
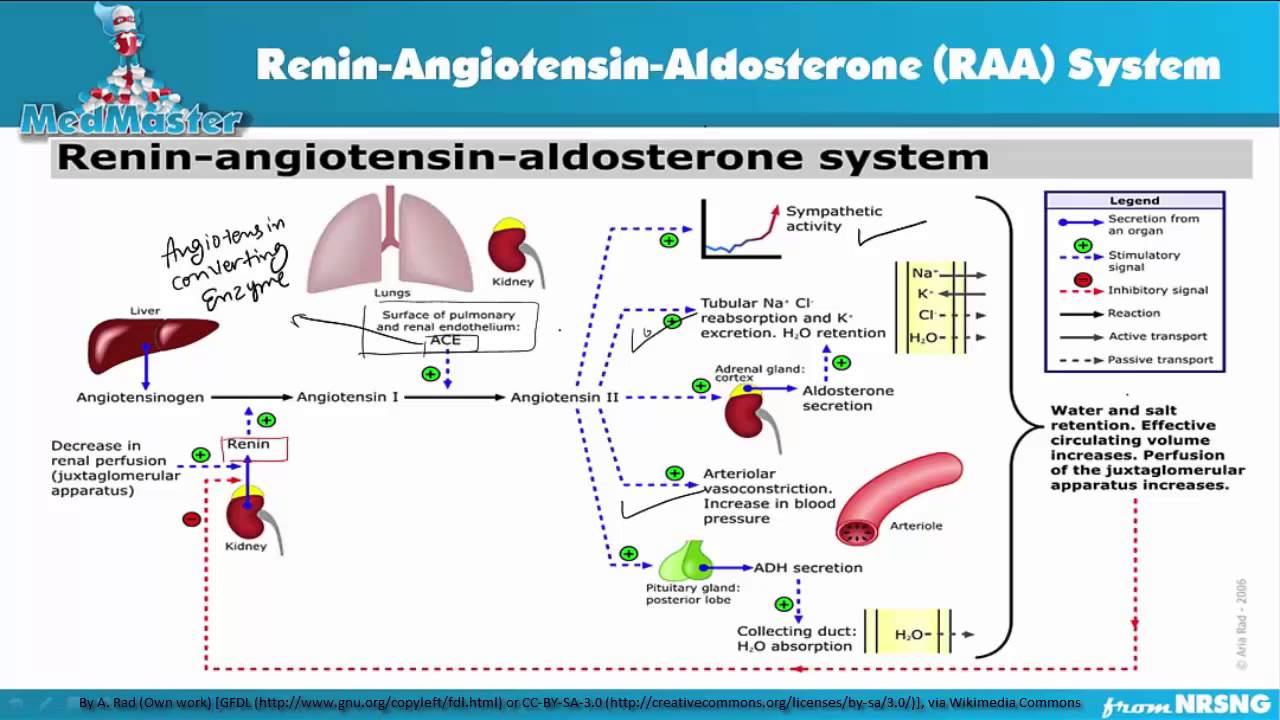
How the RAAS Works (step-by-step):
- Blood pressure drops too low ->
- Sympathetic Nervous System ( fight or flight system) is stimulated and sends nerve impulses to Juxtaglomerular Cells in the kidneys to release RENIN ->
- With RENIN present in the circulation it will activate a substance in the liver called ANGIOTENSINOGEN. ...
What is the RAA system and what causes it?
The RAA system involves a cascade of events that are triggered by different hormones. While the effects of some hormones are rapid, such as that of angiotensin II, others, such as aldosterone, take hours to days. The net effect of the RAA system is to elevate blood pressure in a prolonged manner. 5 Why is the RAA system important?
What is the role of Raas in blood pressure?
The RAAS is a complex multi-organ endocrine (hormone) system involved in the regulation of blood pressure by balancing fluid and electrolyte levels, as well as regulating vascular resistance & tone. RAAS regulates sodium and water absorption in the kidney thus directly having an impact on systemic blood pressure.
