How does voltage affect current flow?
How does voltage make current flow?
How does voltage difference affect current?
How the potential difference causes current to flow in a circuit?
This is the basis of current electricity. Negatively- charged electrons are removed from atoms, the atoms being left as positive ions. The potential difference between the two causes the electrons to be attracted back, producing a flow of electric charge: current electricity.
Does voltage cause current or does current cause voltage which is the cause and which is the effect?
It is possible to have voltage without current, but current cannot flow without voltage. current can flow. current cannot flow.
What is the difference between volts and voltage?
Why does voltage increase with current?
What is the relationship between voltage and current?
Why does voltage decrease when current increases?
Is potential difference the same as voltage?
Why is voltage called potential difference?
What is difference between electric potential and potential difference?
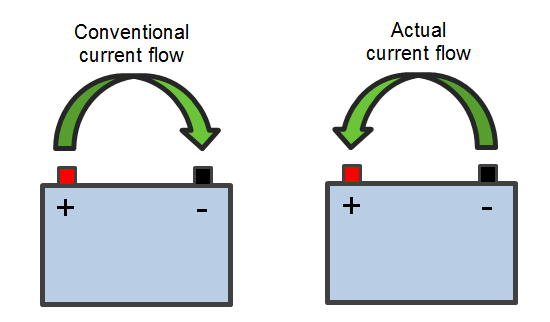
Which terminal does current flow from?
NOTE: It is interesting to know Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive. Conventionally, Current flows from the positive terminal to the negative.
Which direction do electrons flow?
Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive. Current flows from the positive terminal to the negative (conventionally).
Why do electrons push one electron?
Same the concept above, electrons are negatively charged and many electrons push one electron (because same charge repel each other) then another electron then another electron this chain continues and electron emits from the source come back to the source if circuit is closed this process cause to flow current (electric charge) in a circuit.
What does it mean when the current is 0?
If current is 0 it makes resistance infinite, means in open circuit (current = 0) resistance is infinite no matter how much voltage is present.
What is the difference between V and R?
Where I is the current through the conductor in units of amperes , V is the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts, and R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms. Ohm’s law states that the R in this relation is constant, independent of the current.
What is the net potential difference of a table and two people pushing it in opposite directions?
We have a table and two person pushing it in opposite direction with different forces, for example “FA=7 N& FB=5 N” so net potential difference (F A – F B) is “2 N” so the table will move in one direction (because A have more force, table will move in direction in which A is pushing/pulling), where N is Newton unit of force
What is net potential difference?
We have a table and two person pushing it in opposite direction with same forces, for example “FA=5 N& FB=5 N” so net potential difference (F A – F B) is “ 0 N ” so the table don’t move in any direction, where N is Newton unit of force
What is the difference between current and voltage?
By definition, the movement of charged particles (electrons in most conductive and semiconductor materials, ions in plasma and molten or solution of electrolyte) is electric current, and the difference of strength (potential) of electric field is voltage. However the charged particles and the electric field exert Coulomb forces to each other and that is the link between current and voltage.
What is the difference between electric current and electric field?
By definition, the movement of charged particles (electrons in most conductive and semiconductor materials, ions in plasma and molten or solution of electrolyte) is electric current, and the difference of strength (potential) of electric field is voltage. However the charged particles and the electric field exert Coulomb forces to each other ...
What happens when you connect two terminals together?
When you connect the terminals together via a conductor, the voltage pulls electrons from one metal to the other through that conductor. This allows ions to move through the electrolyte and the chemical reaction to take place . But again, to be clear, when disconnected, nothing is moving.
How does a conductor work when you connect two terminals together?
When you connect the terminals together via a conductor, the voltage pulls electrons from one metal to the other through that conductor. This allows ions to move through the electrolyte and the chemical reaction to take place .
How does a transformer work?
In the primary the transformer effectively produces a back-emf equal to the emf of the generator. Since the Voltages are the same no current can flow through the wires. When you attach a load to the secondary, the voltage generates a current which causes it to collapse some of the electric field.
Why are there electrons in a battery?
In another case if we consider, inside a battery, there are electrons due to chemical reaction or due to the liquid, these electrons are ready to find least impedance path to move out. In this case, the accumulation of charges cause some voltage that is the difference in the potential because of this potential, ...
How does a batter work?
answer to how a batter works is.... "Batteries have three parts, an anode (-), a cathode (+), and the electrolyte. The cathode and anode (the positive and negative sides at either end of a traditional battery) are hooked up to an electrical circuit.
