
Circulatory systems in fish, amphibians and mammals
- The heart has two chambers; atrium and ventricle.
- Blood entering the heart goes to the atrium then the ventricle
- The ventricle then pumps blood to the gills
- As the blood leaves the gills, the capillaries carry oxygen-rich blood to the capillary beds throughout the body, then it returns to the heart.
What type of circulatory system do fish have?
Fish: Overview: Fish have a single circulatory system meaning that blood only passes through the heart once on one complete circuit around the blood system of the body. The result is a limit in the amount of oxygen that can reach some of the organs and tissues of the body, reducing the metabolic capacity.
Does a fish have a single circuit circulatory system?
In fish, the system has only one circuit, with the blood being pumped through the capillaries of the gills and on to the capillaries of the body tissues. This is known as single cycle circulation. Fish have a closed-loop circulatory system. The heart pumps the blood in a single loop throughout the body.
What type of circulatory system is found in most mollusks?
Open Circulatory System A type of circulatory system found in some invertebrates, such as arthropods and most mollusks, that includes an open space (the hemocoel) in which blood directly bathes body tissues.
What type of circulatory system does a squid have?
The squid has a posh circulatory system for an invertebrate, with a closed circulatory system. The squid has two branchial hearts on the base of the gills which ship unoxygenated blood by means of the gills. The third ventricular coronary heart then pumps this oxygenated blood all through the physique.
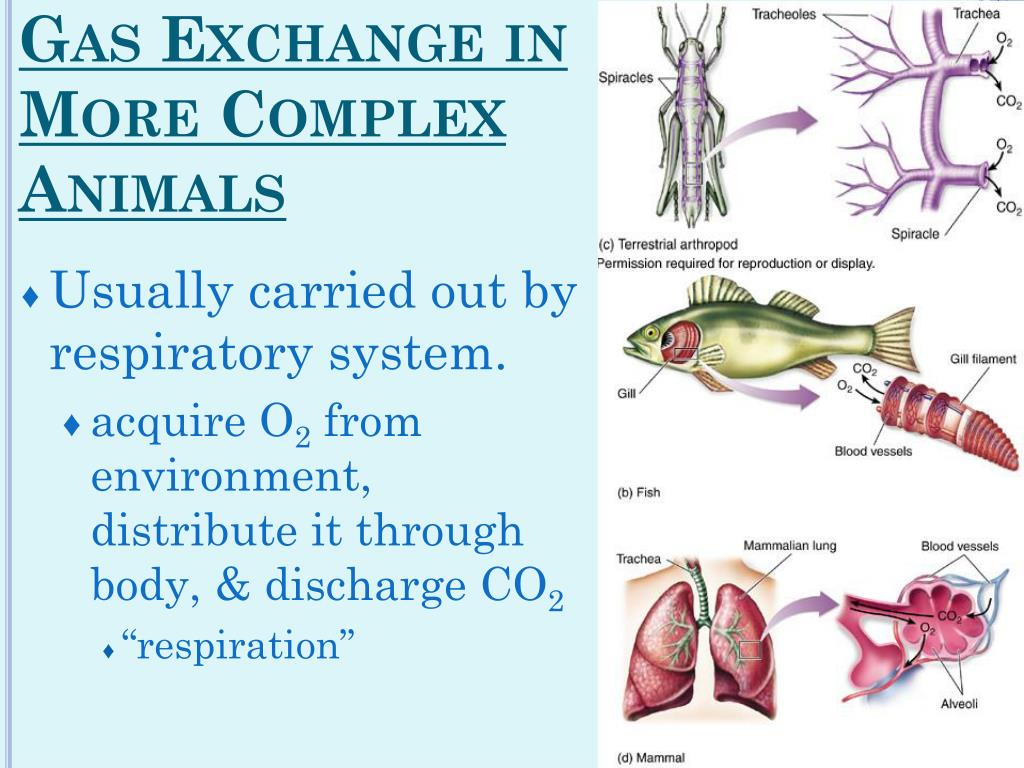
What are the parts of the fish circulatory system?
A fish's cardiovascular system comprises of two main parts: the heart and the system of pipes (veins, arteries and capillaries) that carry blood throughout the body. Every organ and cell in the fish's body is connected to this system, which serves a wide variety of purposes.
How does the circulatory system of a fish differ from the circulatory system of a human?
Heart of a fish is two chambered with one atrium and one ventricle. There is unidirectional flow of blood....Complete answer:S.NoHUMAN CIRCULATORY SYSTEMFISH CIRCULATORY SYSTEM1Humans are warm blooded animals.Fishes are cold blooded animals.2They have 4 chambered hearts.They have 2 chambered hearts.2 more rows
How is the circulation of a fish different?
In humans, the right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood and the left side receives oxygenated blood. In fishes, the deoxygenated blood flows once through the heart which is called single circulation. Only venous blood flows through the heart in fishes. So it is known as venous circulation.
Do fish have closed or open circulatory system?
The vascular system consists of arteries, veins and capillaries. Vertebrates (animals with backbones like fish, birds, reptiles, etc.), including most mammals, have closed cardiovascular systems.
Why do fish have a closed circulatory system?
The circulatory system of fishes is responsible for transporting blood and nutrients throughout the body. It has a closed circulatory system, i.e. blood travels across the body through the network of blood vessels. Fish heart carry only deoxygenated blood that is why it is called as Venous heart.
How many circulatory routes do fish have?
Animal Circulatory SystemFrogFishOpen or closed circulatory systemClosedClosedNumber of circuits for circulationThreeOneChambers in the heartThreeTwoNumber of hearts in bodyOneOneApr 24, 2019
What is blood circulation in fish called?
