The primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing. It also contains the vocal cords and functions as a voice box for producing sounds, i.e., phonation. What are the two functions of larynx?
What are the two functions of the larynx?
Function What does the larynx do? Your larynx has three main functions in your body: Breathing. Creating vocal sounds. Preventing food and other particles from getting into your trachea, lungs and the rest of your respiratory system.
What are the five primary functions of the respiratory system?
What are the five primary functions of the respiratory system?
- Gas Exchange – oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Breathing – movement of air.
- Sound Production.
- Olfactory Assistance – sense of smell.
- Protection – from dust and microbes entering body through mucus production, cilia, and coughing.
What does the larynx do to help the body function?
Your larynx is made of:
- The cartilage that gives it structure.
- Ligaments that connect the areas of cartilage and attach your larynx to nearby structures.
- Membranes, which also help hold cartilage together.
- Muscles, which move your larynx while swallowing, help with breathing and produce vocal sounds.
Is the larynx and pharynx the same thing?
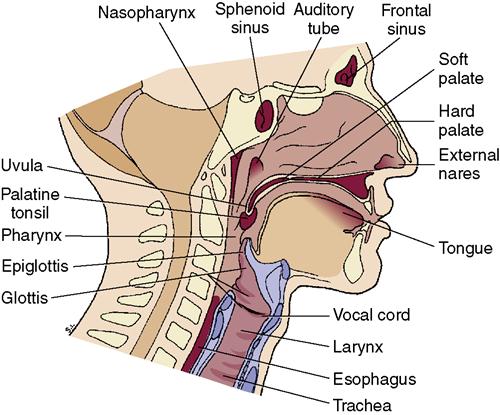
• Although the two terms sound alike, the location and functions are different. • Larynx is mainly an organ while pharynx is a set of regions. • Pharynx has three different regions, whereas larynx has different structures to produce sound. • The pharynx connects nasal airflow with trachea and food pathway from the oral cavity to the oesophagus.

How does the larynx protect the lower airways?
During the movement of the larynx, the vocal folds and aryepiglottic folds adduct preventing material from entering the lower airway. Additionally, the epiglottis folds over the glottal space to act as another layer of protection from material entering the lower airway.
How does the larynx help the respiratory system?
Your larynx is part of your respiratory system. It's a hollow tube that lets air pass from your throat (pharynx) to your trachea on the way to your lungs. It also contains your vocal cords and is essential to human speech, so it's often called the voice box.
What protects the lower respiratory tract during swallowing?
When we swallow, the epiglottis covers the larynx to prevent food and liquid from going into the lungs. The trachea (windpipe) is the part of the airway that continues below the larynx (LAIR-inks). The walls of the trachea (TRAY-kee-uh) have stiff rings of cartilage to keep it open.
Does the larynx protect the lungs?
The larynx functions as a mechanical barrier to protect the lungs from aspiration, vibrates vocal folds to produce sound, fine-tunes ventilation, assists in the cough reflex, and provides a closed valve to facilitate the production of a voluntary Valsalva maneuver.
What are the three main functions of the larynx?
What Is the Function of the Larynx?Speech production. Also called the voice box, the larynx is comprised of two pairs of vocal folds (mucous membrane structures) ... Air passage in the respiratory system. ... Channeling food into the digestive system.
Why is the larynx important?
The larynx plays an essential role in human speech. During sound production, the vocal cords close together and vibrate as air expelled from the lungs passes between them. The false vocal cords have no role in sound production, but help close off the larynx when food is swallowed.
What are the 3 protective mechanisms of the respiratory system?
Protective Mechanisms In the nasal cavity, hairs and mucus trap small particles, viruses, bacteria, dust, and dirt to prevent entry. If particulates make it beyond the nose or enter via the mouth, the bronchi and bronchioles contain several protective devices.
What is the primary function of the lower respiratory system?
