatty liver. This is because the sugar present in fruits, known as fructose, can cause abnormal amounts of fat in the blood when consumed in large amounts.
Does fructose get stored as fat?
While every cell in the body can use glucose, the liver is the only organ that can metabolize fructose in significant amounts. When people eat a diet that is high in calories and high in fructose, the liver gets overloaded and starts turning the fructose into fat.
Is fructose worse than glucose?
Different sugars can have different metabolic effects, regardless of whether the sugars are consumed in calorically equal amounts. For example, fructose can be more harmful than glucose, raising the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease.
Which sugar is healthiest?
Brown sugar is definitely a healthier option than refined white sugar. It is processed in a completely natural way to maintain as much of the sugarcane's natural nutrition as possible, including vitamins and minerals.
Why is glucose better than fructose?
The glycemic index is lower in fructose when compared to glucose. The binding of fructose to cellular protein is seven times faster than glucose. Fructose is also called fruit sugar or D- fructose. Its functional group is the ketone.
How is fructose metabolized vs glucose?
Transport and metabolism of fructose do not require insulin; only a few tissues such as the liver, intestine, kidney, adipose tissue, and muscle can metabolize it. Glucose and fructose have similar metabolic fates because most of the dietary fructose converts into glucose.
How is fructose metabolized differently from glucose?
If excess glucose is consumed in the diet, it will first be stored as glycogen, and secondarily as fat. Fructose on the other hand, takes a different path. When fructose is consumed, it is exclusively metabolized in the liver, where a particular enzyme, fructokinase, will allow for the uptake of fructose (3).
How is fructose digested and absorbed?
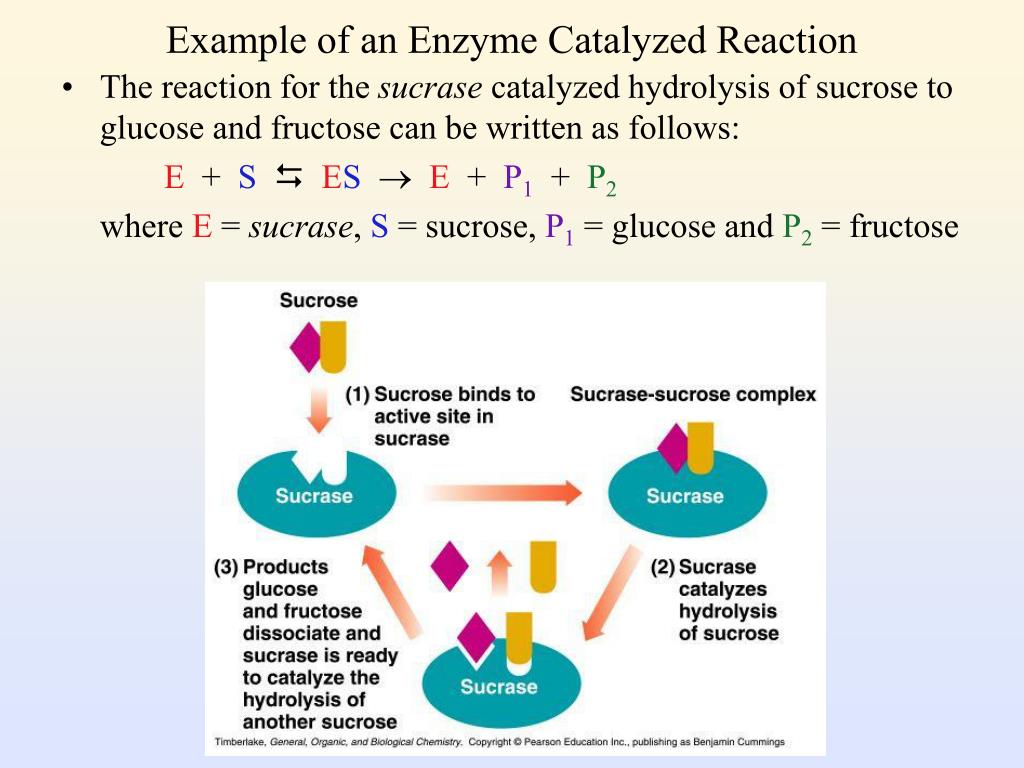
Digestion and Absorption Fructose digestion begins in the small intestine. Your body cannot absorb intact polysaccharide molecules. Therefore, if fructose is present in the form of sucrose, sucrase, an enzyme, must first break up sucrose into separate glucose and fructose components.
