See more

How is ozone depletion affect Antarctica?
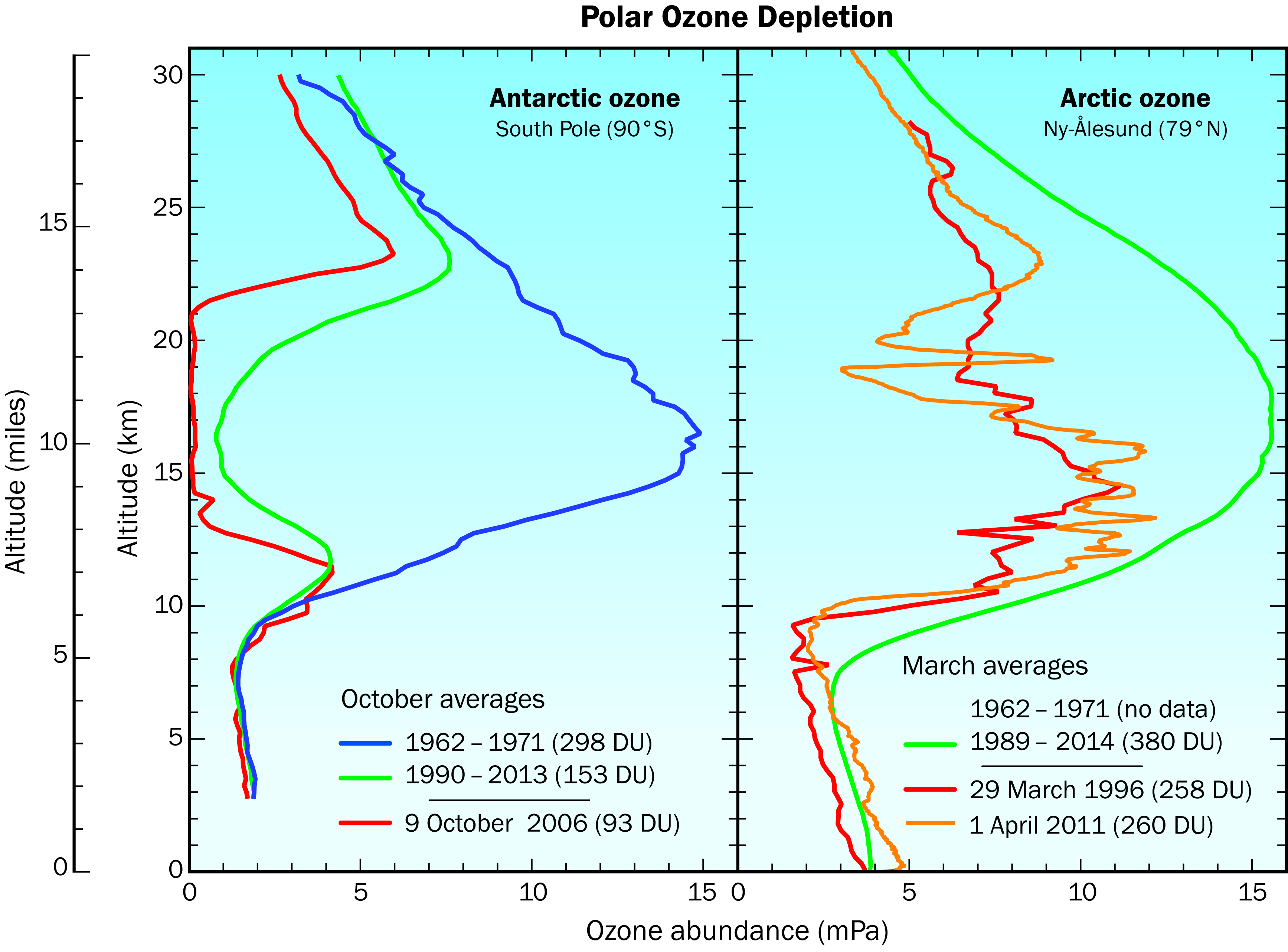
Antarctic ozone hole The Antarctic is much colder than the rest of the planet and experiences consistent strong winds. The Antarctic ozone hole develops in August and dissipates in late November when warmer weather and ozone rich air from outside the polar vortex disrupts the chemical reactions causing ozone depletion.
Why is the ozone hole worse over Antarctica?
The wintertime temperatures in the Arctic stratosphere are not persistently low for as many weeks as over Antarctica, which results in correspondingly less ozone depletion in the Arctic (see the next question).
Why is the ozone layer in Antarctica significant?
World of Change: Antarctic Ozone Hole. The stratospheric ozone layer protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet light, which damages DNA in plants and animals (including humans) and leads to sunburns and skin cancer.
What is the ozone hole in Antarctica?
What we call the ozone hole is a thinning of the protective ozone layer in the stratosphere (the upper layer of Earth's atmosphere) above Antarctica that begins every September. Chlorine and bromine derived from human-produced compounds are released from reactions on high-altitude polar clouds.
Why does the ozone loss occur most severely in October in Antarctica?
The severe depletion of the Antarctic ozone layer known as the “ozone hole” occurs because of the special meteorological and chemical conditions that exist there and nowhere else on the globe. The very low winter temperatures in the Antarctic stratosphere cause polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) to form.
