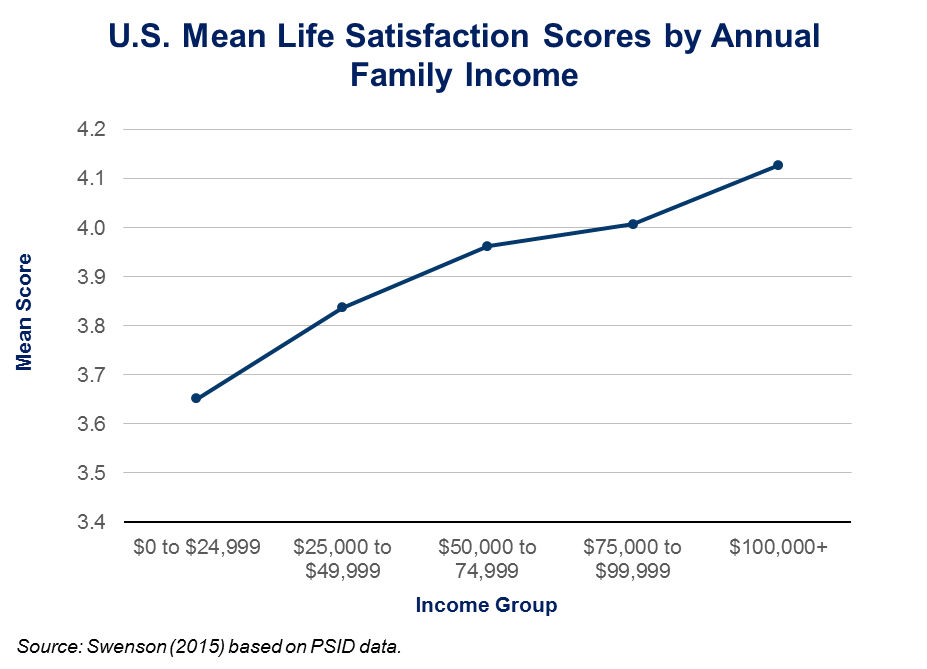
What is the relationship between poverty and welfare?
The relationship between poverty reduction and differing levels of welfare expense as a percentage of GDP. The effects of social welfare on poverty has been studied. Studies have shown that in welfare states, poverty decreases after countries adopt welfare programs.
Does Welfare really help the poor?
Welfare is just another capitalist system that allows money to flow through the system and continue the class division. Welfare CAN help the poor but really only in some cases, as welfare can't ever be enough to pay for education.
Does Welfare perpetuate poverty?
Welfare Does Not Perpetuate Poverty (Nor Will It End Poverty) An issue which consistently divides along party lines is social spending. The position I hear the most from the right side of the aisle is that welfare creates a system of perpetual poverty and that a high percentage of people using welfare are exploiting the system.
What are social issues related to poverty?
Social Problems Related to Poverty or Wealth
- Economic Cycles. Obvious social ills of poverty include higher crime, higher mortality rates and homelessness and hunger.
- Economic Inequality. The Congressional Budget Office released disheartening reports covering the years between 1979 and 2007 that indicate the gap between the classes is widening.
- Impact on Health. ...
- The Vanishing Middle Class. ...
Does welfare lead to poverty?
Welfare does not reduce poverty; it may actually increase it. The Census Bureau determines the poverty status of a family by comparing the family's pre-tax cash income with a poverty threshold that depends on family size and composition.
How has welfare helped poverty?
Census data show that economic security programs lifted nearly 37 million people above the poverty line in 2018, including 7 million children. Government benefits and tax policies cut the poverty rate from 24.0 percent to 12.8 percent in 2018; among children, they cut the poverty rate from 23.3 percent to 13.7 percent.
How is poverty related to social welfare?
Social work values and poverty It leads to denial of resources required for a decent life. Poverty causes shame and affects peoples' sense of their worth. Respecting the right to self-determination: Poverty causes social exclusion, thereby disempowering people from involvement in issues affecting them.
Do welfare programs reduce poverty?
Some 83 million people are below the poverty line when government assistance income and taxes are not considered, 44 million when they are. Government benefits and tax policies cut the poverty rate from 25.6 percent to 13.5 percent in 2017, and from 25.5 percent to 13.6 percent among children.
How does welfare attempt to raise poor?
How does welfare attempt to raise poor people's standard of living? It does not. The purpose of welfare and the entire welfare system is to provide individuals that have have made mistakes, or fallen on bad times through chance, the opportunity to pull themselves from their terrible situation.
Why is welfare important?
Social welfare policy — which guides the government programs that assist people in need — builds on the idea that a government has a responsibility to protect its citizens from harm. According to the principle, a society can thrive only when it provides safeguards for those who face risks to their well-being.
How does welfare hurt the economy?
Accordingly welfare tends to diminish both self-sufficiency, since it leads more people to accept unemployment, and production, since the productive potential of those people is not turned into goods.
What are welfare issues?
Poverty, unemployment, unequal opportunity, racism, and malnutrition are examples of social problems. So are substandard housing, employment discrimination, and child abuse and neglect. Crime and substance abuse are also examples of social problems.
What are the 5 causes of poverty?
Here are 11 of those causes, fully revised for 2020.INEQUALITY AND MARGINALIZATION. ... CONFLICT. ... HUNGER, MALNUTRITION, AND STUNTING. ... POOR HEALTHCARE SYSTEMS — ESPECIALLY FOR MOTHERS AND CHILDREN. ... LITTLE OR NO ACCESS TO CLEAN WATER, SANITATION, AND HYGIENE. ... CLIMATE CHANGE. ... LACK OF EDUCATION. ... POOR PUBLIC WORKS AND INFRASTRUCTURE.More items...•
Is Social Welfare effective?
Aside from adults, social welfare can also brighten the future for poverty-stricken kids, ultimately halting the cycle of poverty in families at risk.
How can we reduce poverty?
These include:Quality education. Education provides children with the knowledge and life skills to realize their full potential. ... Access to Health care. Access to health care is essential. ... Water & sanitation. Water and sanitation are also essential for every child's survival. ... Economic security. ... Child participation.
What government can do to reduce poverty?
Here are five poverty reduction initiatives in India. Saansad Aadarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY): Prime Minister Narendra Modi started Saansad Aadarsh Gram Yojana (SAGY) after considering the increasing poverty rates in October 2014. SAGY is a government program that focuses on the social and cultural development of villages.
Does welfare help the economy?
Improves the economy Unemployment benefits also provide people leeway to find jobs that match their skill sets, rather than snapping up the first available position. In other words, overall economic productivity increases as a result of government assistance.
How has welfare helped families?
Government economic security programs such as food assistance, housing subsidies, and working-family tax credits — which bolster income, help families afford basic needs, and keep millions of children above the poverty line — also have longer-term benefits, studies find: they help children to do better in school and ...
How has welfare reform affect the way state and national governments work together to fight poverty?
How has welfare reform affected the way state and national govt. s work together to fight poverty? they both will work together to fight poverty by paying welfare receptants and representing a strong economy.
What was a benefit of the welfare reform act?
Purposes of the 1996 Reforms The 1996 legislation stated that the purposes of the program were to assist needy families, fight welfare dependency by promoting work and marriage, reduce nonmarital births, and encourage the formation and maintenance of two-parent families.
How does welfare affect people?
A first observation is that the incentives associated with welfare tend toward unwanted results (not that they necessarily bring about these results, only that they cause a tendency in that direction). The benefits go to people who, for a host of reasons, are relatively unproductive, while the funds to pay for them come, through taxation, from people who are relatively productive. Now we know that for human beings, benefits are positive incentives while taxes are negative incentives. Thus the welfare system tends to encourage unproductiveness and discour age productivity. A person who could bring home only a few dollars more per week working than taking advantage of the welfare system has an incentive not to work. Accordingly welfare tends to diminish both self-sufficiency, since it leads more people to accept unemployment, and production, since the productive potential of those people is not turned into goods. The effect may not be a large one, but it is something to consider.
How can poverty be overcome?
As one considers the problem of poverty, one should keep three basic truths in mind. The first of these is obvious, that is: poverty is finally overcome only when people are self-supporting. It is not enough that they be living for the moment at an acceptable standard if they remain dependent, just as one is not cured of a disease when he is taking medicine that eliminates his symptoms. Thus an essential objective of any antipoverty program must be to maximize self-sufficiency.
When did the two wars against poverty begin?
In an article called “The two wars against poverty: economic growth and the Great Society” ( The Public Interest, Fall 1982), Charles A. Murray demonstrates that around 1968, when Great Society antipoverty spending was booming and unemployment stood at 3.5%, progress against poverty slowed, and then stopped.
Why do bureaucrats have an incentive to expand the numbers encompassed by those programs?
Since the amount of taxpayers’ money that passes through their hands depends on the size and perceived importance of their programs , the bureaucrats have an incentive to expand the numbers encompassed by those programs, and to find new reasons for increased funding.
What is latent poverty?
Like official poverty, latent poverty as a percentage of population decreased steadily until the late sixties, from about 33% in 1950 to 19% in 1968. In 1968, however, the trend reversed; the proportion of Americans dependent on the government began to increase. With the exception of one dip after 1975, it has increased since, back to 23% in 1980.
How does prosperity depend on production?
Unless physical goods are produced in the first place and then replaced as necessary, there can be no prosperity for anyone. If this stock of goods is not constantly increased, higher levels of well-being overall are impossible. Other things being equal, the more goods there are in the world food, shelter, medicine, electric light, shoes, water heaters, and so on the more there is to go around and the less poverty there will tend to be. (Of course things are not always equal, and different people end up with different amounts of these goods, but the principle stands nonetheless: if there is literally not enough to go around, some poverty is inevitable. At the other extreme, if goods should become overabundant, their price would approach zero and the poorest could afford all they could use.) Thus an important means of reducing poverty is increasing production.
What percentage of the population was poor in 1950?
Since 1950, the number of (official) poor as a percentage of population was approximately 30%. From then until 1968, the figure dropped steadily, to about 13%. But then, right in the heart of the Great Society years, when more money than ever was being spent to decrease poverty even faster, the trend line flattened.
Shrinking Middle Class Analysis
1) Watch: The Shrinking Middle Class: Coping with Loss and Defining the Middle Class (summarize, what 's your opinion?) Studies show that 85% of respondents would agree that it is harder to live in the middle class today than it was in the past.
Effects Of Poverty In America
The Effects of Poverty in America “In 2007 about one out of every eight children in America was on food stamps. Today that number is one out of every five” (U.S Census Bureau). This statistic from the U.S Census Bureau illustrates how the poverty level of Americans is getting worse and worse.
Foreign Aid Persuasive Speech
The US is more than 66 trillion dollars in debt, has more than 560,000 people that are homeless and poverty rates are up to 13.5% (43.1 million people). Other countries are like that too, and we help those countries with foreign aid, but we barely help our own country.
Crime And Bad Parenting Analysis
The graph showed that rich areas obtain more profit than poor, but another research indicated that schools get $4000 more fundings for free reduced lunch. A finding which was astonishing was that a poor district of 251, which are know to be are
Germany's Economic Consequences
Expenses amounted 150 billion marks, and accumulated in the the years of war resources - only 35 billion marks. Public debt increased from 5 to 160 billion marks. Were killed and injured 7.5 million of people.
Waiting For Superman Vs Idiot Nation Essay
Did you know that the United States ranks 17th in education performance? That is a huge drop from 1980 when the United States was ranked 1st. Clearly, our education system has gone in a downward spiral and is struggling to keep up with other countries.
Poverty In America Essay
Poverty In America There are many issues going on inside of our country from climate change to domestic violence. However,today i will be addressing a topic that I find more important. This topic is affecting 45 million people, or 14.5 percent of all Americans. The topic I will be addressing is poverty.
Why are liberals dissatisfied with child poverty?
The primary reason is that the substantial earnings increases by mothers have not been matched by the ability of government programs to remove them from poverty as effectively as in the past . In short, liberals believe that government programs are letting these families down.
Why is child poverty important?
Child poverty will be an important issue as the welfare reform reauthorization debate heats up in the 107th Congress. Since the federal government adopted a standard definition of poverty in the 1960s, scholars, politicians, the media, and the public have used poverty as a measure of the strength and success of government policy and the economy.
Why should we examine food stamps?
Because fewer than half the mothers leaving welfare continue to receive the food stamps to which they are entitled, Congress should carefully examine food stamps to ensure that eligible children and parents have every opportunity to receive these entitlement benefits. Several changes in food stamp policy could boost participation among the working poor. The federal quality control system, designed to control fraud and abuse, should be modified because it has led many states to take administrative actions that reduce participation among working families. The food stamp program itself should be simplified. Asset tests, in particular, should be revisited, because current tests make the program hard to administer and make too many low-income working families ineligible. The adequacy of the food stamp benefit structure also warrants reexamination, particularly in light of the cuts in benefits enacted in 1996. Another reform supported by many conservatives would be to provide states with a food stamp block grant and then allow them to solve coordination issues without interference from the federal government.
How can tax code change help with poverty?