What enzyme breaks down fructose?
enzyme xylose isomeraseFructase is a supplement that contains the enzyme xylose isomerase. This enzyme helps your body to completely digest the fructose in food.
Can Fructose Be Broken Down Into Glucose?
Glucose and fructose are both chemically classified as monosaccharides, meaning they are single sugar units. They taste sweet, are common in foods -- both are constituents of sucrose, or table sugar -- and provide energy to cells. While the body can't convert fructose directly to glucose, it is possible to make glucose from fructose through a longer, indirect pathway. Cells require a constant supply of energy to keep them running and able to engage in cellular processes. Either glucose or fructose can supply this energy, though some cells -- particularly brain cells -- show a marked preference for glucose. Glucose, too, has importance in terms of stored energy, explain Drs. Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham in their book "Biochemistry." The liver and muscles synthesize a long molecule called glycogen out of glucose, and they can break the glycogen down and release it as needed. Glucose and fructose have identical chemical formulas, note Drs. Mary Campbell and Shawn Farrell in their book "Biochemistry"; both are C6H12O6. Since in biochemistry, the phrase "break down" refers to chemical alteration of a molecule into one or more smaller molecules, it's not technically possible to "break down" fructose into glucose. Instead, the process could theoretically take place through chemical bond rearrangement. Continue reading >>
What is the conversion of glucose 6 phosphate to fructose 6 phosphate?
Why is glucose 6 phosphate converted to fructose 6 phosphate in glycolysis? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytosol of every cell. During glycolysis, one molecule of 6-carbon glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of 3-carbon pyruvate & 2 molecules each of ATP & NADH are produced. The first step of glycolysis is not the committed step as the glucose-6-phosphate produced can be shuttled to other metabolic pathways such as pentose phosphate pathway. The committed step in glycolysis is the conversion of fructose- 6-phosphate into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by PFK-1 (phosphofructokinase-1). This step requires that glucose-6-phosphate gets first converted into fructose-6-phosphate. As per the name, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate has 2 phosphate groups attached to it- one at C-1 & another at C-6. In the structure of glucose, C-1 is an aldehyde group that can't be phosphorylated, it is first reduced to an alcoholic group by molecular interconversion with C-2 which gets converted into a ketone. The G value is very small for this reaction & therefore this reaction occurs readily in eituer direction. Now both C-1 & C-6 have hydroxyl group that can be phosphorylated hence fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is formed. Also, step 4 of glycolysis which is the breakdown of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde-6-phosphate & dihydroxyacetone phosphate requires the presence of a ketonic group at C-2 ( not present in glucose but fructose). Hence, the interconversion of glucose into fructose during glycolysis is a necessary prelude to subsequent reactions. I have written this answer to best of my knowledge & would appreciate corrections if any. Answered Jan 13, 2017 Author has 61 answers and 13.9k answer views Lets procced from the reverse direction. In the fourth step of g Continue reading >>
What are the steps of glycolysis?
In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol. This pathway can be thought of as comprising three stages (Figure 16.3). Stage 1, which is the conversion of glucose into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, consists of three steps: a phosphorylation, an isomerization, and a second phosphorylation reaction. The strategy of these initial steps in glycolysis is to trap the glucose in the cell and form a compound that can be readily cleaved into phosphorylated three-carbon units. Stage 2 is the cleavage of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into two three-carbon fragments. These resulting three-carbon units are readily interconvertible. In stage 3, ATP is harvested when the three-carbon fragments are oxidized to pyruvate. Go to: 16.1.1. Hexokinase Traps Glucose in the Cell and Begins Glycolysis Glucose enters cells through specific transport proteins (Section 16.2.4) and has one principal fate: it is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate. This step is notable for two reasons: (1) glucose 6-phosphate cannot diffuse through the membrane, because of its negative charges, and (2) the addition of the phosphoryl group begins to destabilize glucose, thus facilitating its further metabolism. The transfer of the phosphoryl group from ATP to the hydroxyl group on carbon 6 of glucose is catalyzed by hexokinase. Phosphoryl transfer is a fundamental reaction in biochemistry and is one that was discussed in mechanistic and structural detail earlier (Section 9.4). Kinases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to an acceptor. Hexokinase, then, catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to a variety of s Continue reading >>
What is the isomerization of (1-13C)-D-glucose?
