Sympathetic Activation. One of the effects of the sympathetic nerves innervating the heart is that they increase its rate of beating. Another effect is that the sympathetic nervous system makes the heart beat harder, forcing out a larger volume of blood with each beat, and forcing blood out with greater strength.
How to calm an overactive sympathetic nervous system?
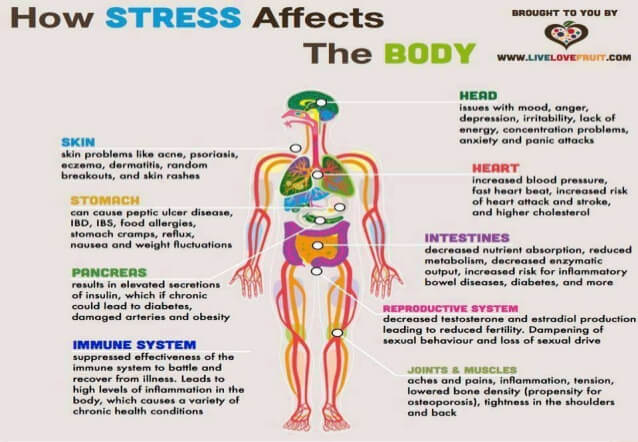
- High blood pressure
- Immune system issues
- Heart disease
- Heart failure
- Mental health problems
What is the function of the sympathetic system?
Sympathetic nerves are responsible for:
- increasing heart rate
- increasing the force of contraction of the myocardium
- the ‘fight or flight’ response, causing our heart to beat faster.
What is the neurotransmitter of the sympathetic system?
These include:
- Alpha-1
- Alpha-2
- Beta-1
- Beta-2
What are the symptoms of an overactive nervous system?
When we are in a consistent state of “fight-or-flight,” this can lead to:
- Tired but wired feeling, not sleeping throughout the night, often wide-awake between 1-4am and exhausted upon waking.
- Digestive issues such as constipation and bloating, despite a healthy balanced diet. ...
- Premature grey hair is very common in those who experienced high stress due to the death of a loved one or trauma at a young age. ...

What are the cardiovascular effects of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) has a wide variety of cardiovascular effects, including heart-rate acceleration, increased cardiac contractility, reduced venous capacitance, and peripheral vasoconstriction.
How does sympathetic nervous system affect the heart failure?
In heart failure, it has been recognized that the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is activated and the imbalance of the activity of the SNS and vagal activity interaction occurs. The abnormal activation of the SNS leads to further worsening of heart failure.
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system have on heart rate and blood pressure?
These sympathetic influences work in conjunction with parasympathetic influences on the SA node to decrease heart rate. During a short-term decrease in blood pressure, the opposite occurs, and the autonomic nervous system acts to increase vasoconstriction, increase stroke volume, and increase heart rate.
What effect does the sympathetic nervous system have on the heart quizlet?
Only sympathetic nerves are located in the skin, parasympathetic nerves will not be found in the skin. Two effects of the PNS are decreased heart rate and pupil constriction, while two effects of the SNS are increased heart rate and pupil dilation.
How does the sympathetic nervous system play a role in blood pressure?
The SNS is activated when baroreceptors, specialised stretch receptors located within thin areas of blood vessels and heart chambers, sense changes in pressure [20]. When arterial pressure drops, the SNS is immediately activated resulting in increased cardiac output and vasoconstriction of peripheral vessels (Fig.
Does the sympathetic nervous system increase or decrease blood pressure?
The increase in sympathetic activity is a mechanism for both initiating and sustaining the blood pressure elevation. Sympathetic nervous activation also confers specific cardiovascular risk.
What happens to blood pressure during sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of arterial pressure, and increased sympathetic nervous system activity has been implicated as a primary precursor of hypertension in both humans and animal models of the disease.
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the heart rate?
These sympathetic influences work in conjunction with parasympathetic influences on the SA node to decrease heart rate . During a short-term decrease in blood pressure, the opposite occurs, and the autonomic nervous system acts to increase vasoconstriction, increase stroke volume, and increase heart rate.
Why is the sympathetic nervous system important?
The sympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining cardiovascular health because of its key effects on both short- and long-term regulation of blood pressure and blood flow to organs.
What happens when sympathetic baroreflex is less sensitive?
When the sympathetic baroreflex is less sensitive, the response of the sympathetic nerves to a given change in arterial pressure will be less pronounced and may be less able to return the pressure to baseline levels. Long-termRegulation ofBloodPressure.
How do baroreceptors respond to stretching?
The baroreceptors respond to stretching of the vessel wall. In general, increases in this stretching as the result of a short-term increase in blood pressure lead to an increase in afferent input into central autonomic nuclei (notably the nucleus tractus solitarius).
Which system controls arterial blood pressure?
The sympathetic nervous system plays a key role in regulating arterial blood pressure in humans. This review provides an overview of sympathetic neural control of the circulation and discusses the changes that occur in various disease states, including hypertension, heart failure, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Does baroreflex increase heart rate?
The shading highlights a small decrease in blood pressure over the course of a few heartbeats, which elicits an increase in sympathetic vasoconstrictor nerve activity (and increased heart rate) via the baroreflex. These baroreflex responses result in a small increase in pressure, which then inhibits nerve activity, also via the baroreflex.
What is the role of the sympathetic nervous system in hypertension?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) plays an important role in the regulation of cardiac performance and peripheral circulation. Changes in SNS activity measured as catecholamines in plasma or organ spillover have been implicated in the pathogenesis ...
Do angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors decrease sympathetic nerve activity?
In contrast, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors seem to directly decrease sympathetic nerve activity.
Is the SNS a regulator of the cardiovascular system?
Thus, the SNS as a regulator of the cardiovascular system also plays an important role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, myocardial infarction and heart failure.
Is blood pressure higher in hypertensive or normotensive parents?
However, during mental arithmetic the increase in muscle sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure was significantly more pronounced in offspring of hypertensive than in offspring of normotensive parents, but resting blood pressure was in the normotensive range and comparable in both groups.
Heart Disease Can Have Long
Patients who receive a diagnosis of coronary heart disease are at higherrisk for cognitive decline later on, a new study shows.
Physical Activity And Diet
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in management of cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Physical activity and a well-balanced diet favor cardiovascular conditioning and improves performance and capacity.
Smoking And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
As well as causing cancer, smoking affects the arteries that supply blood to your heart and other parts of your body. It reduces the amount of oxygen in your blood and damages your artery walls.
Heart Disease And Stroke Risk Factors
There is no single cause for CVD, but there are risk factors that increase your chance of a heart attack or stroke. There are modifiable factors and non-modifiable factors .
How Can Vasculitis Affect The Nervous System
Vasculitis can cause problems in the central and peripheral nervous systems, where it affects the blood vessels that nourish the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. A vasculitis syndrome may begin suddenly or develop over time.
Being Overweight And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Being overweight or obese increases your risk of a number of health problems, including:
Family History And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
A personâs family history of disease can increase their tendency to develop:
