The disk diffusion test, or agar diffusion test, or Kirby–Bauer test, is an antibiotic susceptibility test. It uses antibiotic discs to test the extent to which bacteria are affected by those antibiotics. In this test, wafers containing antibiotics are placed on an agar plate where bacteria have been placed, and the plate is left to incubate. If an antibiotic stops the bacteria from growing or kills the bacteria, there will be an area around the wafer where the bacteria have not grown ...
What is disk diffusion testing?
The disk diffusion method is among the most flexible susceptibility testing methods in terms of antimicrobial agents that can be tested.
What is a disk-diffusion susceptibility test?
PRINCIPLES OF THE PROCEDURE In the disk-diffusion susceptibility test, disks containing known amounts of an antimicrobial agent are placed on the surface of an agar plate containing a nonselective medium that has been inoculated with a suspension of a strain of N. gonorrhoeae to give a confluent lawn of growth.
What is disk diffusion method (DDM)?
The disk diffusion method (DDM) is classified as an agar diffusion method (ADM) because the plant extract to be tested diffuses from its reservoir through the agar medium seeded with the test microorganism. Generally, the reservoir is a filter paper disk, which is placed on top of an agar surface.
How is agar plate inoculated in disk diffusion method?
Similarly to the procedure used in disk-diffusion method, the agar plate surface is inoculated by spreading a volume of the microbial inoculum over the entire agar surface. How is the information from a Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test used for the recommendation of the clinical use of an antimicrobial drug?

How does the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test work?
In Kirby-Bauer testing, bacteria are placed on a plate of solid growth medium and wafers of antibiotics (white disks, shown) are added to the plate. After allowing the bacteria to grow overnight, areas of clear media surrounding the disks indicate that the antibiotic inhibits bacterial growth.
How can the disk diffusion method determine antibiotic susceptibility?
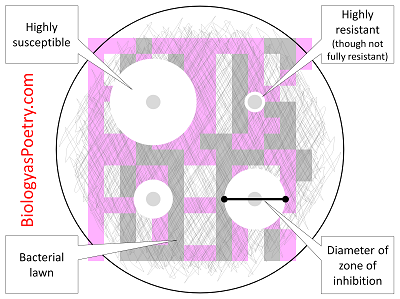
In diagnostic laboratories, the disk diffusion test is used to determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to different antibiotics. An effective antibiotic will produce a large zone of inhibition (disk C), while an ineffective antibiotic may not affect bacterial growth at all (disk A).
What is the benefit of disk diffusion method test?
Disk diffusion has many advantages, as it is cheap, flexible and allows visibility of growth, correct inoculum, mixed cultures and other abnormalities. Another benefit is the possibility of executing direct susceptibility testing (DST).
How is antibiotic susceptibility measured?
Antibiotic susceptibility is determined by measuring the diameter of the zones of bacterial inhibition around the antibiotic disks and comparing the diameter with disk diffusion interpretive criteria updated annually by CLSI 12,15.
What does the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test assess quizlet?
Blood agar is used in the Kirby-Bauer disk-diffusion test because it allows for easy diffusion of the antimicrobial agent through the agar. The disk-diffusion method determines which antibiotics are resistant to the bacteria.
Does disk-diffusion determine MIC?
Moreover, the agar disk-diffusion method is not appropriate to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), as it is impossible to quantify the amount of the antimicrobial agent diffused into the agar medium.
What are the limitations of the disc diffusion method?
There are serious limitations to the use of disk diffusion method. Results may be unexpected or borderline. In such cases another method of testing may be required or the test may need to be repeated for confirmation.
What is the meaning of disc diffusion?
Disk Diffusion Method. NCI Thesaurus. Code C85595. A method to determine microbial susceptibility to antibiotics in which filter paper disks containing known concentrations of antibiotics are placed on the agar surface that has been previously inoculated with the bacteria of interest.
What is the basis of resistance and susceptibility in the agar disc diffusion test?