The isomerization of (1-13C)-D-glucose to an equilibrium mixture of (1-~3C)-D-glucose and (1-13C)-D-fructose by the enzyme glucose i somerase (E.C. 5.3.1.5) has been followed using 13C NMR spectroscopy. It is concluded that the ~-D-glucopyranose and the ~-D-fructofuranose form are the Immobilized glucose isomerase (D-xylose ketol isomerase; E.C. 5.3.1.5) is used on an industrial scale for the isomeri- zation of D-glucose syrups into D-fructose-containing sy- rups1-3. The D-glucose-D-fructose interconversion is thought to take place via a eis-enediol intermediate coordinated to a metal ion [Mg (II) or Co (II)] of the enzyme Fig. 1. Proposed cis-enediol intermediate It has been assumed that a basic centre of the enzyme is involved in the intramolecular hydrogen transfer from C-2 of mentally, no exchange between the transferred hydrogen and the eis-enediol enzyme complex will induce, using the prin- ciple of least molecular motion, ~-D-glucopyranose formation by attack of O-5 at C-1. This indeed has been recently verified results obtained for the D-xylose-D-xylulose interconversion With respect to the ketose reactant of the enzymatic isomeri- zation, it is generally assumed that the ~-furanose from of cular models, however, shows that conversion of the -enediol intermediate (Fig. 1) into [~-D-fructofuranose re- quires a substantial geometric reorientation. According to the principle of least molecular motion, ~-D-fructofuranose is This consideration, together with the fact that the 13C NMR nation of the reactive D-fructose lie close to the experimental error, led us to reinvestigate the nature of the reactive species for the enzymatic D-glucose-D-fructose interconversion. The fast mutarotation of D-fructose at the optimum tempera- ture (65C) for the isomerization with glucose Continue reading >>
Is fructose a source of energy?
Diets containing large amounts of sucrose (a disaccharide of glucose and fructose) can utilize the fructose as a major source of energy. It should be pointed out that the difference between the amount of fructose available from sucrose obtained from cane or beet sugars is not significantly less than that from corn syrup. Corn syrup is somewhat improperly identified as high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) giving the impression that it contains a large amount of fructose. However, whereas the fructose content of sucrose is 50% (since it is a pure disaccharide of only glucose and fructose), the content in HFCS is only 55%. The reason HFCS has more than 50% fructose is because the glucose extracted from corn starch is enzymatically treated to convert some of the glucose to fructose. This is done in order to make the sugar sweeter which is why it is particularly popular in the food industry. Therefore, any disorder and/or dysfunction (see below), attributed to the consumption of fructose, can be manifest whether one consumes cane or beet sugar or HFCS. The pathway to utilization of fructose differs in muscle and liver due to the differential distribution of fructose phosphorylating enzymes. Hexokinases are a family of enzymes that phosphorylate hexose sugars such as glucose. Four mammalian isozymes of hexokinase are known (Types IIV), with the Type IV isozyme often referred to as glucokinase. Glucokinase is the form of the enzyme found in hepatocytes and pancreatic -cells. Several of the hexokinases (but not type IV) can phosphorylate various different hexoses including fructose. In addition to hexokinases, fructose can be phosphorylated by fructokinases. Fructokinases are formally referred to as ketohexokinases (KHK). There are two forms of KHK in mammals that result from alter Continue reading >>
Is fructose a carbohydrate?
Feinman and Fine; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.2013 Whether dietary fructose (as sucrose or high fructose corn syrup) has unique effects separate from its role as carbohydrate , or, in fact, whether it can be considered inherently harmful, even a toxin, has assumed prominence in nutrition. Much of the popular and scientific media have already decided against fructose and calls for regulation and taxation come from many quarters. There are conflicting data, however. Outcomes attributed to fructose obesity, high triglycerides and other features of metabolic syndrome are not found in every experimental test and may be more reliably caused by increased total carbohydrate. In this review, we try to put fructose in perspective by looking at the basic metabolic reactions. We conclude that fructose is best understood as part of carbohydrate metabolism. The pathways of fructose and glucose metabolism converge at the level of the triose-phosphates and, therefore, any downstream effects also occur with glucose. In addition, a substantial part of ingested fructose is turned to glucose. Regulation of fructose metabolism per se, is at the level of substrate control the lower Km of fructokinase compared to glucokinase will affect the population of triose-phosphates. Generally deleterious effects of administering fructose alone suggest that fructose metabolism is normally controlled in part by glucose. Because the mechanisms of fructose effects are largely those of a carbohydrate, one has to ask what the proper control should be for experiments that compare fructose to glucose. In fact, there is a large literature showing benefits in replacing total carbohydrate with other nutrients, usually fat, and such experiments sensibly constitute the proper control for comparisons of the two suga Continue reading >>
Is postprandial blood glucose a predictor of cardiovascular events?
