What diseases are caused by the nervous system?
Viral Diseases of the Nervous System
- Viral Meningitis. Although it is much more common than bacterial meningitis, viral meningitis is typically less severe.
- Zika Virus Infection. ...
- Rabies. ...
- Poliomyelitis. ...
- Cytomegalovirus Infections. ...
- Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies. ...
What is a virus that attacks the nervous system?
Viruses that infect the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) include herpesviruses (see also herpes simplex virus infections), arboviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and enteroviruses. Some of these infections affect primarily the meninges (the tissues covering the brain and spinal cord) and are called meningitis.
What is the basic function of the nervous system?
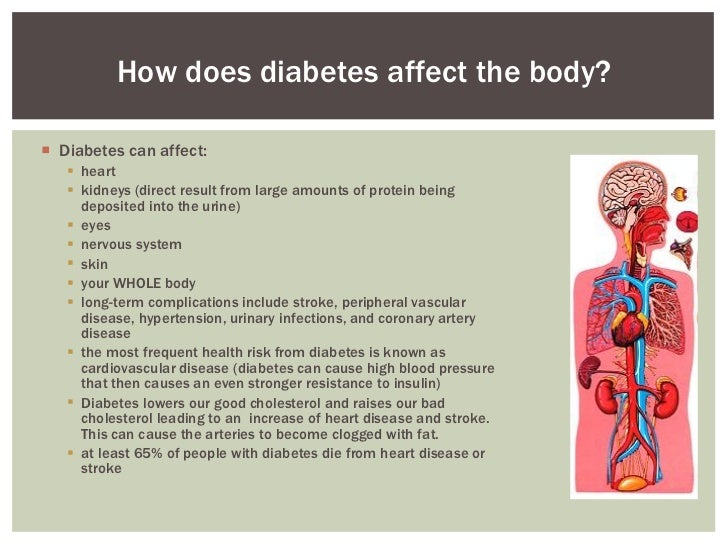
The nervous system is responsible for:
- intelligence, learning and memory: your thoughts and feelings
- movement: how your body moves
- basic body functions like the beating of your heart, breathing, digestion, sweating and shivering
- the senses: sight, hearing, taste, touch and smell
What are the 4 main parts of the nervous system?
autonomic nervous system. central nervous system (CNS) fight or flight response. homeostasis. parasympathetic nervous system. peripheral nervous system (PNS) somatic nervous system
Why is the nervous system the most important body system?
The human nervous system is responsible for coordinating every movement and action your body makes. More importantly, it controls every function inside the human body as well. For your heart to beat, your lungs to breath, and your feet to walk, your nervous system must be functioning properly.
What would happen if your nervous system isn't functioning properly?
You may experience the sudden onset of one or more symptoms, such as: Numbness, tingling, weakness, or inability to move a part or all of one side of the body (paralysis). Dimness, blurring, double vision, or loss of vision in one or both eyes. Loss of speech, trouble talking, or trouble understanding speech.
What are the 4 main functions of the nervous system?
The four main functions of the nervous system are:Control of body's internal environment to maintain 'homeostasis' An example of this is the regulation of body temperature. ... Programming of spinal cord reflexes. An example of this is the stretch reflex. ... Memory and learning. ... Voluntary control of movement.
What are 2 common problems that can occur within the nervous system?
Disorders of the nervous system Infections, such as meningitis, encephalitis, polio, and epidural abscess. Structural disorders, such as brain or spinal cord injury, Bell's palsy, cervical spondylosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, brain or spinal cord tumors, peripheral neuropathy, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
What is the most common damage to the nervous system?
Some of the most common causes of nerve damage include:Disease: Many infections, cancers, and autoimmune diseases like diabetes, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause nervous system problems. ... Stroke: A stroke happens when one of the brain's blood vessels becomes blocked or suddenly bursts.More items...•
What are 3 things the nervous system controls?
The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs. In this way, the nervous system's activity controls the ability to move, breathe, see, think, and more.
What does the nervous system control?
The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. It controls much of what you think and feel and what your body does. It allows you to do things like walk, speak, swallow, breathe and learn. It also controls how the body reacts in an emergency.
What is the most important nervous system?
Central nervous system It receives information from the sensory organs via nerves, transmits the information through the spinal cord, and processes it in the brain.
What are the 4 divisions of the nervous system?
15.4B: Subdivisions of the Nervous SystemCentral Nervous System.Gray Matter and White Matter.Peripheral Nervous System.Autonomic and Somatic Nervous Systems.Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Nervous Systems.
What are the 4 structures of the nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. These are found housed within the skull and vertebral column respectively. The brain is made of four parts; cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum and brainstem.
What are the 4 types of nerves in the nervous system?
