How does sympathetic activity increase stroke volume?
* Increased sympathetic activity increases heart contractility. This causes cardiac fibers to contract more forcefully at all levels of preload. Regardless of end diastolic volume, this mechanism increases stroke volume by reducing end systolic volume. ...
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect cardiac output?
This happens thanks to the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, we see that the sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate, which increases cardiac output. We also see that the parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart rate, which decreases cardiac output.
How does end diastolic volume affect stroke volume?
An increase in stroke volume or cardiac output occurs when end-diastolic volume is increased (the Frank-Starling relation). What is the effect of increased sympathetic activity on heart rate and stroke volume?
How does contractility increase stroke volume?
* by increasing available calcium), thus increasing stroke volume. Contractility causes an increase in stroke volume by decreasing end systolic volume; it does not change end diastolic volume. By what mechanism would an increase in venous return increase stroke volume? increased end diastolic volume.
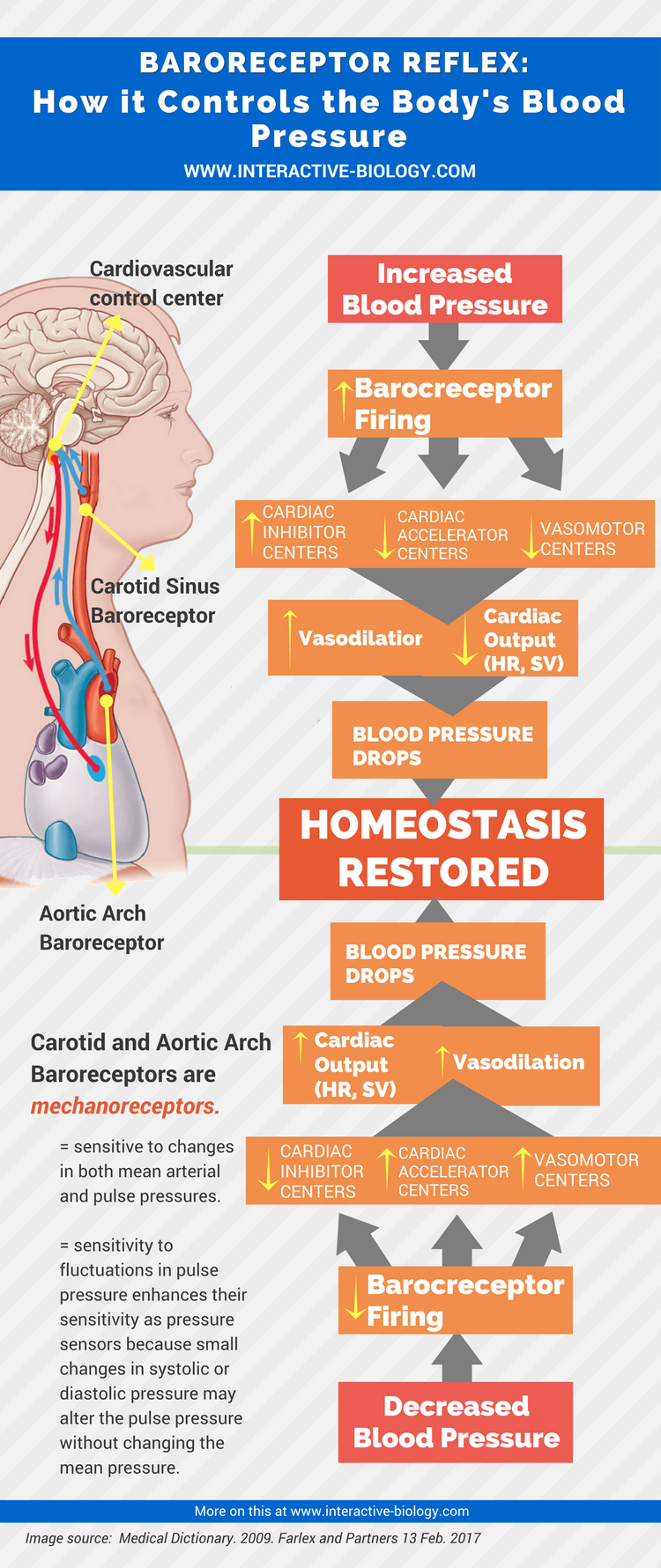
How does the arterial baroreflex work?
Why does sympathoexcitation occur in idiopathic hypertension?
What is ECG in medical terms?
How does respiration affect blood pressure?
Where is SNA measured?
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the heart rate?
What is sympathetic innervation?
