Electron Cloud Electron cloud model is a model of an atom
Atom
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-milliont…
What is electron cloud model of the atom?
Electron cloud model is a model of an atom, in which the atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The electron cloud model says that we cannot know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but the electrons are more likely to be in specific areas.
What is Schrodinger's electron cloud model?
► Schrodinger built on his idea and came up with an electron cloud model. It consisted of a nucleus surrounded by clouds of electrons. The clouds indicate the probable positions of electrons in an atom. Greater density of electrons in a certain area is indicative of a higher probability of finding electrons in that atomic region.
What is the edge of the electron cloud?
The electron cloud has fuzzy edges, dissipating as it moves away from the nucleus. It doesn't really have an edge where it ends, but it does decrease in density very quickly as distance from the nucleus increases. Electron Cloud Model: What Does the Electron Cloud Model Describe?
How does a better model view the electron's orbit?
A better model views the electron's orbit as a cloud, where its position is uncertain and exists as a probability. In the electron cloud model, the nucleus is still in the center, but the election does not have a set path around it.
See more
How is electron cloud model explained?
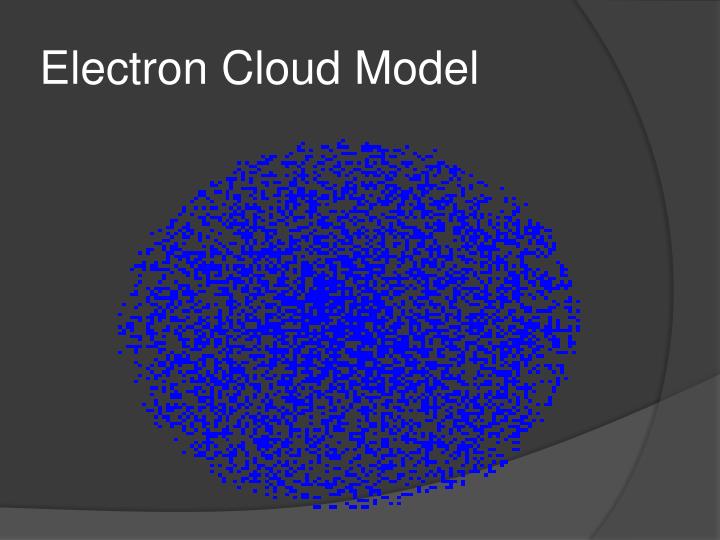
The modern model is also commonly called the electron cloud model. That's because each orbital around the nucleus of the atom resembles a fuzzy cloud around the nucleus, like the ones shown in the Figure below for a helium atom. The densest area of the cloud is where the electrons have the greatest chances of being.
What is the electron cloud model based on?
quantum theoryBased on quantum theory, which states that all matter has properties associated with a wave function, the Electron Cloud Model differs from the Bohr Model in that it does not define the exact path of an electron.
How was the electron cloud model developed?
Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger (1887-1961) developed an “Electron Cloud Model” in 1926. It consisted of a dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons at various levels in orbitals. Schrödinger and Werner Heisenburg (1901-1976) mathematically determined regions in which electrons would be most likely found.
What makes up the electron cloud?
Electron cloud: A group of electrons circulating around a nucleus or a molecule. Usually refers to the valence electrons. Methane's electron cloud. plus six electrons (E) in the electron cloud.
Which best describes an electron cloud?
What best describes an electron cloud? The electron cloud is a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. We can't say exactly where an electron is, but we can use its wave function to show the probability that it is in a particular area. That probability field is the called the electron cloud.
Why is it important to understand the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model best represents our current understanding of the atomic structure. The electron cloud model describes the atom as containing a dense nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by regions of space (clouds) where electrons are most likely to be found.
How do you make an electron cloud?
1:135:00electron cloud model - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipUnderstand or explain it but we have two electrons per cloud now remember electrons don't like eachMoreUnderstand or explain it but we have two electrons per cloud now remember electrons don't like each other so it like be next to each other as well the first cloud is round.
What is meant by electron cloud?
: the system of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom.
Do electrons move in electron cloud?
1. Generally atoms' electrons do not move in anything like the classical sense. In particular, for the lowest energy state of the hydrogen atom, the electron cloud goes absolutely nowhere, keeping a fixed distribution in time.
Where is the electron cloud located?
1 Answer. Electron cloud is located in the area around the nucleus.
What is a sentence for electron cloud?
It consists of a dense core called the atomic nucleus surrounded by a space occupied by an electron cloud . In 1999 it served as an observatory for the electron cloud phenomenon.