Postprandial Blood Glucose Is a Stronger Predictor of Cardiovascular Events Than Fasting Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Particularly in Women: Lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study
What is the name of the transformation of fructose into glucose?
This is called Lobry de Bruyn–Alberda van Ekenstein transformation.
What is the substrate of the enzyme Glucose 6?
Its substrate is glucose 6-phosphate (not glucose), and the product is fructose 6-phosphate (not fructose). Normally, the enzyme works in that direction (G-6-P → F-6-P) because the F-6-P is further metabolized by the downstream glycolytic pathway.
How is fructose converted to fructose 1?
In the liver, fructose is rapidly converted to fructose 1-phosphate via fructokinase. Fructose 1-phosphate is then converted into the trioses dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde via aldolase B. Aldolase B also functions in the liver for normal glycolysis (glucose metabolism). 174 views.
What is the metabolic conversion of fructose to glycogen?
The metabolic conversion of fructose to glycogen in the liver. Fructose is converted to Glycolysis intermediates; DHAP and GA-3-P in the liver. Increased concentrations of DHAP and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in the liver drive the gluconeogenic pathway toward glucose-6-phosphate, glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen formation.
What enzyme converts glucose to fructose?
Industrially, glucose is converted to fructose with glucose isomerase, a bacterial enzyme. The discovery of this enzyme and its industrial application has brought us into the world of high fructose corn syrup. In humans, conversion of glucose to fructose should not be confused with conversion of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in ...
How many molecules are produced during glycolysis?
During glycolysis, one molecule of 6-carbon glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of 3-carbon pyruvate & 2 molecules each of ATP & NADH are produced. The first step of glycolysis is not the committed step as the glucose-6-phosphate produced can be shuttled to other metabolic pathways such as pentose phosphate pathway.
Where is fructose stored?
In humans, fructose is metabolized by the liver to products (DHAP and glyceraldehyde 3-P) that can be recombined into glucose via gluconeogeneis. Most of the time, this glucose will be stored in the liver as glycogen ( a glucose polymer that is a storage molecule). If glycogen stores fill up, fructose (as with excess carbs in general) will be converted to fat. See details at Fructolysis - Wikipedia
What is the process of isomerizing glucose to fructose?
The isomerization of glucose to fructose is part of the glycolysis cycle that converts glucose to pyruvate. The way this is done is to isomerize the aldehyde (hemiacetal) glucose to the ketone (as a hemiacetal) fructose,and make another phosphate ester. The isomerization takes advantage of the ease of breakage of a C-H bond which involves a carbon next to a carbonyl carbon
What enzyme converts glucose to fructose?
Industrially, glucose is converted to fructose with glucose isomerase, a bacterial enzyme. The discovery of this enzyme and its industrial application has brought us into the world of high fructose corn syrup.
What is the conversion of glucose into pyruvate?
The conversion is in the glycolisis cycle and its made enzimatically by glucose isomerase. The glycolisis cycle converts glucose into pyruvate.
How is glucose converted into phosphate?
Glucose is converted into Glucose-6-phosphate through the process of Phosphorylation. In this reaction ATP act as phosphate donor and magnesium ion cofactor. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase or glucokinase. The hexokinase enzyme, have a U shaped structure, that joins two substrates at its active site. First is ATP and second is Glucose.
What is the name of the transformation of glucose into fructose?
This is called Lobry de Bruyn–Alberda van Ekenstein transformation.
Why does glucose escape the cell?
The main reason is to trap glucose in the cell, thereby concentrating it. Most of the transporters for glucose are passive, so glucose can “escape” the cell by the same route it entered. By converting glucose to a form that is not recognized by the transporter, the effect is similar to active transport of glucose.
Which step of glycolysis is the breakdown of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into gly?
