Which organ of the human body regulates the body temperature?
Body temperature is mainly controlled by an area known as the hypothalamus in the brain. Through opening and closing sweat glands and contracting muscles, the hypothalamus sets the body’s temperature and regulates it. By supplying a layer of insulation directly under the skin, adipose tissue controls body temperature.
How to maintain a normal body temperature?
What are some physical activities I can do?
- Jumping jacks. While “getting your blood flowing” does help increase core body temperature, intense or long-term cardio exercise (such as running) can actually lead to a short-term decrease in skin ...
- Walking. If you need to do work outside or just have to get some fresh air, the key is to keep moving. ...
- Putting your hands in your armpits. ...
- Clothing. ...
How does the temperature of body affect the human?
•A 1 degrees C decrease in temperature was associated with a 1.35%increase in the daily number of total natural deaths and a 1.72% , 3.30% and 1.25% increase in cardiovascular, respiratory, and cerebrovascular deaths, respectively.
How the temperature of the body is regulated?
The temperature of the body is regulated by neural feedback mechanisms which operate primarily through the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus contains not only the control mechanisms, but also the key temperature sensors.
.PNG)
What are three ways the body regulates temperature?
How does thermoregulation work?Vasoconstriction: The blood vessels under your skin become narrower. ... Thermogenesis: Your body's muscles, organs, and brain produce heat in various ways. ... Hormonal thermogenesis: Your thyroid gland releases hormones to increase your metabolism.
What are the 4 mechanisms for temperature regulation?
When the environment is not thermoneutral, the body uses four mechanisms of heat exchange to maintain homeostasis: conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation.
How does the body regulate temperature when cold?
How does thermoregulation work? Thermoregulation is controlled by the hypothalamus, which is a small structure in your brain. If the hypothalamus senses your body's temperature is too high or low, it sends signals to your nervous system, muscles, organs, and glands. These signals help cool you down or warm you up.
Which organ of body controls the body temperature?
The hypothalamusThe hypothalamus helps keep the body's internal functions in balance. It helps regulate: Appetite and weight. Body temperature.
What causes your body to not regulate temperature?
Some health disorders affect your body's ability to regulate body temperature. Examples include an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), poor nutrition or anorexia nervosa, diabetes, stroke, severe arthritis, Parkinson's disease, trauma, and spinal cord injuries.
Why do I go from hot to cold?
The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that regulates body temperature. A dysfunction of the hypothalamus can cause your body to temporarily become over heated (hot flash) or chilled (cold flash). Sometimes, chills and shivering may occur as a hot flash fades, causing you to feel hot and cold.
How does the human body keep warm on a cold day?
When you enter a cold environment, your body redistributes blood to the torso, protecting and maintaining the warmth of the vital organs there. At the same time, your body constricts blood flow to the skin. Narrowing the roads to the skin means less heat can make the journey, and so less is lost to the environment.
What are two mechanisms the body uses to heat itself?
Endotherms can alter metabolic heat production to maintain body temperature using both shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis.
What are the 4 mechanisms of heat loss?
Heat can be lost through the processes of conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation. Conduction is the process of losing heat through physical contact with another object or body.
What are the 3 mechanisms of heat?
Heat can be transferred in three ways: by conduction, by convection, and by radiation.
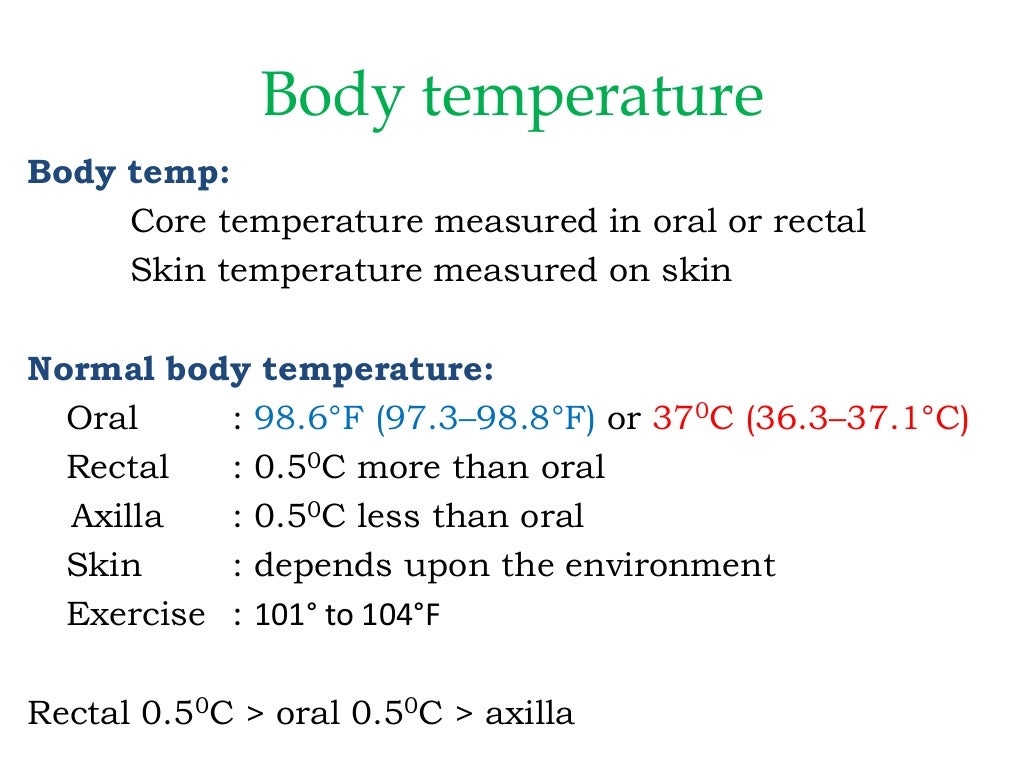
What is the body temperature?