What's the difference between electron cloud and orbital?
1 showed no defined orbitals circling the nucleus in rings, but rather an overall area around the nucleus where the electrons were located. In an electron cloud model the electrons still exist within orbitals, but the shapes of the orbitals are more like a probability map of the location of electrons.
Which statement about the electron cloud model is true?
Which statement about the electron-cloud model is true? It is the currently accepted atomic model. Which atomic model states that it is impossible to know the exact location of electrons around the nucleus? The Bohr model of the atom explained why emission spectra are discrete.
What is meant by electron cloud?
: the system of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom.
What are the essential features of the electron cloud model of the atom?
The electron cloud model says that we cannot know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but the electrons are more likely to be in specific areas. These areas are specified by orbitals. The orbitals are specified by shells and sub-orbitals. In the Bohr model, electrons are assigned to different shells.
What is the basis for quantum mechanical model of the atom?
Solution : The basis of quantum mechanical model for an atom is dual nature of electron i.e electron possesses particle nature as well as wave nature.
Why is it called an electron cloud?
An electron cloud kind of looks like a cloud. It is thicker in the center and fades out at the edges. The term cloud also describes the many possib...
Who came up with the electron cloud model?
Erwin Schrodinger came up with the electron cloud model, building on the work of several other physicists. Louis de Broglie's particle-wave duality...
What best describes an electron cloud?
The electron cloud is a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. We can't say exactly where an electron is, but we can use its wave fu...
What is another name for an electron cloud?
An electron cloud can be thought of as a probability field, the area in space where an electron is likely to be. In an atom, these fields, specific...
Why is it called the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model shows a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. In a simple atom like Helium for instance, the probability f...
What is the electron cloud model used for?
The electron cloud is used to describe the behavior of electrons, and it is useful in building a model of the atom. The electron cloud shows the ar...
What is the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model shows a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. In a simple atom like Helium for instance, the probability field is a sphere surrounding the nucleus, and the electron is more likely to be closer to the nucleus than far away from it. The probability field is denser in the middle and fizzles outward, and so it actually resembles the cloud of possible and probable locations for the electron.
Why did Schrodinger create the electron cloud model?
Schrodinger created the electron cloud model to explain certain unknowns in quantum physics, but he knew that it didn't explain everything. He did not like this his equation did not directly describe the properties of a particle, and that it didn't really even define what a wave function was. The electron cloud model was built as a compromise, leaving some unknowns but erasing some others. In time, perhaps a better model will emerge.
What was Heisenberg's idea of quantum physics?
In 1927, Heisenberg realized that there was an inherent uncertainty when measuring quantum particles. His thought experiment described an attempt to measure the position of a very small particle with a microscope. For an observer to do that, light would have bounce off of the quantum particle, but that photon of light would be enough to change the direction of a particle that small. This would mean that its direction or momentum would now be off, and the observer wouldn't know by precisely how much. More precise measurements of a quantum particle's position would require a stronger microscope, meaning higher-energy photons, meaning more uncertainty about the particle's momentum after the observation. Heisenberg realized that this was an essential component of quantum physics, not a limitation.
What was Schrodinger's wavefunction?
In 1926, Schrodinger developed his wavefunction model, giving a probability for an electron to be in a particular location. He wrote to Albert Einstein in April of 1926, "This whole conception falls entirely within the framework of wave mechanics ." Schrodinger's wavefunction was especially exciting to the physics community at large because it complemented Heisenberg's then-new mathematics for determining the position and energy of quantum particles, rather than correcting or refuting it.
What is the quantum physics of electrons?
Electrons are very small particles, having a mass of {eq}9.1094 cdot 10^ {-31}: kg {/eq}, so their behavior is explained mostly by quantum physics. So for an electron, the uncertainty principle holds, and we can confidently treat it as a wave function. With the proper math, we can describe an electron's position as a probability field, normally distributed around the nucleus of an atom. The wave function of an electron also explains why the electron doesn't hang out in the nucleus. The energy needed to keep it there is too high.
How many electrons does a hydrogen atom have?
Let's look at a simple atom to see what the electron cloud model describes. A Hydrogen atom has one proton and one electron. A classic and probably more familiar model for the Hydrogen atom looks like this
What is the nucleus in red?
The nucleus in red is a single proton, and the electron in yellow orbits it in a circular path.
How does the electron cloud model differ from the Bohr model?