Interpretation of susceptibility and resistance was based only on the presence or absence of a zone of inhibition surrounding the disk, and two or three different concentrations of the same antimicrobial were routinely tested against the pathogen (1).
Does the disc diffusion technique measure bacteriostatic or bactericidal activity?
Is the disk-diffusion technique measuring bacteriostatic or bacterial activity? Explain. Measuring bacteriostatic because instead of killing the microorganisms they inhibit microbial growth.
Why is the disk-diffusion method not a perfect measure of how an antimicrobial agent performs in vivo?
Why is the disk-diffusion method not a perfect measure of how an antibiotic agent performs in vivo (in a living patient)? Because in the disk method it is placed directly on the tested substance which is not the case in the living patient.
What is the Kirby Bauer method in susceptibility testing?
The Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test determines the sensitivity or resistance of pathogenic bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds in order to assist physicians in selecting treatment options their patients.
What is disk diffusion test?
In diagnostic laboratories, the disk diffusion test is used to determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates of bacteria to different antibiotics. An effective antibiotic will produce a large zone of inhibition (disk C), while an ineffective antibiotic may not affect bacterial growth at all (disk A). Antibiotics to which a bacterial isolate is ...
When was agar diffusion first used?
Agar diffusion was first used by Martinus Beijerinck in 1889 to study the effect of auxins on bacterial growth. However, the method has been developed, refined and standardized by many scientists and scientific organizations over the years including George F. Reddish, Norman Heatley, James G. Vincent, Alfred W. Bauer, William M.M. Kirby, John C.
What is Kirby-Bauer test?
Standard Kirby–Bauer testing: White disks containing antibiotics shown on an agar plate of bacteria. Circular zones of poor bacterial growth surround some disks, indicating susceptibility to the antibiotic.
What is an assay used for?
In diagnostic labs, the assay is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria isolated from a patient's infection to clinically approved antibiotics. This allows physicians to prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic treatment.
How long does it take to incubate a plate?
This must be done within 15 minutes of inoculation. Flame-sterilized forceps are used to gently press each disk onto the agar and ensure it is attached. Plates are then incubated overnight, usually at a temperature of 35 °C. Plates must be incubated within 15 minutes of applying antibiotic disks.
Where are antibiotic disks placed?
Disks containing increasing antibiotic concentrations are placed on a seeded bacterial lawn on the agar surface and plates are incubated. Zone sizes are measured from the edge of the disk to the end of the clear zone. Interpretation is more complicated in mixed susceptibility populations.
What is KB test?
Not to be confused with the Kleihauer–Betke test, which is also often called a "KB test". Microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. It has been suggested that this article be merged into Antibiotic sensitivity testing. ( Discuss) Proposed since July 2020.
What is the disk diffusion test?
In the disk-diffusion susceptibility test, disks containing known amounts of an antimicrobial agent are placed on the surface of an agar plate containing a nonselective medium that has been inoculated with a suspension of a strain of N. gonorrhoeae to give a confluent lawn of growth. The antimicrobial agent diffuses into the medium, causing a zone of inhibition of growth of the strain around the disk corresponding to the susceptibility of the strain to the agent. Interpretative inhibition zone diameters have been established for susceptibility test results to permit classification of an isolate as being susceptible, intermediate (or exhibiting decreased susceptibility), or resistant to an antimicrobial agent ( Table 1; 1, 2 ).
How to adjust turbidity of cell suspension?
Adjust the turbidity of the cell suspension by adding additional Mueller-Hinton broth or organisms, as required, until the turbidity of the suspension is equivalent to the turbidity of a 0.5 McFarland BaSO4 standard. Discard this cell suspension if it is not used within 15 to 20 min after preparation, and prepare a fresh suspension for testing.
What is the gold standard for agar dilution?
Agar dilution susceptibility testing is the “gold standard” for susceptibility testing of N. gonorrhoeae. However, when performed correctly, the disk-diffusion and Etest susceptibility tests can be used to identify isolates of N. gonorrhoeae that exhibit decreased susceptibility, intermediate resistance, and resistance to antimicrobial agents.