The hypothalamus checks our current temperature and compares it with the normal temperature of about 37°C. If our temperature is too low, the hypothalamus makes sure that the body generates and maintains heat. If, on the other hand, our current body temperature is too high, heat is given off or sweat is produced to cool the skin.
What temperature is considered a fever?
Our body produces prostaglandins to fight off germs. A body temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or more is considered to be a fever. Temperatures above 39.5°C (103.1°F) are considered to be a high fever, and very high fever is defined as any temperature above 41°C (105.8°F).
Why do babies have a higher body temperature?
That is why they are more likely to react with a fever. Babies and young children have a higher body temperature than older children. This is because their body surface area is larger in relation to their body weight. Their metabolism is more active too. Newborns usually have an average body temperature of 37.5°C.
What is the temperature of a child?
A temperature between 37.5°C and 38°C is an elevated body temperature. The regulation of body temperature doesn't always work perfectly in younger children. Compared to older children and adults, they also sweat less when it is warm, and it takes longer for them to start sweating.
How does the body regulate temperature?
And it is lower at night, and higher in the afternoon than in the morning. Our internal body temperature is regulated by a part of our brain called the hypothalamus.
What is the best temperature for a healthy body?
A healthy body functions best at an internal temperature of about 37°C (98.6°F). A body temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or more is considered to be a fever. A healthy body functions best at an internal temperature of about 37°C (98.6°F). A body temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or more is considered to be a fever. NCBI.
Where is body temperature measured?
Strictly speaking, body temperature refers to the temperature in the hypothalamus and in the vital internal organs. Because we cannot measure the temperature inside these organs, temperature is taken on parts of the body that are more accessible. But these measurements are always slightly inaccurate.
Why is heatstroke so serious?
An ounce of prevention: Because heatstroke is so serious, Ward strongly advises focusing on prevention. This is especially true for people age 65 and older, who are at higher risk for heat illness simply because the regulating mechanism becomes less effective with time. Additionally, cardiovascular and neurological conditions increase ...
What happens when you sweat in heat?
In prolonged heat exposure, the body sweats so much that it depletes itself of fluids and salts, leaving nothing to sustain the evaporation process. When this process ceases, body temperature soars and heat illnesses may result — including the most serious: heatstroke.
How does the hypothalamus react to temperature?
On most days, the hypothalamus reacts to increases in outdoor temperature by sending messages to the blood vessels , telling them to dilate. This sends warm blood, fluids and salts to the skin, setting off the process of evaporation.
How does heat affect sweat glands?
When heat activates sweat glands, these glands bring that water, along with the body's salt, to the surface of the skin as sweat. Once on the surface, the water evaporates. Water evaporating from the skin cools the body, keeping its temperature in a healthy range.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
It not only helps to balance body fluids and maintain salt concentrations, it also controls the release of chemicals and hormones related to temperature. The hypothalamus works with other parts of the body's temperature-regulating system , such as the skin, sweat glands and blood vessels — the vents, condensers and heat ducts ...
What to do if your temperature rises?
If temperatures rise, drink lots of fluids and stay in a cool place.
What is hot flashes?
Hot flashes. The female body has a regular monthly cycle of hormonal ups and downs. During menopause and the years prior to it, this cycle becomes erratic and extreme, with large fluctuations in estrogen levels.
What happens if the body cannot maintain a temperature?
The healthy temperature range for the human body is very narrow. If the body cannot maintain a temperature within this range, thermoregulation disorders can develop.
What is the function of the afferent sensing system?
Afferent sensing involves a system of temperature receptors around the body to identify whether the core temperature is too hot or cold. The receptors relay the information to the hypothalamus, which is part of the brain.
What is the temperature range of mammals?
In humans, the healthy range is within a degree or two of 98.6°F (37°C).
What is heat cramps?
heat cramps, which present as heavy sweating and muscle cramps during exercise
How many mechanisms of thermoregulation are there in the human body?
The human body uses three mechanisms of thermoregulation:
Why are infants at higher risk for thermoregulation?
The reason for this is that these individuals have a lower muscle mass, a decreased shiver reflex, and lower immunity.
Why do we have to let a fever run its course?
Many doctors recommend letting a fever run its course so that the body can adequately protect itself.
Why do we sweat?
As your body temperature rises, your body will automatically perspire to release salty liquid from your sweat glands to help cool you down .
What are the vents and condensers of the body's heating and cooling system?
It works with other parts of the body’s temperature-regulating system. The skin – sweat glands and blood vessels are the vents, condensers and heat ducts of your body’s heating and cooling system.
What minerals do you lose when you sweat?
Electrolytes – You lose electrolytes when you sweat. Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect the amount of water in your body, the acidity of your blood (pH), your muscle function, and other important processes. Magnesium – Magnesium helps with body temperature regulation.
Why do people get heat exhaustion?
The reason for that can be linked in part to their medications and also to their body’s ability to regulate or cool down once they become overheated.
What is the best mineral for body temperature regulation?
Magnesium – Magnesium helps with body temperature regulation. Magnesium is an essential mineral for staying healthy and is required for more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body.
How to escape extreme heat?
Drink plenty of fluids, don’t wait until you feel thirsty. Don’t rely on fans for your primary means to escape extreme heat . Try to avoid using the stove or oven because they will make your house temperature rise. Limit your time outside when it is the hottest time of the day. Pace yourself.
Is sweating a temporary process?
The distinction arises when we begin to recognize that sweating, or simple perspiring, is not temporary or allowing us to cool down. When we sweat, we also lose water and electrolytes (i.e., “salts” such as sodium, chloride, potassium).