See 4 more
About this website

How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the stroke volume and the cardiac output?
Sympathetic nervous system activation will stimulate the SA and AV nodes to increase the heart rate, which will increase cardiac output. Parasympathetic nervous system activation will conversely act on the SA and AV nodes to decrease the heart rate, which will decrease cardiac output.
Is stroke volume sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Stroke volume is also controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It has both sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagal) innervation that act to increase or decrease heart rate and contractility (inotropy). The sympathetic nervous system acts via B1 adrenoceptors and increases contractility (positive inotropic effect).
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect blood volume?
Sympathetic-induced constriction of veins (capacitance vessels) decreases venous compliance and blood volume, and thereby increases venous pressure.
Does the sympathetic nervous system increase cardiac output?
Additionally, sympathetic stimulation is increased, resulting in further increases to heart rate, as well as stroke volume, which in turn results in an even greater restoration of cardiac output.
What system increases stroke volume?
An increase in stroke volume is achieved primarily by an increase in the ejection fraction and a reduction in the end-systolic volume but can also be achieved by a decrease in afterload, which is primarily a function of aortic or pulmonary impedance (the resistance and reactance of the vasculature to ejection).
How does the body increase stroke volume?
Your heart can also increase its stroke volume by pumping more forcefully or increasing the amount of blood that fills the left ventricle before it pumps. Generally speaking, your heart beats both faster and stronger to increase cardiac output during exercise.
How does sympathetic nervous system affect cardiac?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) has a wide variety of cardiovascular effects, including heart-rate acceleration, increased cardiac contractility, reduced venous capacitance, and peripheral vasoconstriction.
Does sympathetic increase blood volume?
One can argue that high levels of sympathetic activity would engage renal mechanisms and tend to increase blood volume and, thus, promote a rise in blood pressure by both renal and vascular mechanisms.
How does sympathetic nervous system control blood flow?
The focus is largely on the sympathetic nerves, which have a dominant role in cardiovascular control due to their effects to increase cardiac rate and contractility, cause constriction of arteries and veins, cause release of adrenal catecholamines, and activate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
What happens when sympathetic nervous system increases?
Your sympathetic nervous system is best known for its role in responding to dangerous or stressful situations. In these situations, your sympathetic nervous system activates to speed up your heart rate, deliver more blood to areas of your body that need more oxygen or other responses to help your get out of danger.
Does parasympathetic stimulation increase stroke volume?
It is through contractility that sympathetic stimulation increases stroke volume in addition to heart rate (as hinted earlier). Predictably, parasympathetic stimulation leads to weaker contractions and lower contractility. Preload is the extent to which the cardiac myocytes in the muscle cells of the heart stretch.
What does the sympathetic nervous system increase?
Heart, sympathetic activation causes an increased heart rate, the force of contraction, and rate of conduction, allowing for increased cardiac output to supply the body with oxygenated blood.
Does parasympathetic affect stroke volume?
These sympathetic influences work in conjunction with parasympathetic influences on the SA node to decrease heart rate. During a short-term decrease in blood pressure, the opposite occurs, and the autonomic nervous system acts to increase vasoconstriction, increase stroke volume, and increase heart rate.
Does parasympathetic control stroke volume?
It is through contractility that sympathetic stimulation increases stroke volume in addition to heart rate (as hinted earlier). Predictably, parasympathetic stimulation leads to weaker contractions and lower contractility. Preload is the extent to which the cardiac myocytes in the muscle cells of the heart stretch.
Does parasympathetic activity affect stroke volume?
It also increases stroke volume by increasing contractility, which results in more complete ejection of blood from the heart (lower ESV). Increased Parasympathetic Stimulation - Parasympathetic activity increases after a crisis has passed.
How does parasympathetic stimulation decrease stroke volume?
Parasympathetic stimulation in the atria decreases the atrial kick and reduces EDV, which decreases ventricular stretch and preload, thereby further limiting the force of ventricular contraction. Stronger parasympathetic stimulation also directly decreases the force of contraction of the ventricles.
What factors affect stroke volume?
Stroke volume is affected by contractility, preload, and afterload. Note that contractility and preload have a positive correlation with SV, while...
What happens when stroke volume increases?
A higher heart stroke volume (SV) means there is more blood being pumped out by the heart. This increases the pressure against the arterial walls,...
What increases or decreases stroke volume?
Stroke volume has a positive correlation with contractility and preload, and a negative correlation with afterload. Thus, higher contractility and...
What effect does sympathetic nerve stimulation have on the heart?