Where to submit Neisseria isolates?
In the United States, it is recommended that isolates from certain infections be submitted to the Neisseria Reference Laboratory at CDC for confirmation; these infections comprise those that fail to respond to CDC-recommended therapy and isolates determined to exhibit intermediate resistance or resistance: Cau Pham, [email protected], 404 718 5642), Neisseria Reference Laboratory, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1600 Clifton Rd. NE, Mailstop A12, Atlanta, GA 30333.
How long to incubate a streak plate?
Examine plates for growth after incubation at 35 C to 36.5 C in 5% carbon dioxide for 24 to 48 h.
Can you use 24-h cultures for susceptibility testing?
Do not use 24-h cultures of strains from the frozen preparation for susceptibility testing; strains must be subcultured at least once after recovery from a frozen suspension before being used to prepare suspensions for susceptibility testing.
Can you inoculate plates with plastic swab?
Note 2: It is recommended that swabs with plastic handles not be used to inoculate plates; the handles bend and may splatter liquid out of the tube when excess suspension is being expressed, creating a biohazard. Repeat step 4, using a new sterile swab, to inoculate each additional plate as needed.
How long to incubate a disk?
Place a duplicate of each disk on the other inoculated plate, using the same procedures. Invert the plates and incubate them at 35°C for 18 to 24 hours. Results. Observe for the presence or absence of growth around each antimicrobial disk on each plate culture.
What happens if a zone of inhibition surrounds the disk?
If a zone of inhibition surrounds the disk, the organism is not automatically considered susceptible (S) to the drug being tested. The diameter of the zone must first be measured (in millimeters) and compared for size with values listed in a standard chart (Table 15.1).
How to test for antimicrobials?
The testing method most frequently used is the standardized filter paper disk agar diffusion method , also known as the NCCLS (National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards) or Kirby-Bauer method. In this test, a number of small, sterile filter paper disks of uniform size (6 mm) that have each been impregnated with a defined concentration of an antimicrobial agent are placed on the surface of an agar plate previously inoculated with a standard amount of the organism to be tested. The plate is inoculated with uniform, close streaks to assure that the microbial growth will be confluent and evenly distributed across the entire plate surface. The agar medium must be appropriately enriched to support growth of the organism tested. Using a disk dispenser or sterile forceps, the disks are placed in even array on the plate, at well-spaced intervals from each other. When the disks are in firm contact with the agar, the antimicrobial agents diffuse into the surrounding medium and come in contact with the multiplying organisms. The plates are incubated at 35°C for 18 to 24 hours.
How to inoculate agar plate?
Dip a swab into the bacterial suspension, express any excess fluid against the side of the tube, and inoculate the surface of an agar plate as follows: first streak the whole surface of the plate closely with the swab; then rotate the plate through a 45° angle and streak the whole surface again; finally rotate the plate another 90° and streak once more. Discard the swab in disinfectant.
What is disc diffusion test?
As the Broth dilution method are time-consuming, many laboratories in the United States adopted disc diffusion tests in the early 1950s. Kirby Bauer tests also known as the Disc diffusion test is used for antibiotic susceptibility testing. Lacks of standardization creates a problem in the 1960s and later Kirby and Bauer reviewed the description. In 1961, WHO standardized the procedure. Currently, CLSI updates and modifies the original procedure which ensures uniformity worldwide. This test is mainly performed to determine the sensitivity or resistivity of aerobes or facultatively anaerobes against different classes of antibiotics.
How to sterilize forceps before picking up antibiotic discs?
Firstly sterilize the forceps with alcohol before picking up antibiotic discs.
Why is antibiotic susceptibility testing important?
Antibiotic susceptibility testing is a very important step to monitor antimicrobial resistance. It guides the clinician to select the best antimicrobial agent. To acquire information on microorganisms of public health importance.
What is the process of swabing the surface area of a plate?
Swab the surface area of the plate completely by rotating the plate. This technique is called lawn culture or carpet culture.