The lower respiratory system, or lower respiratory tract, consists of the trachea, the bronchi and bronchioles, and the alveoli, which make up the lungs. These structures pull in air from the upper respiratory system, absorb the oxygen, and release carbon dioxide in exchange.
What happens to the larynx during swallowing?
When you swallow, a flap called the epiglottis moves to block the entrance of food particles into your larynx and lungs. The muscles of the larynx pull upward to assist with this movement. They also tightly close during swallowing. That prevents food from entering your lungs.
What are the two major functions of the larynx?
The primary function of the larynx in humans and other vertebrates is to protect the lower respiratory tract from aspirating food into the trachea while breathing. It also contains the vocal cords and functions as a voice box for producing sounds, i.e., phonation.
Can someone live without a larynx?
If you have had all of your larynx removed (total laryngectomy), you will not be able to speak normally, because you'll no longer have vocal cords. There are a number of different ways you can learn to communicate again, although they can take weeks or months to learn.
Is the larynx the gatekeeper to prevent aspiration?
Aspiration Pneumonia The larynx is the gatekeeper to the lower respiratory system. In this respect, its function is to prevent entry of foreign materials into the lower airway and to readily expel any foreign materials that may gain entry to the lower airway.
How does the larynx produce sound?
The larynx is involved in swallowing, breathing, and voice production. Sound is produced when the air which passes through the vocal cords causes them to vibrate and create sound waves in the pharynx, nose and mouth. The pitch of sound is determined by the amount of tension on the vocal folds.
What is the function of the larynx quizlet?
the larynx (specifically the epiglottis) helps to maintain a patent airway by protecting the respiratory system from the entrance of food and foreign substances. -The larynx is also responsible for the production of sound and speech (phonation).
How does the larynx function in voice production?
The vocal folds (vocal cords) are attached within the larynx to the largest of the laryngeal cartilages known as the thyroid cartilage or "Adam's apple". The vocal folds produce sound when they come together and then vibrate as air passes through them during exhalation of air from the lungs.
What is the function of larynx pharynx?
The throat (pharynx and larynx) is a ring-like muscular tube that acts as the passageway for air, food and liquid. It is located behind the nose and mouth and connects the mouth (oral cavity) and nose to the breathing passages (trachea [windpipe] and lungs) and the esophagus (eating tube).
Which muscle covers the larynx?
It is covered anteriorly by the infrahyoid muscles, and laterally by the lobes of the thyroid gland. The larynx is also closely related to the major blood vessels of neck, which ascend laterally to it.
Where is the larynx located?
The larynx (voice box) is an organ located in the anterior neck. It is a component of the respiratory tract, and has several important functions, including phonation, the cough reflex, and protection of the lower respiratory tract. The structure of the larynx is primarily cartilaginous, and is held together by a series of ligaments and membranes.
What is the inferior laryngeal artery?
Inferior laryngeal artery – a branch of the inferior thyroid artery (derived from the thyrocervical trunk). It follows the recurrent laryngeal nerve into the larynx.
How is the larynx formed?
The larynx is formed by a cartilaginous skeleton, which is held together by ligaments and membranes. The laryngeal muscles act to move the components of the larynx for phonation and breathing. More information about each of these structures can be found in their respective sections.
What is the opening between the vocal cords?
The opening between the vocal cords is known as rima glottidis, the size of which is altered by the muscles of phonation. Subglottis – From inferior border of the glottis to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage. The interior surface of the larynx is lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
What happens when the vocal folds are partially damaged?
In situations where the nerves are only partially damaged, the vocal folds become paralysed in a fully adducted position. If this occurs bilaterally, the rima glottidis (space between the vocal cords) is completely closed, and emergency surgical intervention is required to restore the airway.
Which muscle is responsible for the production of speech?
The vocal cords are responsible for the production of speech. Their movement is controlled by the intrinsic muscles of the larynx – the majority of which are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve (an exception is the cricothyroid muscle; innervated by the external laryngeal nerve).