How is voltage generated?
Voltage can be generated by means other than rubbing certain types of materials against each other. Chemical reactions, radiant energy, and the influence of magnetism on conductors are a few ways in which voltage may be produced.
When a voltage source is connected to a circuit, the voltage will cause a uniform flow of charge carriers through
When a voltage source is connected to a circuit, the voltage will cause a uniform flow of charge carriers through that circuit called a current.
How do charge carriers flow in a circuit?
As long as the battery continues to produce voltage and the continuity of the electrical path isn’t broken , charge carriers will continue to flow in the circuit. Following the metaphor of water moving through a pipe, this continuous, uniform flow of charge through the circuit is called a current. So long as the voltage source keeps “pushing” in the same direction, the charge carriers will continue to move in the same direction in the circuit. This single-direction flow of current is called a Direct Current, or DC. In the second volume of this book series, electric circuits are explored where the direction of current switches back and forth: Alternating Current, or AC. But for now, we’ll just concern ourselves with DC circuits. Because electric current is composed of individual charge carriers flowing in unison through a conductor by moving along and pushing on the charge carriers ahead, just like marbles through a tube or water through a pipe, the amount of flow throughout a single circuit will be the same at any point. If we were to monitor a cross-section of the wire in a single circuit, counting the charge carriers flowing by, we would notice the exact same quantity per unit of time as in any other part of the circuit, regardless of conductor length or conductor diameter. If we break the circuit’s continuity at any point, the electric current will cease in the entire loop, and the full voltage produced by the battery will be manifested across the break, between the wire ends that used to be connected:
What happens when a wire is placed between a charged wax and wool?
If a conductive wire is placed between the charged wax and wool, electrons will flow through it, as some of the excess electrons in the wax rush through the wire to get back to the wool, filling the deficiency of electrons there: The imbalance of electrons between the atoms in the wax and the atoms in the wool creates a force between ...
What is potential energy?
When the charge carriers are poised in that static condition (just like water sitting still, high in a reservoir), the energy stored there is called potential energy, because it has the possibility (potential) of release that has not been fully realized yet. When you scuff your rubber-soled shoes against a fabric carpet on a dry day, you create an imbalance of electric charge between yourself and the carpet. The action of scuffing your feet stores energy in the form of an imbalance of charges forced from their original locations. This charge (static electricity) is stationary, and you won’t realize that energy is being stored at all. However, once you place your hand against a metal doorknob (with lots of electron mobility to neutralize your electric charge), that stored energy will be released in the form of a sudden flow of charge through your hand, and you will perceive it as an electric shock! This potential energy, stored in the form of an electric charge imbalance and capable of provoking charge carriers to flow through a conductor, can be expressed as a term called voltage, which technically is a measure of potential energy per unit charge or something a physicist would call specific potential energy.
How does electric charge form between two materials?
The electric charge formed between these two materials by rubbing them together serves to store a certain amount of energy. This energy is not unlike the energy stored in a high reservoir of water that has been pumped from a lower-level pond:
How does gravity affect a pond?
The influence of gravity on the water in the reservoir creates a force that attempts to move the water down to the lower level again. If a suitable pipe is run from the reservoir back to the pond, water will flow under the influence of gravity down from the reservoir, through the pipe: It takes energy to pump that water from ...
Generating Voltage
How Do Voltage Sources Work?
- Any source of voltage, including batteries, have two points for electrical contact. In this case, we have point 1 and point 2 in the above diagram. The horizontal lines of varying length indicate that this is a battery, and they further indicate the direction which this battery’s voltage will try to push charge carriers through a circuit. The fact that the horizontal lines in the battery symbol appear s…
Understanding The Concept of Electric Current
- As long as the battery continues to produce voltage and the continuity of the electrical path isn’t broken, charge carriers will continue to flow in the circuit. Following the metaphor of water moving through a pipe, this continuous, uniform flow of charge through the circuit is called a current. So long as the voltage source keeps “pushing” in the...
What Is The Polarity of A Voltage drop?
- Notice the “+” and “-” signs drawn at the ends of the break in the circuit, and how they correspond to the “+” and “-” signs next to the battery’s terminals. These markers indicate the direction that the voltage attempts to push the current, that potential direction commonly referred to as polarity. Remember that voltage is always relative between two points. Because of this fact, the polarity …