What agar is used to test for sulphonamides?
The organism to be tested must be incubated overnight in broth and must be compared with the 0.5 McFarland Turbidity standard. Mueller- Hinton agar must be used as it does not inhibit sulphonamides and ensures reproducibility and with composition and PH of the medium. The agar when poured on Petri dishes should be 4mm.
How long to incubate a plate upside down?
Incubate the plate upside down for 24 hours at 37ºC.
Why is a bacterial test important?
It can be useful in monitoring antimicrobials and for the selection of proper antibacterial agents. It doesn’t require special equipment to perform and can be interpreted by all medical personnel.

Overview
The disk diffusion test (also known as the agar diffusion test, Kirby–Bauer test, disc-diffusion antibiotic susceptibility test, disc-diffusion antibiotic sensitivity test and KB test) is a culture-based microbiology assay used in diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. In diagnostic labs, the assay is used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria isolated from a patient's infection to clinically approv…
History
Agar diffusion was first used by Martinus Beijerinck in 1889 to study the effect of auxins on bacterial growth. However, the method has been developed, refined and standardized by many scientists and scientific organizations over the years including George F. Reddish, Norman Heatley, James G. Vincent, Alfred W. Bauer, William M.M. Kirby, John C. Sherris, Hans Martin Ericsson, the World Health Organization, the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, the Swedish Referenc…
Principle
A pure bacterial culture is suspended in saline, its turbidity is standardized, and it is swabbed uniformly across an agar plate. An antibiotic- or extract-impregnated filter paper disk is then placed on the surface of the agar. The disk constituent(s) diffuse from the filter paper into the agar. The concentration of these constituents will be highest next to the disk and will decrease as the distance from the disk increases. If the antibiotic or extract is effective against bacteria at a …
Standard method
All aspects of the Kirby–Bauer procedure are standardized to ensure consistent and accurate results. Because of this, a laboratory must adhere to these standards. The media used in Kirby–Bauer testing must be Mueller–Hinton agar at only 4 mm deep, poured into either 100 mm or 150 mm Petri dishes. The pH level of the agar must be between 7.2 and 7.4. Bacterial inoculum is prepared …
Alternate methods
Several variations of the disk diffusion method have been developed including the Oxford penicillin cup and Etest methods used in hospital diagnostic laboratories, and the well diffusion, cylinder diffusion and bioautography methods used in drug discovery and development laboratories.
Disks containing increasing antibiotic concentrations are placed on a seeded bacterial lawn on t…
Other images
• Agar diffusion was first used in 1889 by Martinus Beijerinck.
• A close-up look at the results of an agar diffusion test.
• An antibiogram of Serratia marcescens. Each disk is labelled with the antibiotic it contains (e.g. AMC30, 30µg amoxicillin/clavulanic acid)
See also
• Antibiotic sensitivity testing
• Double-disk diffusion test
• Etest
Intended Use
Antimicrobial Resistance in N. gonorrhoeae
- N. gonorrhoeae usually develops resistance to antimicrobial agents within a few years of their introduction for gonorrhea therapy. Antimicrobial resistance in N. gonorrhoeae occurs as chromosomally mediated resistance to a variety of antimicrobial agents, including penicillin, tetracycline, spectinomycin, and fluoroquinolones (3, 4), and high-level, plasmid-mediated resist…
Disclaimer
- This brochure contains current CLSI-recommended procedures and interpretive criteria for agents used for the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea and for routine surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in N. gonorrhoeae (1, 2). The CLSI may revise interpretive criteria contained in this brochure. Consumers in the United States are advised always to consult current CLSI publicatio…
Principles of The Procedure
- In the disk-diffusion susceptibility test, disks containing known amounts of an antimicrobial agent are placed on the surface of an agar plate containing a nonselective medium that has been inoculated with a suspension of a strain of N. gonorrhoeae to give a confluent lawn of growth. The antimicrobial agent diffuses into the medium, causing a zone ...