There are a host of tax code changes that could help reduce poverty. One change on which there appears to be broad agreement is to reduce the marriage penalty in the EITC by starting the phase-out range (the income at which the benefit begins to fall) at a higher income for married families. Another option is to make the child tax credit partially refundable (meaning that, in a kind of negative income tax, low-income families without tax liability would be given a cash return equal to the amount of the credit). One approach outlined in an earlier brief in this series is to provide a significant credit to parents who work full time by phasing in the credit as earnings increase. The recent tax bill signed into law by President Bush in June 2001 adopted this approach and included modifications of the EITC to reduce the marriage penalty. Another tax policy that favors low-income families would add another tier to the EITC that would provide higher benefits for families with three or more children. All of these policies would significantly reduce child poverty.
What is the first piece of information about child poverty?
The first piece of information is how the federal government measures poverty. The Census Bureau, the official scorekeeper for federal poverty measures, computes poverty by comparing individual or family income from earnings, cash government payments, and a few other sources to a criterion income level, adjusted for family size and inflation, that represents a minimally adequate standard of living. In 2001, the criterion income, or poverty line, was about $14,600 for a family of three.
How much did the poverty gap decrease in 1993?
Even more revealing, means-tested cash and non-cash programs (government programs that provide benefits to families whose income is less than a given amount) reduced the poverty gap by $23.4 billion in 1993, but only $11.9 billion in 1999.
What was the poverty line in 2001?
In 2001, the criterion income, or poverty line, was about $14,600 for a family of three. Both the definition of income and the poverty line criterion are controversial. One criticism of the Census Bureau’s official measure of poverty is that not all sources of family income are included.
Why is welfare programs failing?
The first failure of government welfare programs is to favor help with current consumption while placing almost no emphasis on job training or anything else that might allow today’s poor people to become self-sufficient in the future.
What is the third flaw in the welfare system?
The third flaw in the government welfare system is the way that benefits phase outs as a recipient’s income increases. As a household’s income approaches the poverty line and rises above it, families on various welfare programs can actually face effective marginal tax rates of 50 or 60 percent (see this CBO report for the details). That means that the combination of taxes owed on new income and benefits lost because of the rising income causes the family to lose 50 to 60 percent of its initial income gain to the federal government.
How much would a basic income replace the current welfare system?
A basic income would replace the current welfare system with payments to all households sufficient to provide everyone with enough money to live on, say $12,000 per year for adults and $4,000 per child. Families keep the basic income regardless of how much other income they earn, so everyone receives it, rich or poor.
How does basic income policy solve the second and third problem?
Therefore, a basic income policy solves the second and third problem, by removing any need for asset tests and by eliminating the high marginal effective tax rates that trap some in poverty and on welfare.
What is the second failure of welfare?
The second failure of government welfare programs is the common requirement to have minimal assets to be eligible for aid. While many states have eliminated their asset tests, they still remain in about one dozen states and can be as low as $1500.
Did job training make people worse off?
In a study for ProPublica, Amy Goldstein documents that people who lost their jobs and participated in a federal job training program were less likely to be employed afterward than those who lost their jobs and did not receive any job training. That is, the job training made people worse off instead of better.
Do welfare benefits have to be phased out?
Clearly, welfare benefits must phase out as incomes rise, but they do not have to phase out this rapidly. An effective marginal tax rate that high can (and by numerous accounts from the real world does) cause families in and near poverty to turn down opportunities for promotions, raises, or more hours of work because the higher earned income is hardly worth it given the losses they face from taxes and lost benefits.
Why did the Indian Child Welfare Act of 1978 stop the removal of American Indian children from their households?
One of the aims of the Indian Child Welfare Act (ICWA) of 1978 was to stop the removal of American Indian children from their households due to poverty . A number of studies had confirmed that social workers were removing American Indian children from households not due to maltreatment or being orphaned but simply due to the perceived poverty status of the household (see MacEachron, Ann E., and Nora Gustavsson, 2005). The ICWA legislation was intended to improve tribal control over the determination and placement of American Indian children within the foster care system.
Is child poverty high in reservations?
While this does not dismiss the fact that child poverty is probably still too high in many American Indian reservations, it does indicate that there may be other activities or practices that exist in non-market (even non-governmental) forms to assist families.
Do OPM and SPM show up as cash income?
These activities do not show up directly as cash income nor are they identified as federal government in-kind transfers. As a result, the OPM and SPM measures may not accurately depict the general welfare of American Indian families or children.
How does welfare affect the poor?