How does the renin-angiotensin (RAA) system work?
How the Renin-Angiotensin (RAA) System Works to Regulate Blood Pressure. It is called a system because each part influences the other parts and all are necessary for the whole to function correctly. The renin-angiotensin system, working together with the kidneys, is the body's most important long-term blood pressure regulation system.
What is the architecture of the RAAS system?
The architecture of the RAAS System is similar to a cascade with each component stimulating the generation of the next component in the pathway. Although synthesis of aldosterone is the final step in the RAAS cascade, the intermediate component Angiotensin II also has potent physiological effects as discussed in the next section.

What are the steps of the RAAS system?
II. Physiology: Overall ProcessImages.Step 1: Renin release. Stimulators of renin release. ... Step 2: Renin mediated step. Renin cleaves Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I.Step 3: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) mediated. Angiotensin I converted by ACE to Angiotensin II. ... Step 4: Angiotensin II Effects.
How does RAAS increase blood pressure?
Renal effects Angiotensin II also acts directly on the kidneys to further help increase blood pressure and blood flow by telling the kidneys to: Constrict its small blood vessels to help increase blood pressure. Increase sodium and water retention. Regulate the rate the kidney filters fluid.
What happens when the RAAS is activated?
In particular, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) leads to increased levels of angiotensin II and plasma aldosterone, and promote development of arterial vasoconstriction and remodeling, sodium retention, oxidative process, and cardiac fibrosis.
How does RAAS regulate fluid balance?
Angiotensin II also triggers the release of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) from the hypothalamus, leading to water retention in the kidneys. It acts directly on the nephrons, decreasing glomerular filtration rate. Thus, via the RAAS, the kidneys control blood pressure and volume directly.
What triggers the release of renin?
Renin is released into your bloodstream when your blood pressure drops too low or when there's not enough sodium in your body. Specifically, renin secretion happens when: Baroreceptors (pressure-sensitive receptors) in your arterial vessels detect low blood pressure. Your kidneys detect low salt (sodium) levels.
Why is RAAS activated in heart failure?
In heart failure with a low cardiac output state, activation of the RAAS serves as a compensatory mechanism to maintain cardiac output. Reduced renal blood flow and sodium delivery to the distal tubule leads to renin release, which is exacerbated further by increased sympathetic tone.
How do you remember RAAS?
Tricks to Remember the RAAS ComponentsRENin = RENal (Renin is released by the kidneys)AngiotensinoGIN = GIN/alcohol = Liver (Angiotensinogen is released by the liver)ACE = AIR = Lungs (ACE is found within the lungs)
How does RAAS mechanism regulate urine volume?
This helps to raise the circulating volume and in turn, blood pressure. It also increases the secretion of ADH from the posterior pituitary gland - resulting in the production of more concentrated urine to reduce the loss of fluid from urination.
What is the main function of renin?
renin, enzyme secreted by the kidney (and also, possibly, by the placenta) that is part of a physiological system that regulates blood pressure. In the blood, renin acts on a protein known as angiotensinogen, resulting in the release of angiotensin I.
What is the role of RAAS in pathophysiology of hypertension?
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is one of the most important hormonal mechanisms in controlling hemodynamic stability by regulating blood pressure, fluid volume, and sodium-potassium balance. For that reason, an alteration in any molecules that compose RAAS contributes to developing AH [8].
How does kidney function affect blood pressure?
Your kidneys play a key role in keeping your blood pressure in a healthy range. Diseased kidneys are less able to help regulate blood pressure. As a result, blood pressure increases. If you have CKD, high blood pressure makes it more likely that your kidney disease will get worse and you will have heart problems.
What is the action of angiotensin II that increases blood pressure quizlet?
Angiotensin II acts on blood vessels to stimulate vasoconstriction (increases blood pressure). It also acts on the adrenal gland to stimulate the release of aldosterone, which acts on the kidneys to stimulate reabsorption of salt and water, causing fluid volume and blood pressure to increase.