Reference Strains
- Gonococcal antimicrobial susceptibility reference strains include strain ATCC 49226, which is the CLSI-designated QC strain for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of N. gonorrhoeae. Additional QC strains are used at CDC to control for resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and spectinomycin; intermediate resistance and resistance to ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin; high MICs of azithromyci…
Recovery, Maintenance, and Storage of Reference Strains
- Re-hydrate the strains in approximately 0.5 ml of trypticase soy broth containing 20% glycerol (freezing medium for N. gonorrhoeae), Mueller-Hinton broth, or sterile saline; phosphate buffered sali...
- Inoculate the suspension of re-hydrated organisms onto plates of a selective medium by the streak plate method to allow growth of individual colonies. Examine plates for growth after in…
- Re-hydrate the strains in approximately 0.5 ml of trypticase soy broth containing 20% glycerol (freezing medium for N. gonorrhoeae), Mueller-Hinton broth, or sterile saline; phosphate buffered sali...
- Inoculate the suspension of re-hydrated organisms onto plates of a selective medium by the streak plate method to allow growth of individual colonies. Examine plates for growth after incubation at...
- Subculture isolated colonies resembling N. gonorrhoeaeonto a nonselective medium (e.g., chocolate agar) and incubate plates at 35 C to 36.5 C in 5% carbon dioxide for 24 h. Confirm that the culture...
- To store strains for future use, prepare a dense suspension with growth from a 24-h pure cult…
Materials
- Gonococcal reference strain ATCC 49226 (F-18) and additional QC strains as required
- Selective medium (Martin-Lewis, modified Thayer-Martin, GC-Lect, or equivalent medium)
- Nonselective medium (chocolate agar supplemented with 1% IsoVitaleX or an equivalent medium)
- Sterile trypticase soy broth containing 20% glycerol, Mueller-Hinton broth, saline, or phosphat…
- Gonococcal reference strain ATCC 49226 (F-18) and additional QC strains as required
- Selective medium (Martin-Lewis, modified Thayer-Martin, GC-Lect, or equivalent medium)
- Nonselective medium (chocolate agar supplemented with 1% IsoVitaleX or an equivalent medium)
- Sterile trypticase soy broth containing 20% glycerol, Mueller-Hinton broth, saline, or phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2
disk-diffusion Test Procedure
- Warm, to room temperature, the appropriate number of GC agar plates for each strain to be tested.Note 1: The number of plates required per strain tested will depend on the anticipated zone inhibiti...
- Suspend isolated colonies from an overnight culture on supplemented chocolate agar medium in 1.0 to 2.0 ml of Mueller-Hinton broth. Mix the suspension thoroughly on a vortex mixer to b…
- Warm, to room temperature, the appropriate number of GC agar plates for each strain to be tested.Note 1: The number of plates required per strain tested will depend on the anticipated zone inhibiti...
- Suspend isolated colonies from an overnight culture on supplemented chocolate agar medium in 1.0 to 2.0 ml of Mueller-Hinton broth. Mix the suspension thoroughly on a vortex mixer to break up clump...
- Adjust the turbidity of the cell suspension by adding additional Mueller-Hinton broth or organisms, as required, until the turbidity of the suspension is equivalent to the turbidity of a 0.5 McFarl...
- Moisten a sterile applicator swab in the standardized cell suspension, and express excess m…
Limitations of The Test
- The MICs and inhibition zone sizes given in this protocol for ATCC 49226 are recommended by CLSI, MIC results for additional QC isolates are derived from testing performed at the NRL, CDC and in the GISP regional laboratories, and disk diffusion inhibition zone diameters were determined at the NRL, CDC; all values were determined on GC II agar base medium supplement…
Special Notes
- At this time, the NCCLS has not published criteria for interpretation of susceptibilities of N. gonorrhoeae isolates to levofloxacin or azithromycin (1, 2, 9). Levofloxacin (250 mg, single dose, oral) is recommended by CDC for the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea in the United States (7). However, based on the pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin, it is estimated that gonococcal iso…