Sympathetic nerve stimulation of the heart results in higher heart rate and stronger contractility, ultimately leading to more stroke volume. Conse...
What is stroke volume?
Heart stroke volume (SV) is the amount of blood that is ejected from the left ventricle after each contraction (beat). It is calculated as the volu...
How is stroke volume increased?
Stroke volume increases when the heart ejects more blood per beat as a result of higher contractility, greater preload, and less afterload. In addi...
Sympathetic nervous system activity and the heart - PubMed
The sympathetic nervous system has been viewed as the critical mechanism for cardiovascular response to increased circulatory needs during acute stress, augmenting cardiac rate and contractility and changing peripheral vascular tone. These physiologic responses, however, are increasingly thought to …
The sympathetic nervous system and blood pressure in humans ...
INTRODUCTION. The autonomic nervous system and its sympathetic arm play important roles in the regulation of blood pressure. 1, 2, 3 Their role in the short-term regulation of blood pressure, especially in responses to transient changes in arterial pressure, via baroreflex mechanisms is well known. 4 However, the role of the sympathetic branch in longer term (days, months, years) blood ...
The Sympathetic Nervous System and Heart Failure - PMC
INTRODUCTION. Heart failure (HF) is a syndrome characterized by upregulation of the sympathetic nervous system and abnormal responsiveness of the parasympathetic nervous system. 1 Evidence for this dysregulation has included the demonstration of abnormalities in HF patients, including increased urinary catecholamine levels, increased plasma norepinephrine, increased sympathetic tone, and ...
Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System in the Sinus Node Resistance to ...
SINUS NODE, POTASSIUM, AND CATECHOLAMINES 349 on a dual infusion-withdrawal pump (Harvard Appa-ratus Company model 942) and the other to a pressure
Blood Pressure Regulation: Hypotension - Easy as 1-2-3 - EZmed
Blood pressure regulation and physiology of hypotension made easy using the blood pressure formula. The sympathetic nervous system and renin angiotensin aldosterone system are increased by the brain and kidneys as compensatory feedback loop mechanisms. Cardiac output and vascular resistance increase
Why do the ventricles contract harder?
Like a rubber band, heart ventricles contract harder when blood volume stretches them. The volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole is referred to as the end-diastolic volume. An increase in end-diastolic volume then results in more stretching of the ventricles because there's more blood there.
Why does my heart beat faster?
This happens thanks to the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.
What happens to the ventricles during diastole?
We previously learned that during the resting phase of the heart, known as diastole, the ventricles of the heart are passively filling with blood. Then at the end of diastole, the atria contract, filling the ventricles even more. Like a rubber band, heart ventricles contract harder when blood volume stretches them.
Why does afterload increase?
If the nozzle is almost closed, afterload will increase because there will be a lot of resistance to the flow of blood through the hose. If the nozzle is opened wide, afterload will decrease because there will be less resistance to flow.
What is the law of the heart?
Two scientists named Frank and Starling noticed that the increase in end-diastolic volume, or preload, results in an increased stroke volume and more blood being pumped out of the heart with each heartbeat. This became a popular law in cardiac physiology and is known as the Frank-Starling law of the heart.
What is the cardiac output of the heart?
The cardiac output of your heart is a constantly changing amount that adjusts to any physical or emotional demands you put on your body. In this lesson, we will look at some of the factors that influence your heart rate and stroke volume.
What does decreased end systolic volume mean?
Therefore, we see that a decreased end-systolic volume indicates an increase in stroke volume. Afterload. Another important influence of end-systolic volume, and therefore stroke volume, is how much pressure exists in the arteries leaving the heart.
Why does cardiac output increase?
Cardiac output increases to meet increased metabolic demand, often by increasing both heart rate and stroke volume at the same time. This occurs, for example, during maximal exercise, when cardiac output may increase to four or five times the resting level.
What is the sum of the electrical activity of all cells in the heart?
the sum of the electrical activity of all cells in the heart. An intracellular recording of electrical activity in either a contractile cell or auto rhythmic cell is known as a(n) Action potential. An extracellular recording of electrical activity of both autorhythmic and contractile cells of the heart is known as a(n)
How do action potentials cause the release of calcium from the SR?
In skeletal muscle cells, action potentials cause the release of calcium from the SR by directly opening SR voltage-gated calcium channels. What causes the release of calcium from the SR in cardiac muscle cells?
What is the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic?
The balance between parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation to the heart controls heart rate. Increased parasympathetic activity decreases heart rate, and sympathetic activity increases heart rate. As part of a blood drive on campus for the American Red Cross, you and your friends have just donated 500 ml of blood.