It is conventional, however, to describe nerve types on the basis of their function: motor, sensory, autonomic or cranial.Motor Nerves. ... Sensory Nerves. ... Autonomic Nerves. ... Cranial Nerves.
What is the role of the peripheral nervous system?
The main role that the peripheral nervous system has to take on is to connect the central nervous system to the organs, limbs, and skin. These nerves extend from the central nervous system to the outermost areas of the body. Additionally, the peripheral nervous system allows the brain and spinal cord to receive and send information to other areas of the body, which allows one to react to stimuli in our environment.
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is composed of two major parts. The central nervous system is the first part that makes up the nervous system. This controls most functions of the body and mind, and consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain is the center of our thoughts, but most importantly it interprets information from our sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch. In addition, the spinal cord is the highway for communication between the body and the brain. If for some reason the spinal cord becomes injured, the exchange of information between the brain and other parts of the body is disrupted.
How does the nervous system affect your body?
Your nervous system affects every aspect of your health, including your: Thoughts, memory, learning, and feelings.
What is the function of the nervous system?
Your nervous system uses specialized cells called neurons to send signals, or messages, all over your body. These electrical signals travel between your brain, skin, organs, glands and muscles. The messages help you move your limbs and feel sensations, such as pain.
Why do nerves get trapped?
Nerves can be pinched or trapped for many reasons, such as overuse (as in carpal tunnel syndrome ), a tumor, or structural problems like sciatica. Toxic substances: Chemotherapy medicines, illegal drugs, excessive alcohol and poisonous substances can cause peripheral neuropathy or nerve damage.
How do nerves regulate your body?
It regulates your body’s systems and allows you to experience your environment. A vast network of nerves sends electrical signals to and from other cells, glands, and muscles all over your body. These nerves receive information from the world around you.
What part of the body sends electrical signals?
Each part contains billions of cells called neurons, or nerve cells. These special cells send and receive electrical signals through your body to tell it what to do. Central nervous system (CNS): Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS. Your brain uses your nerves to send messages to the rest of your body.
How to prevent nerve damage?
It needs care to keep working correctly. See your doctor regularly, eat a healthy diet, avoid drugs, and only drink alcohol in moderation . The best way to avoid nerve damage from disease is to manage conditions that can injure your nerves, such as diabetes.
What do motor neurons tell you?
Motor neurons tell your muscles to move. Sensory neurons take information from your senses and send signals to your brain. Other types of neurons control the things your body does automatically, like breathing, shivering, having a regular heartbeat and digesting food.
How does the nervous system help the body?
After a crisis or danger has passed, the system helps to calm the body by slowing heart and breathing rates, resuming digestion, contracting the pupils, and stopping sweating. Exploring the Peripheral Nervous System.
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The primary form of communication in the CNS is the neuron. Together, the brain and the spinal cord are the literal "center" of the body’s communication system. The brain and spinal cord are vital to human life and functioning. The body employs a number of protective barriers ...
What is the PNS?
The Peripheral Nervous System. The peripheral system (PNS) is composed of nerves that extend outside of the central nervous system. The nerves and nerve networks that make up the PNS are actually bundles of axons from neuron cells.
How many neurons are in the nervous system?
These organized networks, composed of up to 1 trillion neurons, make up what is known as the nervous system . The human nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which is composed of nerves and nerve networks throughout the body.
Which organ controls the release of hormones from other glands that are part of the endocrine system?
It's also involved in producing our emotional and stress responses. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary glands, which, in turn, controls the release of hormones from other glands that are part of the endocrine system. How the Endocrine System Regulates Hormones.
What is the CNS responsible for?
The CNS is responsible for processing every sensation and thought that you experience. The sensory information that is gathered by receptors throughout the body. It then passes the information on to the central nervous system. The CNS also sends messages to the rest of the body to control movement, actions, and responses to the environment.
What is the function of neurons in the brain?
on October 23, 2019. While neurons are the building blocks of the body’s communication system, it is the network of neurons that allow signals to move between the brain and body.
The Neurophysiology of Sleep
The hypothalamus is a peanut-sized structure located deep within the brain that contains nerve cells responsible for controlling things such as sleep and arousal.
The Role of Neurotransmitters In Sleep
There are clusters of sleep-promoting neurons responsible for regulating sleep that become more active as we get ready for bed. These nerve-signaling chemicals called neurotransmitters switch off or dampen the activity of cells that signal arousal or relaxation. GABA secretes to stifle muscle activity.
The Effect of Sleep on the Nervous System
You might be under the impression that your nervous system and your brain go to sleep while you sleep but that couldn’t be further from the truth. In fact, some parts of the brain and nervous system are actually more active during sleep than wakefulness.
Central Nervous System
Your central nervous system (CNS) is the information highway of your body and sleep is responsible for the necessary recalibration that facilitates the proper function of the CNS. For example, chronic insomnia can disrupt how your body sends and processes information.
Sleep and the Immune System
While you sleep your immune system produces protective infection-fighting substances like antibodies and cytokines. Your immune system uses these substances to combat foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. Some cytokines can also help produce sleep, giving your immune system more efficient to defend against body illness.
Conclusion- What Are the Effects of Sleep on the Nervous System?
Sleep has numerous effects on the body’s performance and failing to adhere to a healthy sleep schedule can drastically hinder your performance and cause damage to various systems in your body such as your immune and nervous system.
How Does Stress Affect the Body?
The first thing that you need to know is that stress response lives in the nervous system. When exposed to a stressful event, the autonomic nervous systems kick in. The ANS is part of the nervous system responsible for controlling body actions.
Mental and Emotional Signs
Stress affects our body and mental health. High level of stress can also affect the way a person feels and reacts to something. In fact, it's difficult to fulfill normal responsibilities and make difficult decisions.
What We Recommend?
Now that you know how stress affects the body, there are a few steps you can follow to reduce stress. Indulge in physical activity, get more sleep, try meditation and yoga. We also recommend keeping a stress diary and socializing with family and friends.
Which part of the peripheral nervous system controls conscious actions within the body?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the part of the peripheral nervous system which controls the conscious actions within the body.
What is the function of nerve cells?
Nerve cells, which are also known as neurons, work as transmitters of the nerve impulses or messages between the brain and the body. The human body is similar to an electrical circuit. A circuit that is made up of many connected wires, This connection means that a light bulb will glow whenever a switch is turned on.
Why is autonomic dysfunction a complication of Parkinson's disease?
Autonomic dysfunction is often a complication of Parkinson’s because of the loss of dopamine-producing cells in addition to the existence of Lewy bodies in the brain, the microscopic protein deposits. Research shows that this peripheral nervous system could be affected before the non-motor symptoms appear.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive disorder, which targets the nervous system that is responsible for body movement in the brain. This disorder causes many symptoms such as slowness, tremors, balance problems, as well as body stiffness.
What is the most important part of the body affected by Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's affects one of the most important functional parts of our body which is our nervous system . Every patient needs to understand this effect and learn how to deal with it. As we always say, within every Parkinson's stage lies a new hope.
How to keep your brain active?
Keep your brain active through playing mind games and writing by hand.
How can science and technology make life easier?
Fortunately, science and technology are putting all their effort to make the life of those patients easier. The key to making that happen is creating solutions and treatments that focus on reducing the symptoms. Thus, enabling a more active lifestyle that includes proper diet, exercise, and medication.
Which part of the brain is responsible for movement?
Specific areas of the brain which contain CB1 receptors include: The basal ganglia: this area of the brain is responsible for movement and also houses your “reward system”, which explains why marijuana may lead to a sensation of slowness, euphoria, and an increased response to pleasurable activities such as eating and sex.
What are the effects of marijuana on the brain?
March 19th, 2021 No Comments. Marijuana can have a variety of effects on your brain, such as euphoria, a sense of relaxation, and heightened sensory perception. If you’re reading this, chances are that you have experienced some of these effects before. Every individual will have a different set of reactions to marijuana culminating in ...
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
The cerebellum: the cerebellum is responsible for coordinating smooth body movements. Feeling unbalanced, uncoordinated, or otherwise off-kilter when you’re under the influence is in part through marijuana’s actions on the cerebellum.
Which part of the brain is responsible for regulating executive function?
The prefrontal cortex: also known as the PFC, this area is responsible for higher-order brain functions such as inhibition and executive processing, which explains why you may experience disinhibition and altered decision-making abilities while high.
Does marijuana affect the nervous system?
Marijuana’s effects on your nervous system are therefore wide-ranging and vary dramatically between users. After all, THC isn’t the only neurotransmitter at play. Adding to this, your subjective experience is inevitably influenced by host of other factors, including your physical environment and your pre-existing mood state.
Does marijuana have a negative effect on cognitive function?
However, some people may experience more negative cognitive effects with marijuana. This is especially true if you are dependent, or if the marijuana you consume is of unexpectedly high potency. Factors like inexperience will put you are higher risk for consuming too much and precipitating a bad trip. These potential negative cognitive effects include:
Does marijuana affect mood?
The mechanisms by which marijuana can alter mood and perceptions are fascinating. At a molecular level, THC’s chemical structure bears resemblance to a naturally produced compound in the brain known as anandamide, or AEA ( Scherma, Nature, 2018 ). This structural likeness allows THC to bind to the CB1 receptors in your brain that anandamide would normally bind to and in order to produce its rewarding, mind-altering effects. In fact, “ananda” is derived from the Sanskrit word for “internal bliss”!