What is circadian rhythm and your internal clock?
Your biological clock tracks your internal time and your circadian rhythm uses this time information to optimize the timing of your body functions. Think about your biological clock as the watch your body has to track your internal time and the circadian rhythm as the schedule that your body then follows based on this time.
How to reset your circadian rhythm to improve your sleep?
- Wake up every day at the same time: Keeping a regular sleep schedule will help reset your circadian rhythm. ...
- Bright light therapy: Exposure to bright artificial lights can reorient circadian rhythms quite effectively. ...
- Melatonin supplements: In addition to the natural hormone produced in the pineal gland, melatonin is also available in supplement form. ...
What is the meaning of circadian rhythm?
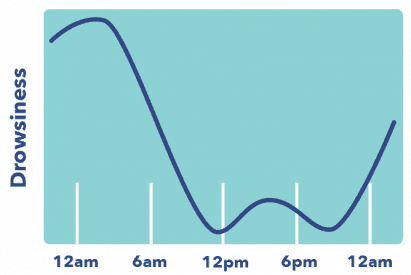
What is Circadian Rhythm? Circadian rhythm refers to the biological tendency to operate in 24-hour cycles of sleeping and waking. It’s also referred to as a biological or internal clock, even though they’re not quite the same thing (we’ll discuss that in a moment).
How does circadian rhythm affect body temperature?
The origin of the circadian rhythm of core temperature is mainly due to circadian changes in the rate of loss of heat through the extremities, mediated by vasodilatation of the cutaneous vasculature. Difficulties arise when the rhythm of core temperature is used as a marker of the body clock, since it is also affected by the sleep-wake cycle.
See more

How does the SCN influence our circadian rhythm?
However, most people notice the effect of circadian rhythms on their sleep patterns. The SCN controls the production of melatonin, a hormone that makes you sleepy. It receives information about incoming light from the optic nerves, which relay information from the eyes to the brain.
How does the SCN control the timing of sleep?
In the brain, a small group of hypothalamic nerve cells, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), functions as a master circadian pacemaker controlling the timing of the sleep-wake cycle and coordinating this with circadian rhythms in other brain areas and other tissues to enhance behavioral adaptation.
What is the function of the SCN?
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a bilateral structure located in the anterior part of the hypothalamus. It is the central pacemaker of the circadian timing system and regulates most circadian rhythms in the body.
How does the SCN work psychology?
The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which lies in the hypothalamus, is the main endogenous pacemaker (or master clock). It controls other biological rhythms, as it links to other areas of the brain responsible for sleep and arousal.
How do cells maintain a 24-hour clock?
The cogs of these clocks are genes and proteins, cycling in a 24-h rhythm within every cell. These cellular clocks are all coordinated by a central, grandfather clock in the brain. Sunlight is used to keep the internal rhythm in sync with the world around us.
What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in circadian rhythms quizlet?
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)-A pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm. In response to light, the SCN causes the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production, modifying feelings of sleepiness.
Is SCN active in day or night?
Diagram to illustrate that, during the day, the SCN cells show only a short-duration current in response to optic nerve stimulation (long thin arrow). During the night, however, an additional current blocked by AP5 can also be detected (short broad arrow).
How does SCN communicate?
Neurons in the SCN core communicate with the neurons in the SCN shell by several neurotransmitters such as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) and SP [39,40,41]. Cells in the SCN shell exhibit a self-sustained rhythmicity [42] driven by the autoregulatory TTL of clock genes.
Does SCN inhibit melatonin?
The SCN is necessary for both circadian regulation and light inhibition of melatonin synthesis and thus it has been difficult to isolate these two regulatory limbs to define the output pathways by which the SCN conveys circadian and light phase information to the pineal.
What is the circadian rhythm controlled by?
suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN)Circadian rhythms are regulated by small nuclei in the middle of the brain. They are called the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN). Nuclei act as control centers. The SCN are connected to other parts of the brain.
What stimulates the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
Many SCN neurons are sensitive to light stimulation via the retina, and sustainedly firing action potentials during a light pulse (~30 seconds) in rodents. The photic response is likely linked to effects of light on circadian rhythms.
What does the suprachiasmatic nucleus respond to?
SCN neurons display a sustained response to light followed by persistence of the response after light offset. These responses are sluggish and relatively unaffected by previous light exposures. Neurons also respond with a brisk, excitatory ON response and often an OFF response that is either excitatory or inhibitory.
Is SCN more active during the day or night?
During the day, the current mediated by the NMDA component of the EPSC in randomly selected cells in the SCN was found less frequently than it was during the night and when it was encountered, its magnitude was significantly smaller in amplitude (see Fig.
Is the SCN active during day or night?
Electrophysiology. Neurons in the SCN fire action potentials in a 24-hour rhythm. At mid-day, the firing rate reaches a maximum, and, during the night, it falls again.
How does SCN communicate?
Neurons in the SCN core communicate with the neurons in the SCN shell by several neurotransmitters such as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) and SP [39,40,41]. Cells in the SCN shell exhibit a self-sustained rhythmicity [42] driven by the autoregulatory TTL of clock genes.
What part of the brain controls sleep/wake cycle?
hypothalamusThe hypothalamus, a peanut-sized structure deep inside the brain, contains groups of nerve cells that act as control centers affecting sleep and arousal.