What ions are released by the SR?
Influx of extracellular calcium ions opens ryanodine receptors allowing Ca2+ to flow out of the SR.
What is the function of a heart valve?
Heart valves ensure one-way flow of blood through the heart chambers.
Why does blood pressure decrease?
Blood pressure decreases, because of the effects of friction between the vessel walls and the moving blood. Consider three blood vessel segments of equivalent length and diameter: vessels A, B, and C. . Pressure at the beginning of each segment is as follows: A) P = 100 mmHg; . B) P = 80 mmHg;
How does the arterial baroreflex work?
The arterial baroreflex senses changes in blood pressure via baroreceptors, which are sensory afferent nerve endings located in the carotid sinus and the aortic arch. The baroreceptors respond to stretching of the vessel wall. In general, increases in this stretching as the result of a short-term increase in blood pressure lead to an increase in afferent input into central autonomic nuclei (notably the nucleus tractus solitarius). This increase in afferent input results in a reflex decrease in sympathetic neural outflow, which in turn decreases vasoconstrictor tone, myocardial contractility (to decrease stroke volume), and heart rate. All of these influences then result in a correction of the original “error signal” of increased blood pressure. These sympathetic influences work in conjunction with parasympathetic influences on the SA node to decrease heart rate. During a short-term decrease in blood pressure, the opposite occurs, and the autonomic nervous system acts to increase vasoconstriction, increase stroke volume, and increase heart rate.
Why does sympathoexcitation occur in idiopathic hypertension?
The causes of sympathoexcitation in association with idiopathic hypertension are unclear but may involve increases in chemoreflex sensitivity to hypoxia or hypercapnia: the responses to chemoreflex stimulation among hypertensive patients are several times higher than the responses exhibited by normotensive controls.45,46Interestingly, secondary hypertension does not appear to be associated with increased MSNA.37
What is ECG in medical terms?
Electrocardiogram (ECG), integrated sympathetic neurogram, and plot of beat-to-beat arterial pressure (AP) (as measured by a brachial artery catheter) from a healthy person. The figure shows the dynamic relationship between AP and muscle sympathetic neural activity (MSNA). The shading highlights an example of a transient decrease in AP that elicits an increase in MSNA via the baroreflex. This increase causes vasoconstriction, which in turn increases AP and leads to a reflex decrease in MSNA.
How does respiration affect blood pressure?
Respiration induces physiologic swings in stroke volume and blood pressure because of changes in both preload and afterload of the right and left ventricles. These changes, which are caused by fluctuations in intrathoracic pressure, can also be sensed by, and can elicit responses in, arterial and cardiopulmonary receptors. Changes in posture also induce changes in blood pressure because of changes in preload, and the baroreflex responds to correct the blood pressure, thereby preserving cerebral perfusion and the ability to maintain the upright position. For example, when a human being stands, a decrease in venous return can lead to a decrease in pulse pressure, systolic pressure, and/or diastolic pressure. This decrease in pressure decreases the rate of firing by baroreceptors in the aortic arch and the carotid sinus, and this change leads to a baroreflex-mediated increase in sympathetic neural outflow to the heart and the peripheral vasculature. This change in neural outflow increases vascular tone, stroke volume, and heart rate so that the level of arterial pressure can be maintained or corrected.
Where is SNA measured?
In humans, SNA is most often measured at the peroneal nerve, and the most common measurement is muscle sympathetic neural activity (MSNA). The technique involves the percutaneous insertion of a high-impedance tungsten microelectrode (the tip of which is only a few microns in diameter).
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect the heart rate?
These sympathetic influences work in conjunction with parasympathetic influences on the SA node to decrease heart rate . During a short-term decrease in blood pressure, the opposite occurs, and the autonomic nervous system acts to increase vasoconstriction, increase stroke volume, and increase heart rate.
What is sympathetic innervation?
Cardiac sympathetic innervation of the heart includes innervation of the sinoatrial (SA) node, which allows sympathetic nerves to increase heart rate by increasing the slope of diastolic depolarization during the spontaneous SA node action potential. Sympathetic nerves also innervate the myocardium; increases in sympathetic activity increase myocardial contractility and, therefore, increase stroke volume. Sympathetic innervation of the peripheral vasculature causes vasoconstriction primarily through the action of norepinephrine at postsynaptic α-adrenergic receptors. Cotransmitters such as neuropeptide Y also have a role in this vasoconstriction.4,5