Also, step 4 of glycolysis which is the breakdown of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into glyceraldehyde-6-phosphate & dihydroxyacetone phosphate requires the presence of a ketonic group at C-2 ( not present in glucose but fructose). Hence, the interconversion of glucose into fructose during glycolysis is a necessary prelude to subsequent reactions.
Does fructose increase uric acid?
Pooled analyses show that although fructose may increase total cholesterol, uric acid , and postprandial triglycerides in isocaloric replacement for glucose, it does not appear to be any worse than glucose in its effects on other aspects of the lipid profile, insulin, or markers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Can you replace fructose with glucose?
In the absence of clear evidence of net harm, there is no justification to replace fructose with glucose in the diet. Depending on the cardiometabolic endpoint in question, fructose has variable effects when replacing glucose.
What are Carbohydrates?
The body converts the food we eat into energy. Even though we obtain calories and energy from different food sources, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, our main source of energy is still from carbohydrates. The body converts these carbs into glucose, which is the main sugar in the blood.
Why are carbohydrates important for the body?
Carbohydrates are efficient when it comes to producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is an energy-providing chemical that drives many cellular processes. For this reason, they remain the body’s main source of energy. The body prefers the breakdown of carbohydrates first, followed by fats. If both carbohydrates and fats are depleted, the body uses proteins for energy.
What happens when you eat a lot of carbohydrates?
One study concluded that a diet containing a high amount of carbohydrates will cause an increase in glucose and insulin levels. The cells take up glucose and either convert it into glycogen or break it down so that energy can be produced. The liver and muscles are the main storage areas of glycogen.
Why is glucose broken down?
Glycogen is broken down so that glucose can be obtained. In order to finally produce ATP, a series of reactions take place. These reactions depend on certain factors, such as enough supply of oxygen and glucose. By using different sets of reactions, glucose can still be broken down if the oxygen level is lacking. However, when it comes to energy, the body will turn to other fuel sources when glucose levels are low.
What are the steps of glucose metabolism?
The following are the steps for glucose metabolism: Glycolysis - In this process, glucose basically breaks down to pyruvic acid. Through this process, a couple of ATP molecules are produced. Krebs Cycle - First, pyruvic acid is converted into acetyl-CoA and enters into the Krebs cycle.
Which organ stores glucose?
Monosaccharides are transported to the liver , which turns galactose and fructose into glucose. The liver then sends the produced glucose into the bloodstream, where it is transported to the cells that need energy. When there are excessive glucose levels in the blood, the liver stores glucose into glycogen or fat.
Where do monosaccharides go?
Monosaccharides are transported to the liver, which turns galactose and fructose into glucose. The liver then sends the produced glucose into the bloodstream, where it is transported to the cells that need energy. When there are excessive glucose levels in the blood, the liver stores glucose into glycogen or fat.
What is the most common type of sugar that is bound to glucose?
In foods, glucose is most commonly bound to another simple sugar to form either polysaccharide starches or disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose ( 1 ).
What is sucrose made of?
Sucrose Is Made up of Glucose and Fructose. Share on Pinterest. Sucrose is the scientific name for table sugar. Sugars are categorized as monosaccharides or disaccharides. Disaccharides are made up of two, linked monosaccharides and broken back down into the latter during digestion ( 1. Trusted Source.
What are the three types of sugars that are found naturally in fruits, vegetables, dairy products and grains?
If you’re trying to cut back on sugar, you may wonder whether the type of sugar matters. Sucrose, glucose and fructose are three types of sugar that contain the same number of calories gram for gram. They’re all found naturally in fruits, vegetables, dairy products and grains but also added to many processed foods.
What happens when your blood sugar is low?
Your body tightly controls your blood sugar levels. When they get too low, glycogen is broken down into glucose and released into your blood to be used for energy ( 9 ).
Why is insulin needed?
Insulin is needed for glucose to enter your cells ( 7 ).
Where is fructose found?
Fructose. Fructose, or “fruit sugar,” is a monosaccharide like glucose ( 1. Trusted Source. ). It’s naturally found in fruit, honey, agave and most root vegetables. Moreover, it’s commonly added to processed foods in the form of high-fructose corn syrup. Fructose is sourced from sugar cane, sugar beets and corn.
Which sugar has the sweetest taste?
Of the three sugars, fructose has the sweetest taste but least impact on your blood sugar ( 2. Trusted Source. ). Summary. Sucrose is made up of the simple sugars glucose and fructose. Sucrose, glucose and fructose are found naturally in many foods but also added to processed products.
