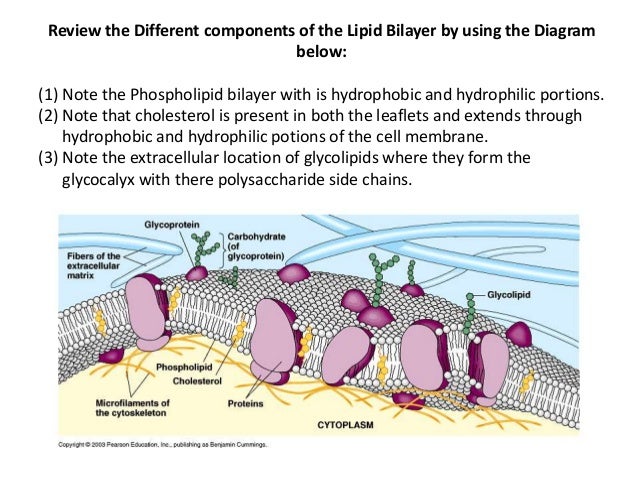
Why does the cell need to be selectively permeable?
To maintain homoestasis in your body, it is essential for the cells to have a “selectively permeable membrane”; as that would allow the entry/exit of ions according to the arising need. Because selective permeability increases and maintain the specificity of that particular cell. 25 insanely cool gadgets selling out quickly in 2021.
Why is the cell membrane considered to be semi permeable?
The membrane is described as semi-permeable since only certain kinds of molecules can pass through the cell membrane on their own. Other molecules require help to pass through the membrane.
Why does cell membrane called a semi permeable membrane?
The cell membrane is semi-permeable, ie, it allows some substances to pass through it and does not allow others. It is thin, flexible and a living membrane , which consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins/ The cell membrane has large content of proteins, typically around 50% of membrane volume.
Is cell membrane same as nuclear membrane?
The main difference between cell membrane and nuclear membrane is that cell membrane is the biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment whereas nuclear membrane is the biological membrane which surrounds the nucleus, encasing the genetic material.
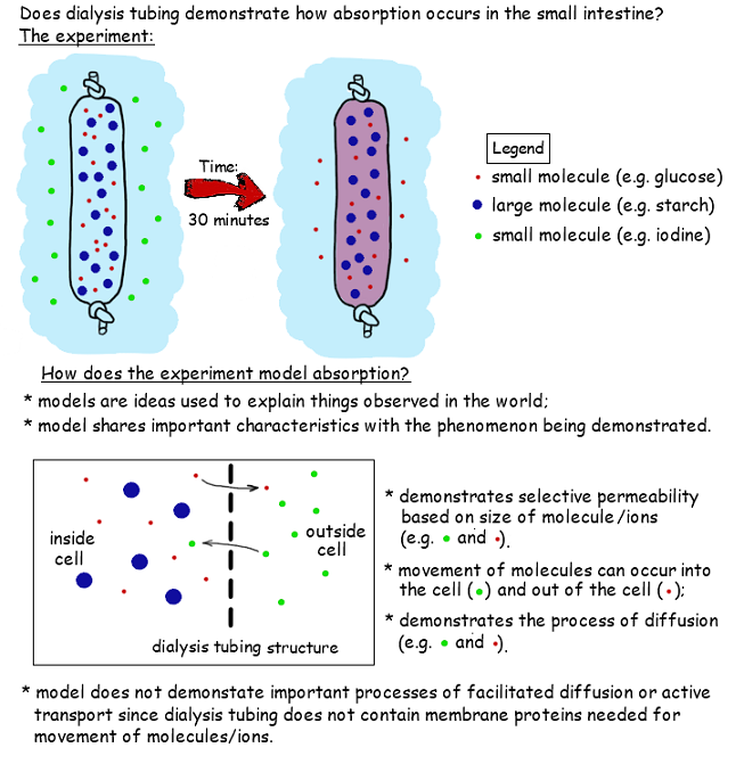
How does the cell membrane structure allow for selective permeability?
