How is a mitochondria like a power plant?
The mitochondria is like an electric power plant because it is the main source of energy in a cell. Explanation: You must think of the cell as if it were a city. This cell is constantly active and has a lot of energy, but that energy is running out.
What do mitochondria use to produce energy for a cell?
How Does the Mitochondria Produce Energy for the Cell?
- Mitochondria. Remember that this energy originally came from the sun and was stored in chemical bonds by plants during photosynthesis.
- outer membrane
- cristae (3) The matrix (4) is the space contained within the inner membrane. Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?
How to enhance your mitochondria for more energy?
- Coffee and tea for polyphenols
- Green leafy vegetables
- tomatoes
- Berries
- Olive oil
- Salmon, sardines and other fatty fish for omega-3s
- Nuts, including almonds and walnuts
- Turmeric
Which cell does mitochondria give the energy?
Mitochondria are the powerhouse energy producers tucked away inside every cell. When you exercise, these tiny, but powerful, organelles, work hard to produce enough ATP to fuel muscle contractions. Beyond being energy producers, researchers now believe that mitochondria play a role in aging as well.
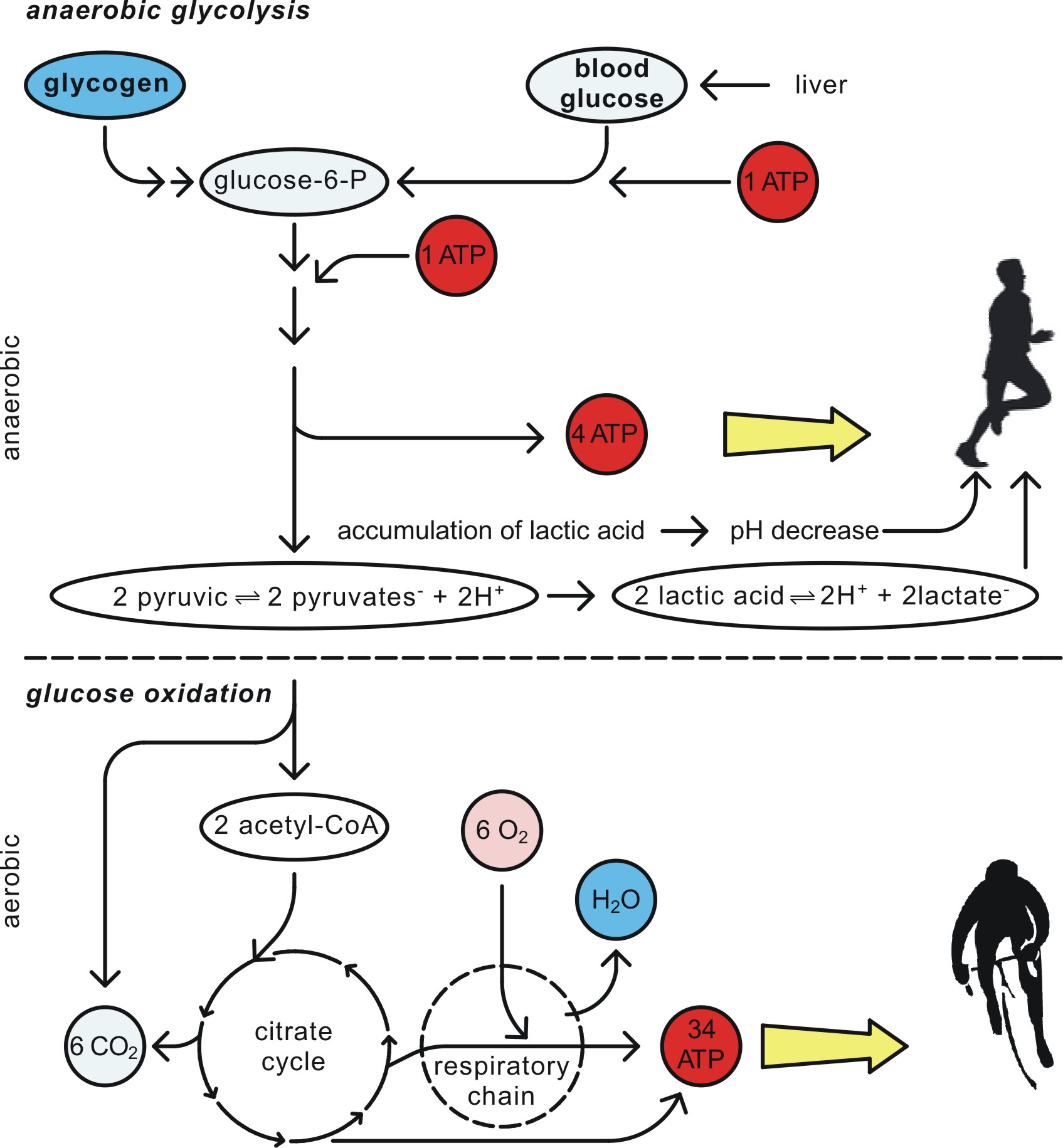
How energy is produced in mitochondria Class 9?