Based on quantum theory, which states that all matter has properties associated with a wave function, the Electron Cloud Model differs from the Bohr Model in that it does not define the exact path of an electron. Instead, it predicts the likely position of the location of the electron based on a function of probabilities.
Who was the first physicist to study electron cloud?
The Electron Cloud Model: During the 1920s, Austrian physicist Erwin Schrodinger became fascinated by the theories Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, Arnold Sommerfeld, and other physicists. During this time, he also became involved in the fields of atomic theory and spectra, researching at the University of Zurich and then ...
Why is the plum pudding model named after the plum pudding?
And from this, the Plum Pudding Model was born, so named because it closely resembled the English desert that consists of plum cake and raisins.
Which model of matter disproved the notion that hydrogen atoms were the smallest unit of matter?
To explain the overall charge of the atom, which consisted of both positive and negative charges, Thompson proposed a model whereby the negatively charged “corpuscles” were distributed in a uniform sea of positive charge – known as the Plum Pudding Model.
Which model of the atom is surrounded by an equal number of electrons in orbital shells?
the Bohr Model ).
What was the smallest known atom?
However, most scientists ventured that this unit would be the size of the smallest known atom – hydrogen .
Where are electrons likely to be found?
Hence, their locations could only be described as being part of a ‘cloud’ around the nucleus where the electrons are likely to be found.
What is the electron cloud?
Electron cloud defines the zone of probability describing the electron’s location, because of the uncertainty principle.In the electron cloud model, the atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons.
How do electrons escape from an atom?
The electrons in an atom are attracted to the protons in the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. This force binds the electrons inside an electrostatic potential well surrounding the smaller nucleus, which means that an external source of energy is needed for the electron to escape.
How many electrons are in an electrically neutral atom?
The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19coulombs. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
What is the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model emerged out of the solution of the Schrödinger equation for the Hydrogen atom. The model predicts clouds of probability around the atom, which we now call ‘atomic orbitals’. Instead of a clear orbit, the electron is spread around the atom in clouds of probability. Every electron is known to have certain ‘quantum numbers’ and it populates only certain regions of space around the atom, according to its energy level. Every electron is spread out in a probability cloud, in space. The cloud model is the archetype, that has now replaced the solar system like model, propounded by Neils Bohr, for the atomic structure.
Where are electrons spread out?
Every electron is spread out in a probability cloud, in space.
What did physicists discover about particles?
Electromagnetic waves were discovered to behave like particles (dubbed as ‘photons’). In fact, all matter showed wave-particle duality. Therefore, physicists stopped talking in certainties and began thinking in terms of clouds of probability, rather than the position of a particle.
What is the theory of quantum mechanics?
Modern physics tells us that the dynamic behavior of atoms and molecules, including subatomic particles like electrons cannot be described by the laws of classical Newtonian physics. To describe the mechanics of these particles of an atom, a radical shift from established classical ideas was required, as things at the microscopic level behaved like nothing at the macroscopic level. The successor as you may know, was quantum physics. The theory of quantum mechanics was able to model the behavior of atoms, molecules, and subatomic particles like electrons.
How do electrons move in the electron cloud?
The e- try to move from negative charged parts to positive one as these are having excess electron, where as +ve one need more electron to full fill it’ s orbital. So, e- will jump one zone to other ones, hence current also flows through in reverse direction.
Why is it called an electron cloud?
This model identified as electron cloud model as each orbital surround the nucleus of the atom be similar to a fuzzy cloud around the nucleus. The deepest area of the cloud is which e- having its highest chances to be present in that time. As it’s very similar to normal cloud and it’s of -vely charged electron, so acknowledged as electron cloud.
Who discovered the neutrons?
James Chadwick invented neutron, used scattering data to calculate the mass of this neutral particle.
What is Bohr's model of electron energy?
Bohr’s model treats electron energy level as evidently well-defined as an orbital path surround the nucleus (similar to a model, just like the way planet is encircling the Sun).
How do electrons move in a circuit?
The move of the electron happens from negatively charged parts to ones that were positively charged. Any circuit’s negatively charged pieces have additional electrons, whereas the pieces want more, additional electrons. The electrons then jump to another level. The current can flow through the system when the electrons move.
What is a negatively charged particle?
A negatively charged (free or bounded) particle an atom and charge on a single electron is a unit -ve charge.
Why do electrons have the same charge?
The electrons maintain particle-like properties; for example, every wave state has the same electric charge because of its electron particle. Each wave state has one distinct, discrete spin (spin up or spin down) determined by its superposition.