How the renin angiotensin angiotensinogen system regulates blood pressure and plasma volume content?
The renin-angiotensin system or RAS regulates blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. When blood volume or sodium levels in the body are low, or blood potassium is high, cells in the kidney release the enzyme, renin. Renin converts angiotensinogen, which is produced in the liver, to the hormone angiotensin I.
How does RAAS affect the renal system?
The renal effects of the RAAS are due to the combined actions of Angiotensin II and aldosterone which coordinate multiple physiological mechanisms to reduce salt and water excretion. Overall, the RAAS serves to significantly sharpen the responsiveness of the pressure natriuresis mechanisms to changes in arterial pressure, and thus allows much better physiological fine-tuning of urinary sodium and water excretion to changes in arterial pressure. Angiotensin II appears to act directly on the proximal tubule to enhance sodium resorption. Because water passively follows resorption of sodium in this segment, the presence of Angiotensin II yields enhanced resorption of both sodium and water in the proximal tubule. Additionally, as discussed in Neuroendocrine Regulation of GFR and RBF, the presence of Angiotensin II results in vasoconstriction principally of the renal efferent arterioles. This effect serves to maintain the glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure and thus prevent drops in the Glomerular Filtration Rate in contexts of falling arterial pressures.
What are the loci of regulation in the RAAS?
The main loci of regulation in the RAAS are the release of renin and synthesis of aldosterone. In contrast, conversion of Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II by ACE appears to occur constitutively and is not subject to regulation. Renin Release. From a phenomenological perspective, release of re nin appears to be inversely correlated with ...
How is aldosterone synthesis stimulated?
As described above, synthesis of aldosterone is stimulated by the RAAS via direct activation of the adrenal cortex by Angiotensin II. It is important to note that other physiological variables can potently impact the aldosterone release by the adrenal cortices, especially the concentration of ECF potassium as described in external potassium balance. Consequently, the rate of adrenocortical synthesis of aldosterone is a balance between the levels of stimulation by Angiotensin II and the ECF potassium concentration. Although this overlap might appear to result in problematic conflicts in physiological regulation of arterial pressure and potassium concentration, features of potassium excretion by the tubules prevent such issues.
Which component of the RAAS cascade is released by juxtaglomerular cells?
Although synthesis of aldosterone is the final step in the RAAS cascade, the intermediate component Angiotensin II also has potent physiological effects as discussed in the next section. Renin Release. Renin is a protein enzyme synthesized and released by juxtaglomerular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, particularly those which surround ...
What is the role of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteorne?
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteorne System (RAAS) is a multi-hormonal system that coordinates a variety of physiological processes for proper regulation of blood volume and pressure.
Does vasoconstriction increase filtration?
However, the vasoconstriction also increases the filtration fraction in the glomerulus, increasing the oncotic pressure of the blood in the peritubular capillaries and reducing the blood flow through them. Together, these modify peritubular capillary transport in such a way as to enhance peritubular resorption of water and solutes, such as sodium. Finally, Angiotensin II stimulates release of aldosterone] which serves to increase sodium resorption by the late distal tubule and collecting ducts. This action of aldosterone is likely mediated by direct activation of the basolateral NaK ATPase on Principal Cells which consequently enhances luminal secondary active transport of sodium.
Does angiotensin II stimulate sodium resorption?
Finally, Angiotensin II stimulates release of aldosterone] which serves to increase sodium resorption by the late distal tubule and collecting ducts.
How does the RAS pathway work?
As a long-term regulator of blood pressure, the classical RAS pathway has a constant baseline level of activity, and actually works much like the gas pedal of a car. 5 Constant pressure on the gas pedal is required to keep the car moving forward, even when you just want to go at the same speed.
What are the effects of RAA?
Other Effects of the RAA Pathway: Neural and Renal. Angiotensin II can bind to receptors located in different areas of the body, aside from the blood vessels. It regulates blood pressure by sending messages to the brain and the kidneys to help raise blood pressure.