Mitochondria is a cell organelle which is also called the powerhouse of the cell. Some processes of cellular respiration take place here, like the Kreb cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. By the reduction of many compounds, energy is produced in the form of NADH2 and FADH.
What is the process of generating ATP in mitochondria?
The electrons pass through different electron carrier complexes of ETS. Now H+ ions are released in the inner mitochondrial space. Now the H+ ions gradient is created across the inner membrane. ATP synthetase enzyme becomes active and ATP is synthesized. This is called oxidative phosphorylation.
Where is mitochondria energy produced?
Mitochondria Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
How is ATP generated 3 ways?
In general, the main energy source for cellular metabolism is glucose, which is catabolized in the three subsequent processes—glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA or Krebs cycle), and finally oxidative phosphorylation—to produce ATP.
What is the process of forming ATP called?
The actual formation of ATP molecules requires a complex process called chemiosmosis. Chemiosmosis involves the creation of a steep proton (hydrogen ion) gradient. This gradient occurs between the membrane-bound compartments of the mitochondria of all cells and the chloroplasts of plant cells.
What is the process of generating ATP in mitochondria and chloroplasts called?
The common pathway used by mitochondria, chloroplasts, and procaryotes to harness energy for biological purposes operates by a process known as chemiosmotic coupling—reflecting a link between the chemical bond-forming reactions that generate ATP (“chemi”) and membrane-transport processes (“osmotic”).
What process produces ATP energy?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
How is ATP produced step by step?
0:592:12ATP Production Overview - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWell the process has three steps the first step of cellular respiration. Glycolysis starts with aMoreWell the process has three steps the first step of cellular respiration. Glycolysis starts with a single glucose molecule glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm.
How does ATP work in the sodium-potassium pump?
ATP powers this process by attaching its terminal phosphate group to the pump. The phosphate group is highly charged. Its attachment pulls and tugs on some regions of the pump and repels other regions due to the fact that many of the amino acids comprising the pump are polar or charged. These electrical, magnetic-like, interactions change the shape of the pump. This causes sodium ions to be pumped outside the cell even though they are more plentiful there. When the phosphate is released, the pump returns to its original shape bringing in potassium ions and reloading sodium. It is this pumping action that, among other things, provides the energy for messages in nerve and muscle cells (action potentials).
How much ATP does the human body have?
An interesting bonus fact: an adult human body only contains about 250 grams of ATP at any one time, but turns over its entire body weight in ATP during the course of a single day.
What happens when molecules meet in an enzyme?
When these molecules meet up in a enzyme, a series of reactions happen (Krebs cicle) which end up in CO2, H20 and energy.
Is energy a substance?
You seem to have misunderstood energy as some sort of substance which is produced as a product of cellular respiration like CO 2 or H 2 O then released into the bonds of ATP molecules. Remembering that it is not a substance and that it is transferred (and not made) by the breaking and formation of bonds in the process of respiration should help clear that out.
Is ATP a chemical energy?
ATP is a form of chemical energy. Hydrolysis of the third phosphate group produces quite a bit of energy: