What do you need to know about the nervous system?
What You Need to Know About the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- A Word About the Spinal Cord
- Sending Signals
- A Word From Verywell
What are the signals of the nervous system?
You may experience the sudden onset of one or more symptoms, such as:
- Numbness, tingling, weakness, or inability to move a part or all of one side of the body ( paralysis ).
- Dimness, blurring, double vision, or loss of vision in one or both eyes.
- Loss of speech, trouble talking, or trouble understanding speech.
- Sudden, severe headache.
How can you protect the nervous system?
You can do various therapies:
- Soak a towel in water and rub your body with it, following the following pattern: hands and shoulders, feet, torso.
- Alternating arm baths. Put your arms in hot water, one at a time. Then, put them in cold water.
- Ending a bath with a cold shower is very beneficial.
- Finally, magnesium sulfate baths are very relaxing and revitalizing.
How do you know if someone is nervous?
These include:
- Writing the Thoughts Out. Does it ever feel as if the same nervous thought is passing through your mind, over and over again? ...
- Go Jogging. Physical tension is a common sign of anxiety and this in itself can be enough to trigger nervous thoughts. ...
- Mental Distractions You can't force yourself to stop thinking a thought. ...

How do sensory neurons work?
Sensory neurons help you sense the world around you – they work with physical and chemical inputs from the external environment. Things like sound, touch, and light are physical inputs, and smell and taste are chemical inputs. These neurons send information from sensory receptors (in your skin, eyes, nose, etc.) toward the central nervous system.
Which type of neuron sends information between sensory neurons and motor neurons?
Interneurons are the most common type of neuron. They send information between sensory neurons and motor neurons, often forming complex circuits to help you react to external stimuli (like signaling to pull your hand away after touching a hot stove).
Where do dendrites receive information?
The dendrites are where a neuron receives information from other cells. They branch out from the cell body like antennae and receive and process signals from the axons of other neurons. Neurons can have multiple sets of dendrites, depending on the neuron’s function. [5]
What is the junction where two neurons meet?
The junction where two neurons meet is called a synapse and is where intercell communication takes place. Neurons communicate with one another through action potentials (changes in a neuron’s electric potential) and neurotransmitters. [6]
What are the three parts of a neuron?
A neuron has three main parts: a cell body (or soma), dendrites, and an axon.
How does the brain affect mental health?
Scientists believe that abnormalities in how certain brain circuits function can lead to the development of a number of mental health conditions. Connections between neurons along specific brain pathways can contribute to challenges with how the brain processes information, sometimes resulting in abnormal mood, thinking, or behavior. [13] Brain communication isn’t only impacted by brain chemistry – the brain also reacts to signals from the gut, or “second brain.” The brain and gut communicate through chemicals like hormones and neurotransmitters, and those chemical messages can be affected by gut bacteria (called the “gut microbiome”). To learn more about the gut-brain connection and other non-medication ways of managing mental health challenges, check MHA’s Science Hub.
What are the basic working units of the brain and nervous system?
Neurons (or nerve cells) are the basic working units of the brain and nervous system. They are information messengers, using electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit information between different regions of the brain and between the brain and the rest of the nervous system. [1] There are thousands of types of neurons, but scientists classify them into three broad types based on function: [2]
How does the nervous system take in information?
The nervous system takes in information through our senses, processes the information and triggers reactions, such as making your muscles move or causing you to feel pain. For example, if you touch a hot plate, you reflexively pull back your hand and your nerves simultaneously send pain signals to your brain.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is made up of all the nerve cells in your body. It is through the nervous system that we communicate with the outside world and, at the same time, many mechanisms inside our body are controlled. The nervous system takes in information through our senses, processes the information and triggers reactions, ...
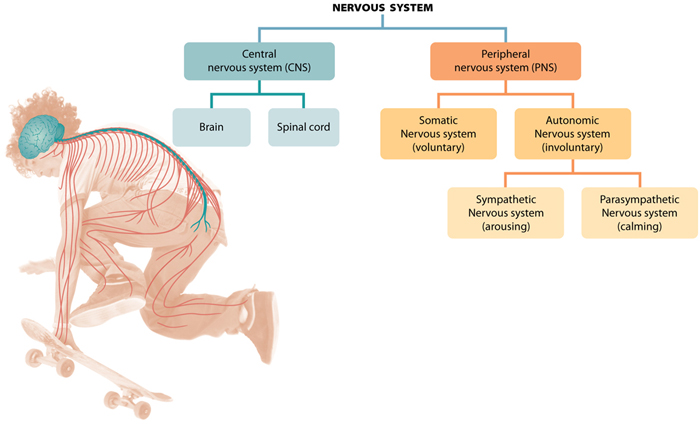
Why does the parasympathetic nervous system help us?
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for bodily functions when we are at rest: it stimulates digestion, activates various metabolic processes and helps us to relax.
Which nervous system prepares the body for physical and mental activity?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems usually do opposite things in the body. The sympathetic nervous system prepares your body for physical and mental activity.
Which nervous system regulates bowel motility?
The enteric nervous system is a separate nervous system for the bowel, which, to a great extent, autonomously regulates bowel motility in digestion.
Which system controls the movement of the body?
The voluntary nervous system (somatic nervous system) controls all the things that we are aware of and can consciously influence, such as moving our arms, legs and other parts of the body. The involuntary nervous system (vegetative or autonomic nervous system) regulates the processes in the body that we cannot consciously influence.
Where is the central nervous system located?
The central nervous system (CNS) includes the nerves in the brain and spinal cord. It is safely contained within the skull and vertebral canal of the spine. All of the other nerves in the body are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Regardless of where they are in the body, a distinction can also be made between voluntary ...
How does a neurotransmitter know which receptor to bind to?
How does a neurotransmitter “know” which receptor to bind to? The neurotransmitter and the receptor have what is referred to as a lock-and-key relationship—specific neurotransmitters fit specific receptors similar to how a key fits a lock. The neurotransmitter binds to any receptor that it fits.
What are the building blocks of the nervous system?
Neurons are the central building blocks of the nervous system, 100 billion strong at birth. Like all cells, neurons consist of several different parts, each serving a specialized function ( [link] ). A neuron ’s outer surface is made up of a semipermeable membrane. This membrane allows smaller molecules and molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules.
How does the axon work?
In some axons, glial cells form a fatty substance known as the myelin sheath, which coats the axon and acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels. The myelin sheath is crucial for the normal operation of the neurons within the nervous system: the loss of the insulation it provides can be detrimental to normal function. To understand how this works, let’s consider an example. Multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disorder, involves a large-scale loss of the myelin sheath on axons throughout the nervous system. The resulting interference in the electrical signal prevents the quick transmittal of information by neurons and can lead to a number of symptoms, such as dizziness, fatigue, loss of motor control, and sexual dysfunction. While some treatments may help to modify the course of the disease and manage certain symptoms, there is currently no known cure for multiple sclerosis.
What is the role of the neuronal membrane?
The neuron exists in a fluid environment—it is surrounded by extracellular fluid and contains intracellular fluid (i.e., cytoplasm). The neuronal membrane keeps these two fluids separate—a critical role because the electrical signal that passes through the neuron depends on the intra- and extracellular fluids being electrically different. This difference in charge across the membrane, called the membrane potential, provides energy for the signal.
Where do neurotransmitters go in the brain?
In healthy individuals, the neuronal signal moves rapidly down the axon to the terminal buttons, where synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse ( [link] ). The synapse is a very small space between two neurons and is an important site where communication between neurons occurs. Once neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, they travel across the small space and bind with corresponding receptors on the dendrite of an adjacent neuron. Receptors, proteins on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, vary in shape, with different shapes “matching” different neurotransmitters.
Where is the nucleus of a neuron located?
The nucleus of the neuron is located in the soma, or cell body. The soma has branching extensions known as dendrites. The neuron is a small information processor, and dendrites serve as input sites where signals are received from other neurons. These signals are transmitted electrically across the soma and down a major extension from the soma known as the axon, which ends at multiple terminal buttons. The terminal buttons contain synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers of the nervous system.
Does sodium move out of the cell?
In the resting state, sodium (Na +) is at higher concentrations outside the cell, so it will tend to move into the cell. Potassium (K + ), on the other hand, is more concentrated inside the cell, and will tend to move out of the cell ( [link] ). In addition, the inside of the cell is slightly negatively charged compared to the outside. This provides an additional force on sodium, causing it to move into the cell.
How does a neurotransmitter know which receptor to bind to?
How does a neurotransmitter “know” which receptor to bind to? The neurotransmitter and the receptor have what is referred to as a lock-and-key relationship—specific neurotransmitters fit specific receptors similar to how a key fits a lock. The neurotransmitter binds to any receptor that it fits.
What are the building blocks of the nervous system?
Neurons are the central building blocks of the nervous system, 100 billion strong at birth. Like all cells, neurons consist of several different parts, each serving a specialized function ( [link] ). A neuron’s outer surface is made up of a semipermeable membrane. This membrane allows smaller molecules and molecules without an electrical charge to pass through it, while stopping larger or highly charged molecules.
How does the axon work?
In some axons, glial cells form a fatty substance known as the myelin sheath, which coats the axon and acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels. The myelin sheath is crucial for the normal operation of the neurons within the nervous system: the loss of the insulation it provides can be detrimental to normal function. To understand how this works, let’s consider an example. Multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disorder, involves a large-scale loss of the myelin sheath on axons throughout the nervous system. The resulting interference in the electrical signal prevents the quick transmittal of information by neurons and can lead to a number of symptoms, such as dizziness, fatigue, loss of motor control, and sexual dysfunction. While some treatments may help to modify the course of the disease and manage certain symptoms, there is currently no known cure for multiple sclerosis.
What is the role of the neuronal membrane?
The neuron exists in a fluid environment—it is surrounded by extracellular fluid and contains intracellular fluid (i.e., cytoplasm). The neuronal membrane keeps these two fluids separate—a critical role because the electrical signal that passes through the neuron depends on the intra- and extracellular fluids being electrically different. This difference in charge across the membrane, called the membrane potential, provides energy for the signal.
Where do neurotransmitters go in the brain?
In healthy individuals, the neuronal signal moves rapidly down the axon to the terminal buttons, where synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse ( [link] ). The synapse is a very small space between two neurons and is an important site where communication between neurons occurs. Once neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, they travel across the small space and bind with corresponding receptors on the dendrite of an adjacent neuron. Receptors, proteins on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach, vary in shape, with different shapes “matching” different neurotransmitters.
Where is the nucleus of a neuron located?
The nucleus of the neuron is located in the soma, or cell body. The soma has branching extensions known as dendrites. The neuron is a small information processor, and dendrites serve as input sites where signals are received from other neurons. These signals are transmitted electrically across the soma and down a major extension from the soma known as the axon, which ends at multiple terminal buttons. The terminal buttons contain synaptic vesicles that house neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers of the nervous system.
Does sodium move out of the cell?
In the resting state, sodium (Na +) is at higher concentrations outside the cell, so it will tend to move into the cell. Potassium (K + ), on the other hand, is more concentrated inside the cell, and will tend to move out of the cell ( [link] ). In addition, the inside of the cell is slightly negatively charged compared to the outside. This provides an additional force on sodium, causing it to move into the cell.
Which unit of the nervous system is the most fundamental?
Neurons are the most fundamental unit of the nervous system, and yet, researchers are just beginning to understand how they perform the complex computations that underlie our behavior.
What is the role of myelin in the brain?
We take a closer look at the anatomy of the neuron and the role myelin plays in the rapid transmission of messages between brain cells. In the neuron, a protective covering called myelin (grey) insulates the axon and increases the speed of electrical communication along the length of the neuron. Image: Opus Design.
Why is myelin important?
Myelin seems to be critical to healthy functioning of the nervous system; in fact, disruptions in the myelin sheath have been linked to a variety of disorders.
What is the purpose of myelin?
“Myelin’s main purpose is to insulate the neuron’s axon,” Barak says. “It speeds up conductivity and the transmission of electrical impulses. Myelin promotes fast transmission of electrical signals mainly by affecting two factors: 1) increasing electrical resistance, or reducing leakage of the electrical signal and ions along the axon, “trapping” them inside the axon and 2) decreasing membrane capacitance by increasing the distance between conducting materials inside the axon (intracellular fluids) and outside of it (extracellular fluids).”
How does the nervous system help the body?
After a crisis or danger has passed, the system helps to calm the body by slowing heart and breathing rates, resuming digestion, contracting the pupils, and stopping sweating. Exploring the Peripheral Nervous System.
Which part of the body controls communication?
The endocrine system is not a part of the nervous system, but it is still essential to communication throughout the body. The hypothalamus connects these two important communication systems. The hypothalamus is a tiny collection of nuclei that is responsible for controlling an astonishing amount of human behavior .
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The primary form of communication in the CNS is the neuron. Together, the brain and the spinal cord are the literal "center" of the body’s communication system. The brain and spinal cord are vital to human life and functioning. The body employs a number of protective barriers ...
What is the PNS?
The Peripheral Nervous System. The peripheral system (PNS) is composed of nerves that extend outside of the central nervous system. The nerves and nerve networks that make up the PNS are actually bundles of axons from neuron cells.
How many neurons are in the nervous system?
These organized networks, composed of up to 1 trillion neurons, make up what is known as the nervous system . The human nervous system has two parts: the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which is composed of nerves and nerve networks throughout the body.
Which organ controls the release of hormones from other glands that are part of the endocrine system?
It's also involved in producing our emotional and stress responses. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary glands, which, in turn, controls the release of hormones from other glands that are part of the endocrine system. How the Endocrine System Regulates Hormones.
What is the CNS responsible for?
The CNS is responsible for processing every sensation and thought that you experience. The sensory information that is gathered by receptors throughout the body. It then passes the information on to the central nervous system. The CNS also sends messages to the rest of the body to control movement, actions, and responses to the environment.
