The integumentary system work with other systems to protect and serve all the other systems the make you. Your skin has tiny glands that secrete sweat and oil. Those glands are termed exocrine glands and are not like the glands of your endocrine system.
What is the function of the endocrine system?
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Controls the reproductive functions.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH): Controls the reproductive functions in both genders.
- Melatonin: Controls the sleep -wake cycle.
- Oxytocin: It is the “love” hormone. ...
- Prolactin: It is required for milk production in mothers with newborns.
What are three functions of the integumentary system?
integumentary system function 3 this system helps keep the body from drying out, provides a natural sunscreen, and acts as storage for fatty tissues necessary for energy, with the aid of sunshine it provides vitamin d, also provides sensory input and unpleasant sensations involving pressure and temperature
How does the endocrine system functions with other systems?
The endocrine system acts as a communication tool for the human body, working in tandem with the nervous system to communicate with the body’s other internal systems. Hormones act as chemical messengers within the body, telling it to perform specific physical and mental functions.
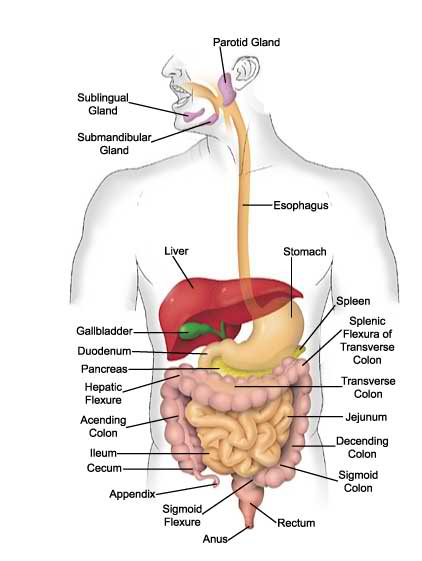
What are the major organs of the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is composed of the following parts:
- Skin
- Skin appendages Hairs Nails Sweat glands Sebaceous glands
- Subcutaneous tissue and deep fascia
- Mucocutaneous junctions
- Breasts
How is the integumentary system associated with the endocrine system?
The skin is an organ closely related to the endocrine system. The endocrine system has an important role in the skin development and its normal physiology. Skin, pilosebaceous unit, eccrine, and apocrine sweat glands have hormonal receptors and are targets of hormones.
How does the endocrine system affect the skin?
Androgens and Skin Health Androgens are a type of male hormone, but women have it too. Higher levels of androgen can cause overstimulation of the oil glands, leading to excess sebum. As skin cells are ready to shed, they become stickier, leading to a buildup in hair follicles that leads to pimples and inflammation.
How does the integumentary system work with other systems?
The skin and other parts of the integumentary system work with other organ systems to maintain homeostasis . The skin works with the immune system to defend the body from pathogens by serving as a physical barrier to microorganisms. Vitamin D is needed by the digestive system to absorb calcium from food.
What body system interacts with the endocrine system?
the nervous systemThe endocrine system works with the nervous system and the immune system to help the body cope with different events and stresses. This branch of medicine – relating to the study of the endocrine system – is called endocrinology and is practiced by endocrinologists.
Is skin complexion regulated by the endocrine system?
Apart from its protective function, the skin is also both hormonally and metabolically active. Many hormones are produced in the skin and the regulation of these changes is controlled, as are other organs, by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
Which hormone is responsible for skin?
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone describes a group of hormones produced by the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and skin cells. It is important for protecting the skin from UV rays, development of pigmentation and control of appetite.
What organs are involved in the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is an organ system consisting of the skin, hair, nails, and exocrine glands. FUN FACT: The skin is the largest organ of the human body! It accounts for about 15% of your body weight, and the average person has about 300 million skin cells.
What are the 4 main functions of the integumentary system?
Function of the Integumentary SystemHelps to protect the body's tissues and organs.Protects against infections and foreign invaders.Keeps the body from becoming dehydrated (by storing water)Helps to maintain a stable body temperature.Transports and gets rid of waste materials.More items...
What is the integumentary system responsible for?
The integumentary system includes the epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, associated glands, hair, and nails. In addition to its barrier function, this system performs many intricate functions such as body temperature regulation, cell fluid maintenance, synthesis of Vitamin D, and detection of stimuli.
Which system does the endocrine system work most closely with?
The endocrine and nervous systems work closely together. The brain sends instructions to the endocrine system. In return, it gets constant feedback from the glands. The two systems together are called the neuro endocrine system.
How does the endocrine system depend on other systems?
Interacting with Other Systems The circulatory system is the transport system for endocrine information. While the nervous system uses neurons, the endocrine chemicals and hormones must circulate through the body via blood vessels. Many glands in your body secrete hormones into the blood.
What is the endocrine system responsible for?
The endocrine system, made up of all the body's different hormones, regulates all biological processes in the body from conception through adulthood and into old age, including the development of the brain and nervous system, the growth and function of the reproductive system, as well as the metabolism and blood sugar ...
Can hormone imbalance affect your skin?
Many women suffer from dry, itchy skin during the menopause as a result of the hormonal imbalances. Since these skin problems are linked to hormonal imbalances and the decline in oestrogen during the menopause, it is possible to alleviate the symptoms with hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
How is the endocrine system important to the esthetician in their treatments?
The Esthetician can learn and appreciate the endocrine glands in simple and effectives ways, in order to educate their clients on the direct connection between hormone imbalances and skin intolerances. Thus, the skin is a direct reflection of what is going on internally within the body.
What hormone affects skin pigmentation?
Melanocytes in the basal epidermis control skin pigmentation through synthesis of melanin, a complex process thought to be primarily regulated by alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (αMSH) (Figure 1—figure supplement 1A and B).