The plasma membrane is capable of being selectively permeable because of its structure. It is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids interspersed with proteins. The phospholipid part of the plasma membrane renders the latter hydrophobic and therefore polar molecules would not be able to easily pass through this layer.
Which structure of cells allows materials to be selectively permeable?
The cell membraneThe cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
How is the cell wall selectively permeable?
Solution : The cell membrane is a very thin layer of protein and fat. It allows only selective substances to pass through it, hence,it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
What is selective permeability How does the cell achieve this?
What is selective permeability? How does the cell achieve this? Cells only allow certain things in and certain things out. It achieves this by using the cell membrane.
Which part of the cell allows for selective permeability quizlet?
The cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable because it lets certain substances pass through while restricting the passage of others.
What causes selectively permeable?
The membrane's lipid bilayer structure provides the first level of control. The phospholipids are tightly packed together, and the membrane has a hydrophobic interior. This structure causes the membrane to be selectively permeable.
What is selectively permeable membrane in short answer?
Selectively permeable membrane is the one which allows entry of certain substances, exit of some substances but prevents the passage of other substances, through it.
Where in the cell is there a selectively permeable membrane?
Selectively permeable membranes can be found around a variety of cells and places. The most common example is the phospholipid bilayer cell membrane that surrounds every cell in our bodies. Another example of a selectively permeable membrane is the inner membranes of an egg.
What cells have a selectively permeable membrane?
All cells are surrounded by a selectively-permeable membrane. This membrane not only surrounds the cellular organelles but also acts as a barrier between the internal and the external environment. A cell membrane that is selectively permeable acts as a boundary or fence of the cell.
Which tissue is selectively permeable?
prurenum and connective tissue, a thin non living non-cellular basement membranebasement membraneThe basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Basement_membraneBasement membrane - Wikipedia is present which is selectively permeable. Basement membrane is secreted by both epithelium and connective tissue and made up of glycoproteins, mucopolysaccharides and protein fibres.
What organelle controls selective permeability?
The Cellular Membrane The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Which cell structure is fully permeable?
The plasma membraneThe plasma membrane is a fully permeable membrane.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is a selectively permeable membrane?
in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Selectively permeable means a membrane allows the passage of some molecules or ions and inhibits the passage of others.
Which cell membrane is semipermeable?
The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane is an excellent example of a membrane which is both semipermeable and selectively permeable.
What is the process of a lipid bilayer vesicle forming around a large particle?
A lipid bilayer vesicle forms around the large particle and fuses with the plasma membrane to either allow the molecule into or out of a cell. In exocytosis, the contents of the vesicle open to the outside of the cell membrane. In endocytosis, a large particle is taken into the cell.
What is selective permeability?
Selectively permeable means a membrane allows the passage of some molecules or ions and inhibits the passage of others. The capacity to filter molecular transport in this manner is called selective permeability.
What molecules can bind to surface proteins?
Transmembrane proteins form channels that permit the passage of sodium, calcium, potassium, and chloride ions. Polar molecules can bind to surface proteins, causing a change in the configuration of the surface and gaining them passage.
What is the function of the hydrophobic fatty acid tails?
The phospholipid arrangement makes the bilayer semipermeable. It allows the passage of small, uncharged solutes. Small lipid-soluble molecules can pass through the hydrophilic core of the layer, such hormones, and fat-soluble vitamins.
Do large molecules cross the lipid bilayer?
Large molecules generally don't cross the lipid bilayer. There are special exceptions. In some cases, integral membrane proteins allow passage. In other cases, active transport is required. Here, energy is supplied in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for vesicular transport. A lipid bilayer vesicle forms around the large particle and fuses with the plasma membrane to either allow the molecule into or out of a cell. In exocytosis, the contents of the vesicle open to the outside of the cell membrane. In endocytosis, a large particle is taken into the cell.
What is selective permeability?
Selective permeability is a property of cellular membranes that only allows certain molecules to enter or exit the cell. This is important for the cell to maintain its internal order irrespective of the changes to the environment. For example, water, ions, glucose and carbon dioxide may need to be imported or exported from ...