Our welfare system discourages work. It discourages families from staying together. And it encourages dependence on government. In other words, welfare keeps the poor poor. In many cases, welfare has harmed the very people it was supposed to help, especially children.
Why did we lose the war on poverty?
We Lost the War on Poverty: Why Welfare Keeps Poor People Poor. Our welfare system discourages work. It discourages families from staying together. And it encourages dependence on government. When President Lyndon Johnson launched his War on Poverty in the 1960s, he pledged to eliminate poverty in America.
What happens to welfare recipients when they have time limits?
In states that have implemented time limits and welfare-to-work requirements, recipients have received job training, found jobs, and increased their incomes dramatically. They’ve also dropped off the welfare rolls.
When did the welfare system fail?
When President Lyndon Johnson launched his War on Poverty in the 1960s, he pledged to eliminate poverty in America. More than five decades, several welfare programs, and $25 trillion later, the welfare system has utterly failed the poor.
Why do people want a social safety net?
Most Americans want a social safety net that helps those who can’t help themselves and they want to help the poor find meaningful work.
Do children grow up on welfare?
Sadly, the cycle continues today as many children who grow up on welfare eventually follow in their parents’ footsteps when they have families of their own.
Is the poverty rate unchanged?
The poverty rate remains mostly unchanged, and tens of millions of Americans are dependent on government assistance.
How does time limit affect welfare?
Time limits on welfare receipt are hypothesized to have ambiguous effects on poverty. Standard economic theory predicts that the elimination of welfare cash benefits unambiguously increases labor supply, but has ambiguous effects on total income. Unearned income will likely fall due to the loss of welfare benefits, but some individuals might increase their labor supply enough to increase earned income by more than the amount of benefits lost (Moffitt and Pavetti 2000). Another factor that further clouds the effect of time limits on poverty is the extent to which women leaving welfare are able to replace unearned income lost from welfare benefits with unearned income from other sources, such as private transfers from friends and relatives. Six policies are identified to capture the multiple dimensions of states’ time limit policies.
What was the poverty rate in the 1990s?
Poverty rates in the United States fell from a 25-year high of 15.1 percent in 1993 to near record lows of 11.3 percent in 2000 and have since increased steadily to 12.7 percent in 2004 (U.S. Census Bureau 2004a). The poverty rates for children and for people in single female-headed families followed a similar pattern, although at considerably higher rates—17.8 percent and 30.5 percent in 2004, respectively (U.S. Census Bureau 2004a, 2004b). Many political leaders pointed to poverty rate declines along with increases in employment and falling welfare caseloads that occurred in the late 1990s as evidence that the 1996 federal welfare reform had been a success (Kaus 2001). During the late 1990s, however, there was concern that welfare reform was leading to increases in deep poverty (living below 50 percent of the poverty threshold) (e.g., Sherman et al. 1998, as cited in Haskins 2001), as deep poverty rates increased in 1996 and were unchanged in 1997 (U.S. Census Bureau 2004c). Deep poverty rates subsequently fell, however.
What percentage of families in poverty receive welfare?
Just 23 percent of all families with children living in poverty receive welfare, according to estimates by the liberal Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. Only in three states — Hawaii, California and Vermont — is the share more than half.
Why did the government spend more on welfare?
Part of the reason was that, under the reform, states could redirect that federal money to programs other than welfare, such as child care, college scholarships and programs that promote marriageas a way to prevent poverty.
Why was welfare reform important?
He argues that welfare reform was an important accomplishment that ended many families' dependence on public assistance and encouraged them to provide for themselves.
Why did the Clinton reforms work?
Proponents of reform argue that the restrictions Clinton enacted encouraged many people to work and end their dependency on help from the government. At the same time, the robust economy might have drawn more workers into the labor force, and the expansion of the Earned Income Tax Credit — a bonus for poor workers that rewards them financially for working and earning more — provided another reason for people to find jobs.
What was the new welfare system called?
In the new system, known as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, applicants must meet a range of strict requirements that vary by state to get help — working, volunteering, looking for a job or participating in skills training.
How can we reduce poverty among children?
Federal policymakers have made reducing poverty among children a priority by offering tax credits to parents and giving kids health insurance and free lunches at school. In recent years, though, the share of children in poverty has not declined as quickly as it had in the past.
How have the lives of the poor changed?
1. Fewer people are on welfare. After Clinton signed the reform, Americans left welfare rolls in droves. People receiving federal welfare payments fell by half in four years , to 6.3 million in 2000.