Which pathway controls blood pressure and body fluid?
Angiotensin- (1-9) While the classical RAS pathway controls blood pressure and body fluid, it also has a complementary negative effect on the body that promotes inflammation. Some of the inflammatory responses of the classical RAS pathway include: 10. Blood vessel narrowing, or constriction.
What is the renin-angiotensin system?
Updated on July 08, 2021. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS), is a group of related hormones that act together to regulate blood pressure and control inflammation. It is called a system because each part influences the other parts and all are necessary for the whole to function correctly.
What is the renin system?
The renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) controls blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate using enzymes like renin and hormones like angiotensin I and II and aldosterone. Explore the pathways, functions, and terms of the RAAS. Updated: 08/24/2021
Which system controls blood pressure?
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) The smaller system that controls blood pressure is the tubuloglomerular feedback system. Your body has a huge system involved in the sensation and control of blood pressure, not only within the kidneys, but all over the body - especially in times of great need.
What enzyme is released by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidneys in response to low blood pressure?
Detection by one or both of these mechanisms leads juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys to release an enzyme called renin. Renin is an enzyme released by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidneys in response to low blood pressure, causing the transformation of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
What is the release of renin?
The Release of Renin. When systemic hypotension, or low blood pressure throughout the body, occurs, receptors in your blood vessels called baroreceptors sense this change. Cells of the kidney's juxtaglomerular apparatus get involved as well.
Which hormone constricts the afferent and efferent arterioles?
Angiotensin II constricts the afferent and efferent arterioles.
Which system regulates glomerular filtration rate?
The most important system involved in the regulation of systemic blood pressure, renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate is called the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, or (RAAS) for short.
Can RAAS kill you?
Finally, you must understand that if the RAAS system was to run wild without any inhibitory control, it would actually kill you . This is why there are several mechanisms in place that try to control the RAAS system so that it doesn't go into overdrive. We'll go over some of the most important aspects of this inhibitory feedback system.
Why are cybercriminals attracted to RaaS?
This vicious model is so enticing to some cybercriminals that you can even see the RaaS provider’s advertisements on the dark web. There are numerous reasons why cybercriminals are attracted to this franchise-like deployment. First and foremost, it enables the ransomware authors to earn some quick money. As for the affiliates, it decreases the need for them to write malicious code. They can simply rent out easy-to-use packages at low prices from the dark web.
What is a ransomware as a service?
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) borrows from the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. This subscription-based malicious model enables even the novice cybercriminal to launch ransomware attacks without much difficulty. You can find various RaaS packages in the market that reduce the need to code malware. As such, it is commonly used by cybercriminals who don’t have much technical knowledge of how to create ransomware. This malicious model allows anyone to become an “affiliate” of an established RaaS package or service.
What is ransomware?
Ransomware is a form of malware where cybercriminals attack your system with malicious code. Their intent is to lock you out of your system and encrypt your important and sensitive data. Further, they demand ransom from you before they provide a decryption key for your locked system and encrypted data.
How to protect yourself from ransomware?
How to protect yourself from this threat. 1. Use a reliable security suite. To protect your system from this malicious threat, you should install a reliable anti-malware software for your system. These smart tools work on advanced algorithms to detect and in some cases remove ransomware threats.
What are the effects of RAAS?
It also stimulates the sympathetic nervous system to increase the release of noradrenaline (NA). This hormone is typically associated with the “fight or flight” response in stressful situations and has a variety of actions that are relevant to the RAAS: 1 Increase in cardiac output. 2 Vasoconstriction of arterioles. 3 Release of renin.
What is the first stage of the RAAS?
The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the enzyme renin. Renin released from granular cells of the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in response to one of three factors:
What is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)?
The RAAS is a complex multi-organ endocrine (hormone) system involved in the regulation of blood pressure by balancing fluid and electrolyte levels , as well as regulating vascular resistance & tone. RAAS regulates sodium and water absorption in the kidney thus directly having an impact on systemic blood pressure.
What is the renin system?
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), or renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) is a regulator of blood pressure and cardiovascular function. Dysregulated RAAS is implicated in high blood pressure, cardiovascular and kidney conditions, and medications targeting RAAS can improve these conditions. Dysfunction of the RAAS is also thought ...
Why is renin secreted?
Normally, renin is secreted if blood pressure is too low thus activating angiotensin II to increase blood pressure and vascular resistance . Abnormal activation of RAAS leads to chronic hypertension, cardiac failure, and kidney conditions, and may be a predictor for risk of complication in COVID-19.
Is ACE2 expression compensatory?
Elevated ACE2 expression may be compensatory in patients with cardiovascular disease and heart failure. Indeed, influenza and coronaviruses (along with viral forms of pneumonia), tend to see reduced ACE2 expression and upregulation of angiotensin II.
Does sars bind to ace2?
When SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, the activity of ACE2 is downregulated, preventing its normal function and leading to respiratory symptoms of cough and edema, as well as upregulation of angiotensin II. SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptor on human cells. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock.com.
Is RAAS a higher risk for pathology?
Thus, there is a theory that those with overactive RAAS ( enhanced angiotensin II and ACE2 expression) may be at a higher risk of developing severe pathology as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Pathophysiology
Mechanism
- When blood pressure drops for any reason, special cells in the kidney detect the change and release renin into the bloodstream. Renin by itself does not really affect blood pressure. Instead, it floats around and converts inactive forms of angiotensin into angiotensin I. These inactive forms of angiotensin, which are produced by the liver, are not able to alter the blood pressure until renin …
Mechanism of action
- Angiotensin I is able to alter the blood pressure to some degree, but it isn't strong enough to cause large changes. Instead, most angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II, a much more powerful hormone that does cause large changes in blood pressure. This second conversion happens mainly in the lungs via the action of another molecule called angiotensin-converting en…
Function
- After a period of time, angiotensin I, angiotensin II, and aldosterone are broken down into other molecules. The renin-angiotensin system, as a whole, responds to both short-term and long-term variations in blood pressure. It is activated by sudden drops in blood pressure, such as those that occur after blood loss, but is also stimulated by smaller...
Research
- Scientific papers, conference presentations, and even entire textbooks have been written about the importance of the renin-angiotensin system in blood pressure regulation. This is an intense area of research that is being pursued by some of the most talented scientists in the world.
Purpose
- The renin-angiotensin system gets so much attention because it is known to be an important factor that could help us understand:
Example
- For example, African-American patients with high blood pressure often don't respond as well to ACE inhibitors as to other medicines. This is likely because African-Americans have a different level of activity in their renin-angiotensin system, which makes them less sensitive to drugs that work by blocking the system.
Treatment
- A number of effective high blood pressure treatments have been developed as a direct result of our understanding of the renin-angiotensin system. Along with ACE inhibitors, which stop the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, other drugs work by targeting different parts of the system. Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), for example, prevent angiotensin I and angiotens…
What Is Ransomware?
What Is Ransomware-as-a-Service (Raas)?
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) borrows from the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. This subscription-based malicious model enables even the novice cybercriminal to launch ransomware attacks without much difficulty. You can find various RaaS packages in the market that reduce the need to code malware. As such, it is commonly used by cybercriminals ...
How Does It Work?
- Under this malicious franchise-like deployment model, cybercriminals write ransomware code and sell/rent it under an affiliate program to other cybercriminals who have the intent to launch an attack. They provide technical know-how and step-by-step information on how to launch a ransomware attack using the service, a platform which may even display the status of the attac…
Conclusion
- While Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is a brain-child and one of the latest threats to prey on digital users, it becomes important to take some preventive measures to fight this menace. In addition to other basic security measures, you can also rely on advanced antimalware programs for better secure you against this threat. About the Author: Chandra Shekhar Choudhary, a Digit…