Why is permeability important in eukaryotic cells?
Selectively permeability of membranes is particularly important for transport across the nuclear membrane in eukaryotic cells. Proteins, nucleic acids, and nucleotides involved in transcription must be selectively and efficiently transported into the nucleus and the products of transcription must be exported in a timely manner.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Currently the cell membrane is said to be made of a selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer whose hydrophillic domains face the aqueous environments inside and outside the cell, and hydrophobic domains face each other to form a bilayer. This lipid bilayer is punctuated by cholesterol molecules, glycolipids, and proteins ...
How are ions transported?
For instance, ions are transported across selectively permeable membranes through channels and pumps. While channels are for passive transport, ion pumps mediate primary active transport against a concentration gradient, with the hydrolysis of a high-energy phosphate bond.
What are some examples of molecules that need to be imported or exported from the cell?
For example, water, ions, glucose and carbon dioxide may need to be imported or exported from the cell depending on its metabolic activity. Similarly, signaling molecules may need to enter the cell and proteins may need to be released into the extracellular matrix. The presence of a selectively permeable membrane allows ...
How does transmembrane transport work?
For example, in most cells, there is a large excess of sodium ions in the extracellular environment along with an excess of potassium ions inside the cell. This is achieved by a transmembrane enzyme called the Na+/K+ ATPase, that catalyzes the movement of three Na+ ions outside the cell along with the import of two K+ ions. For each such transport cycle, the enzyme uses the energy released from the conversion of one molecule of ATP into ADP. This is called primary active transport, where the movement is directly coupled to the hydrolysis of a high-energy phosphate bond. A similar process is used to pump protons against their concentration gradient and this is a crucial part of both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Why is selective permeability important?
Selective permeability is crucial for creating a distinctly different environment inside the cell as compared to the extracellular matrix. It is equally relevant in maintaining the integrity of various organelles inside the cell. Each organelle is a small compartment with a specialized function, requiring optimal concentrations of proteins, ...
What are transmembrane proteins?
Transmembrane proteins are embedded within the membrane from the extracellular fluid to the cytoplasm, and are sometimes attached to glycoproteins (proteins attached to carbohydrates) which function as cell surface markers . Carrier proteins and channel proteins are the two major classes of membrane transport proteins.
What is the tail of lipids?
Lipids are composed of fatty acids which form the hydrobic tail and glycerol which forms the hydrophilic head; glycerol is a 3-Carbon alcohol which is water soluble, while the fatty acid tail is a long chain hydrocarbon (hydrogens attached to a carbon backone) with up to 36 carbons.
Which part of the plasma membrane is hydrophilic?
Part B - The plasma membrane. Phospholipids form the main fabric of the plasma membrane. . . . This self-assembly occurs because phospholipids are hydrophilic at one end (the phospholipid head) and hydrophobic at the other end (the phospholipid tails).
What is the framework of a membrane?
2)The framework of a membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids with their hydrophilic heads facing the aqueous environment inside and outside of the cell and their hydrophobic tails clustered in the center. 3)Because membranes are fluid, membrane proteins and phospholipids can drift about in the membrane.
How many different solutions are there for red blood cells?
A red blood cell has been placed into three different solutions. One solution is isotonic to the cell, one solution is hypotonic to the cell, and one solution is hypertonic to the cell. Determine which type of solution is in each beaker based on the cell's reaction. Drag each item to the appropriate bin.
How many layers of phospholipids are there?
Two layers of phospholipids with proteins either crossing the layers or on the surface of the layers.
How does glucose get into a cell?
In many animal cells, the uptake of glucose into the cell occurs by a cotransport mechanism, in which glucose is cotransported with Na+ ions.
What is the main ion pump in animal cells?
In animal cells, the main ion pump is the sodium-potassium pump.
Which arm of the tube has less free water?
2) There is less free water in the right arm of the tube than in the left arm of the tube.
