
The topography of an area can influence the weather and climate. Topography is the relief of an area. If an area is close to a body of water it tends to make milder climates. Mountainous areas tend to have more extreme weather because it acts as a barrier to air movements and moisture.
How does topography affect climate?
How Does Topography Affect Climate? How Does Topography Affect Climate? Mountains, valleys and local topography affect the movement of air, precipitation and temperature. This results in areas that are wetter, drier or warmer than surrounding flatlands. Mountains are natural barriers to the movement of wind.
How do large bodies of water affect the climate?
That’s why large bodies of water affect the climate more than small ones. Your backyard pond will not affect the climate in your village or city. Besides the vertical movement of water, which accentuates the temperate temperatures of water bodies, there is the horizontal movement of water.
How do mountains affect the climate of a plain?
This results in areas that are wetter, drier or warmer than surrounding flatlands. Mountains are natural barriers to the movement of wind. They are colder than surrounding flatlands because the temperature decreases with elevation. As a result, there may be a tropical climate at the bottom of the mountain and snow on top.
How does local topography affect air currents?
Local topography near large bodies of water affect the temperature of air currents causing them to absorb more water than usual. Did Thomas Edison Really Invent the Lightbulb?
How does topography from the ocean affect climate?
The topography of an area also helps determine the climate. This is because of ocean currents that carry masses of warm or cool air to coastal locations. Much of the U.S.' eastern coast, for instance, experiences warmer temperatures because of the Gulf Stream, a warm ocean current.
How does a body of water affect climate?
Large bodies of water such as oceans, seas, and large lakes affect the climate of an area. Water heats and cools more slowly than land. Therefore, in the summer, the coastal regions will stay cooler and in winter warmer. A more moderate climate with a smaller temperature range is created.
How does topography affect the climate?
The topography of an area can influence the weather and climate. Topography is the relief of an area. If an area is close to a body of water it tends to make milder climates. Mountainous areas tend to have more extreme weather because it acts as a barrier to air movements and moisture.
How does topography affect climate answer?
Topography creates differences in climate across very small distances. These differences in temperature, moisture, and exposure to wind and sun are called microclimates, and they are important predictors as to where various natural communities can be found.
How do mountains affect the weather?
Mountains, valleys and local topography affect the movement of air, precipitation and temperature. This results in areas that are wetter, drier or warmer than surrounding flatlands. Mountains are natural barriers to the movement of wind.
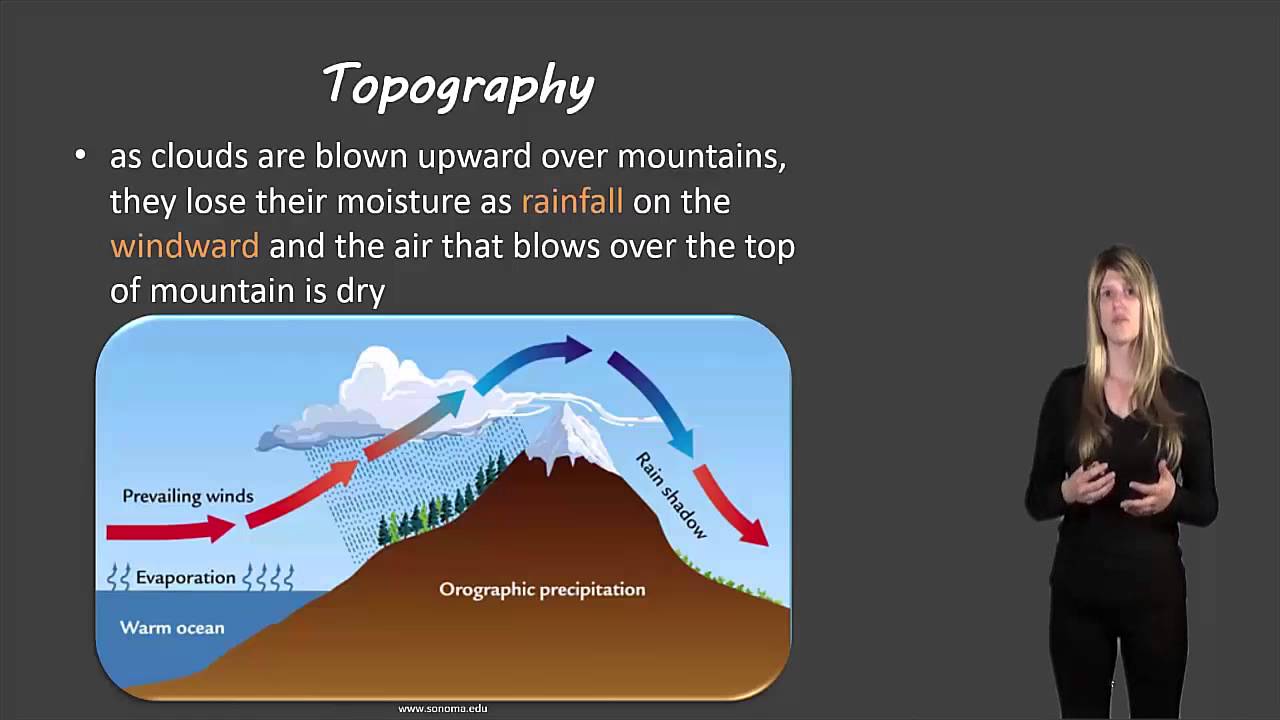
Why are mountains wetter on the windward side?
Mountains are wetter on the windward side because of this temperature differential. Winds carrying moist air rise when they reach the mountain and cool as they rise higher.
Why is the Sierra Nevada dry?
It is dry because dry air descends from the Sierra Nevada mountains and into the valley. As it descends down into the valley, it warms and settles there. Local topography near large bodies of water affect the temperature of air currents causing them to absorb more water than usual. ADVERTISEMENT.
Which side of a mountain is drier?
However, the leeward side of the mountain tends to be drier because the wind loses all of its moisture on the windward side, and the air compresses and warms as it works its way down the mountain. Valleys tend to be warmer than surrounding flatlands.