Why does ozone hole form over Antarctica How will enhanced ultraviolet radiation affect us?
The formation of the ozone hole will result in an increased concentration of UV - B radiations on the Earth's surface. UV −B damages DNA and activates the process of skin ageing. It also causes skin darkening and skin cancer.
Why is there a hole in Antarctica?
A few years ago, a giant hole opened up in the Antarctic sea ice, capturing attention around the world. Not since the 1970s had such a chasm appeared in the mid-ocean ice of the Weddell Sea. Scientists showed in previous research that ocean processes and cyclones contributed to the hole, called a polynya.
Which country has the biggest hole in the ozone layer?
According to the World Meteorological Organization, the ozone layer hole over Antarctica is one of the largest and deepest in the past 15 years. The hole peaked at 24 million square kilometers (approximately 9.3 million square miles).
In what season in the Antarctic is the ozone hole largest?
spring seasonEach year between August and October – during the southern hemisphere's spring season – the ozone depletes over the Antarctic region, with the hole reaching a maximum size between mid-September and mid-October.
How long does the ozone hole typically last over Antarctica?
around 2050However, due to the long residence time of many of these gases in the atmosphere (for example CFC-12 resides in the atmosphere for approximately 100 years), the ozone layer will not fully recover until around 2050.
Has the ozone hole over Antarctica closed?
It closed on 23 December, the third latest date after 1999 and 2020. The extent and longevity of the 2021 ozone hole can be explained by very cold temperatures in the stratosphere and a very stable polar vortex. This video shows the evolution of the 2021 Antarctic ozone hole.
When was the ozone hole detected in Antarctica?
1985In 1985 Jonathan Shanklin was a junior researcher at BAS when he discovered a hole in the invisible shield that protects us from solar radiation. We catch up with him to learn about his work and how it has made a difference. It's 36 years since scientists first discovered the hole in the ozone layer.
Why is the ozone layer loss more in cold regions?
Low temperatures give rise to a special kind of clouds, so-called polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). On the surface of these cloud particles, chemical reactions take place that convert innocuous halogen compounds into active chlorine (ClO) that is very efficient at destroying ozone.
Why is ozone depletion worse in Antarctica quizlet?
Because of the warmer temperatures, there are no PSCs outside of the Polar Regions, and therefore ozone depletion occurs much more slowly outside of the Polar Regions, resulting in a 4-6% drop in stratospheric ozone since 1979.
How long does the ozone hole typically last over Antarctica?
around 2050However, due to the long residence time of many of these gases in the atmosphere (for example CFC-12 resides in the atmosphere for approximately 100 years), the ozone layer will not fully recover until around 2050.
Is ozone also depleted over the North Pole?
Summary: Researchers have established that the destruction of ozone over the Arctic in the spring causes abnormal weather throughout the northern hemisphere, with many places being warmer and drier than average -- or too wet.
What is so special about Antarctic conditions?from nas.nasa.gov
Temperatures hover around or below -80'C for much of the winter and the extremely low antarctic temperatures cause cloud formation in the relatively ''dry''stratosphere. These Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSC's) are composed of ice crystals that provide the surface for a multitude of reactions, many of which speed the degredation of ozone molecules.
What is the effect of spring on the stratosphere?from nas.nasa.gov
4. Spring brings an increase of ultraviolet light to the lower antarctic stratosphere, providing the energy needed needed for the rapid catalytic break-down of ozone by ClO and its dimer ClOOCl. Another mechanism involving Bromine adds another 33% to the depletion total. Over 50% of the stratospheric ozone is destroyed by these two mechanims, most of the damage occuring in the lower stratosphere.
What instrument is used to measure ozone?from nasa.gov
When the polar sun rises, NOAA scientists also make measurements with a Dobson Spectrophotometer, an optical instrument that records the total amount of ozone between the surface and the edge of space known as the total column ozone value. This year, scientists recorded the lowest total-column ozone value of 102 Dobson Units on Oct. 7, the 8th-lowest since 1986. At altitudes between 8 and 13 miles (14 to 21 kilometers) ozone was nearly completely absent during the ozone hole’s maximum.
Which layer of the atmosphere protects life on Earth?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
PNG. All. The stratospheric ozone layer protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet light, which damages DNA in plants and animals (including humans) and leads to sunburns and skin cancer.
When does the vortex break up?from nas.nasa.gov
Towards the end of spring (mid-December) the warming temperatures cause the vortex to break up; ozone-rich air from the surrounding area comes flooding in and masses of ozone-depleated air go wandering off, temporarly lowering the ozone in areas of South America and New Zealand by up to 10%.
When will the concentration of chlorine in the stratosphere return to pre-1980 levels?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
Models suggest that the concentration of chlorine and other ozone-depleting substances in the stratosphere will not return to pre-1980 levels until the middle decades of the 21st century.
What caused CFCs to break apart?from earthobservatory.nasa.gov
When they reached the stratosphere, however, their behavior changed. In the upper stratosphere (beyond the protection of the ozone layer), ultraviolet light caused CFCs to break apart, releasing chlorine, a very reactive atom that repeatedly catalyzes ozone destruction.