Which structure provides structural support in the airway?
Structural support is instead provided by fibrous connective tissue along with more prominent smooth muscle layers.
Which epithelium covers the vocal cords?
Passing the lower border of the ventricle, the epithelium changes again to non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that covers the true vocal cords. At this point, the lamina propria is avascular, thin, and lacks glands and lymphatic tissue. The additional cell layers replace those lost during the closed phase of vibration.
What is the primary bronchi?
The primary bronchi enter the lungs and further divide into secondary (intrapulmonary) bronchi. These smaller bronchi are kept open by plates of hyaline cartilage, instead of the C-shaped rings observed in the trachea and primary bronchi. The lining of respiratory epithelium continues from the primary bronchi into the lumen of the secondary intrapulmonary bronchi .
Which ligament attaches to the vocalis muscle?
Dense elastic fibers of the vocalis ligament project into the lamina propria and attaches to the vocalis muscle (skeletal muscle). The epithelium again changes to pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with the cricoid cartilage (hyaline) forming the lower border between the larynx and the trachea.
What is the trachea bifurcate?
After about 10 – 15 cm, the trachea bifurcates at the carina to form a left and a right primary bronchus. The bronchi are also kept patent by C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage and their lumens are also lined with respiratory epithelium.
What is the trachea attached to?
Trachea. The trachea is attached to the cricoid cartilage of the larynx by the cricothyroid membrane and lies anterior and adjacent to the esophagus. It is a mucocartilagenous tube that is completed posteriorly by smooth trachealis muscle.
How is air introduced to the lungs?
Air is introduced to the lungs through an interconnected pathway with constantly changing epithelial linings. While the upper respiratory tract acts solely as a conducting portion, the lower respiratory tract serves as both conducting and respiratory portions of the airway.
Which part of the pharynx is responsible for preventing air from entering the digestive system?
A section of the pharynx called the nasopharynx hosts the epiglottis. This keeps the passage to the esophagus covered, preventing air from entering the digestive system.
What are the parts of the lower respiratory tract?
The lower respiratory tract includes: 1 the lungs 2 the trachea 3 the diaphragm
Why is it important to have a healthy respiratory system?
This means that having an efficient respiratory system is essential to quality of life. If the lungs do not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently, it can lead to health issues such as shortness of breath and fatigue. With so many working parts, keeping the respiratory system healthy is important.
What are the parts of the respiratory system?
Parts of the respiratory system. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. The upper tract comprises: the nose and nasal cavity. the sinuses. the pharynx. the larynx. The lower respiratory tract includes: the lungs.
What is the pharynx?
The pharynx, or throat, is a versatile muscular tube, shaped like a funnel, that delivers air from the mouth and nose to the trachea, or windpipe. It also connects the nasal and oral cavities with the larynx and esophagus. The pharynx is key to the respiratory and digestive systems. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, ...
What is the only part of the respiratory system that is externally visible?
The nose is also unique, as it is the only part of the system that is externally visible. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. It is the best entrance for outside air, as hairs and mucus line the inside wall and operate as air cleansers. Within this hollow space, the air is warmed, ...
What system protects against harmful particles?
While the respiratory system helps a person breathe, it also protects against the intake of harmful particles through coughing, sneezing, or swallowing. This article examines the various parts of the respiratory system , some respiratory conditions, and how a person breathes. It also looks at lung function and the processes ...
What are the structures that pull air out of the respiratory system?
Other structures, namely the thoracic cage (or rib cage) and the diaphragm, protect and support these functions. 1. The Trachea, or "Windpipe", Is the Main Airway to the Lungs. The trachea is a tube less than an inch in ...
What is the effect of relaxation of smooth muscle in the bronchioles?
When we exercise, relaxation of smooth muscle in the bronchioles causes them to dilate. This bronchodilation allows greater ventilation. Allergic reactions and histamines cause the opposite effect, bronchoconstriction. 3. The Lungs Are the Essential Organs of the Respiratory System.
Why does the diaphragm move?
The action of the diaphragm is key to the physical process of breathing. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves inferiorly, toward the abdominal cavity. This allows the volume of the thoracic cavity and the lungs to increase. It also explains why your abdomen puffs out when you take a deep breath.
How many alveoli are there in the human body?
Hundreds of millions of alveoli exist inside each lung. They are the terminal ends of the respiratory tract and the sites of external respiration—the exchange of gases between the air and the bloodstream. During inhalation, the alveoli fill with air from the bronchioles.
What is the cartilaginous ring?
The cartilaginous rings support the tube of the trachea and prevent it from over-expanding or from collapsing, like when you suck on a straw too hard. They are C-shaped, with a gap on the posterior side. This allows the trachea to bend when the esophagus presses against it as food is swallowed. 2.
Where does air go when inhaling?
During inhalation, air filtered and warmed by the upper respiratory system passes from the pharynx and larynx into the trachea, then down to the bronchi and into the lungs. Deoxygenated air from the lungs passes back up through ...
Where does carbon dioxide go in the body?
Oxygen from the air is then absorbed into the bloodstream: it passes through millions of microscopic sacs, the alveoli, into surrounding capillaries. Carbon dioxide waste diffuses the opposite way, from the capillaries to the alveoli.
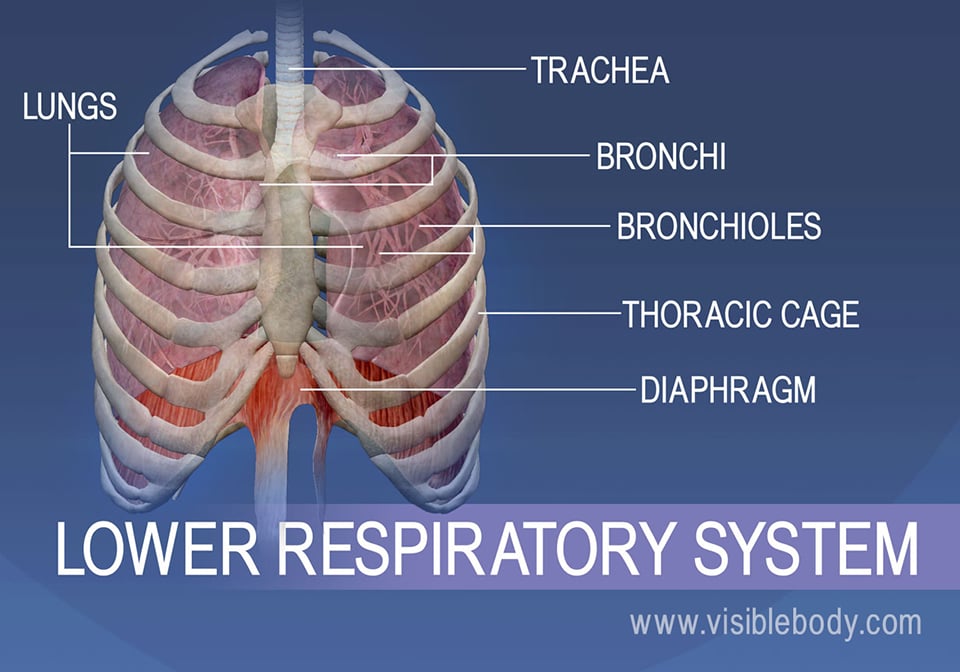
What Is The Lower Respiratory Tract
- The vocal cords are responsible for the production of speech. Their movement is controlled by the intrinsic muscles of the larynx the majority of which are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve (an exception is the cricothyroid muscle; innervated by the external laryngeal nerve).
Lower Respiratory Tract Structural and Functional Anatomy
Health Conditions Associated with The Lower Respiratory System