Fish blood circulation is called as venous circulation as its heart receives blood from veins and send it to the gills for oxygenation. Fishes have 2-chambered heart and thus, there is single circulation.
Why blood goes only once through the heart in fishes?
Solution : Fish have 2- chambered heart which pumps only venous blood. It is oxygenated in gills from where the blood flows to the rest of the body. So during one cycle the blood goes to the heart only once.
How do fish obtain oxygen?
Fish take water into their mouth, passing the gills just behind its head on each side. Dissolved oxygen is absorbed from—and carbon dioxide released to—the water, which is then dispelled. The gills are fairly large, with thousands of small blood vessels, which maximizes the amount of oxygen extracted.
Is fish blood the same as human blood?
It has been found that blood types exist in fish as they do in humans, although the types are not identical. It has also been determined that, as in humans, the frequencies of different blood types vary, depending on the population sampled.
What organs do fish have that humans dont?
Most fish have an organ called the swim bladder. It is a flexible, gas-filled sac located in the dorsal or top portion of the body cavity and helps to control the fish's buoyancy. Since fish have a density that is heavier than water, they need this swim bladder to not sink when they stop swimming.
What is the difference between blood circulation in fishes and birds?
Blood circulation is once (single circulation) in fishes due to presence of two-chambered heart whereas double circulation is seen in birds due to presence of four-chambered heart.
What are the two main parts of a fish's cardiovascular system?
PetMD Editorial. A fish’s cardiovascular system comprises of two main parts: the heart and the system of pipes (veins, arteries and capillaries) that carry blood throughout the body. Every organ and cell in the fish’s body is connected to this system, which serves a wide variety of purposes.
What is fish blood made of?
Fish blood is complex, as in all living things. Thirty to fifty percent is made up of red and white blood cells -- the reds carry oxygen while the whites are part of the immune system. The rest of the blood consists of plasma, which is a mixture of water, salts, and whatever matter the blood is carrying ...
Why do fish beat faster?
In fact, the fish’s extremities operate so inefficiently that there’s frequently a buildup of waste in the tissues. If more blood or faster circulation is needed in response to environmental changes, the endocrine system releases hormones that stimulate the heart and tell it to beat faster.
Do fish have a heart?
Fish do not have a very powerful heart. It’s a simple, four-chambered pump with two valves that circulates blood slowly throughout the body, which in turn slows the movement of oxygen and food in the body. In fact, the fish’s extremities operate so inefficiently that there’s frequently a buildup of waste in the tissues.
What are the parts of a shark's heart?
The heart of a shark contains four parts, the aforementioned atrium and ventricle, the sinus venosus, and the bulbus arteriosus. The sinus venosus is a small sac with thin walls which collects deoxygenated blood from the fish’s veins, after which the blood flows into the atrium, a large muscular chamber. The atrium is a one-way compartment for blood to flow into the ventricle (which does the pumping for the heart). The bulbus arteriosus is a large tube into which the blood is pumped from the ventricle. The bulbus arteriosus then leads the blood to the aorta, through which blood flows to the shark’s gills – where carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen bubbles.
What is the beat of a shark's heart called?
The beat is blood being pumped out of the heart, and the space is when the ventricle relaxes and is filled with blood. The beat is called a systole , and a space is called a diastole. Together, they make one beat of the heart of a shark.
Do sharks have a circulatory system?
Sharks are fish, and as such, they have a closed circulatory system (the blood never leaves the web of blood vessels). The blood is pumped through a singular loop throughout the body, to transport nutrients, gases, hormones, blood cells, nitrogen waste products, etc. back and forth through cells in the body. These nutrients help fight disease and stabilize body temperature/pH in order to maintain homeostasis. The blood travels from the two chambered heart (one atrium and one ventricle) to the gills, after which it is transported throughout the whole body, and finally back to the heart.
Which organ pushes blood to the capillary beds in organs and tissues in the body?
Contractions of the heart pushes the blood to the capillary beds in organs and tissues in the body.
What happens to the blood flow in the ventricle?
The ventricle then pumps blood to the gills. As the blood leaves the gills, the capillaries carry oxygen-rich blood to the capillary beds throughout the body, then it returns to the heart. When blood flows through a capillary bed, blood pressure decreases, which limits blood flow in the body. When the animals swims, the contraction ...
How many chambers does an amphibian have?
Amphibians. Most have three chambers; two atria and one ventricle. The ridge in the ventricle takes most of the oxygen-poor blood from the right atrium to the pulmocutaneous circuit and most of the oxygen- rich blood from the left atrium to the systemic circuit.
What are the two chambers of the circulatory system?
Circulatory systems in fish, amphibians and mammals. The heart has two chambers; atrium and ventricle. As the blood leaves the gills, the capillaries carry oxygen-rich blood to the capillary beds throughout the body, then it returns to the heart. When blood flows through a capillary bed, blood pressure decreases, which limits blood flow in the body.
Which side of the heart pumps oxygen rich blood?
Have two atria and two completely divided ventricles. The left side of the heart pumps and receives only oxygen-rich blood while the right side of the heart pumps and receives only oxygen-poor blood. Mammals are typically bigger and take up more energy so their circulatory systems need to deliver more oxygen to their tissues.
How many pumps are there in the heart?
There are two pumps that are connected to the heart for the two circuits. One pump delivers oxygen-poor blood to the capillary beds in the gas exchange tissues, where O2 is added and CO2 is excreted out of the blood, this is called pulmonary circuit if it uses capillaries from the lungs in in reptiles and mammals and pulmocutaneous circuit in ...
