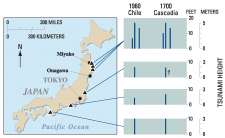
How fast do tsunamis hit Puget Sound?
This Cascadia study builds on previous studies of impacts to Puget Sound communities from earthquakes produced on the Seattle Fault. The study finds the first tsunami waves would reach Whidbey Island within one hour and 30 minutes after the earthquake, and more inland locations of Puget Sound some 2 to 4 hours after.
How often does the Cascadia subduction zone produce major earthquakes?
The Cascadia subduction zone produces a major earthquake every 300 to 600 years. It has already been 320 years since the last magnitude 9 earthquake struck back in 1700.
What would happen if a tsunami hits Washington?
Besides the approaching tsunami, the state would also be dealing with any damage from the earthquake, including impacts to buildings and critical infrastructure, such as roadways out of vulnerable areas. The Cascadia subduction zone produces a major earthquake every 300 to 600 years.
How do I get the most complete tsunami data coverage?
Therefore, to get the most complete tsunami data coverage for California's coast, you must utilize the 2021 and 2009 data together. California Tsunami Hazard Area Maps and data are prepared to assist cities and counties in identifying their tsunami hazard for tsunami response planning.

How far inland can a 100 ft tsunami go?
10 miles inlandMost tsunamis are less than 10 feet high when they hit land, but they can reach more than 100 feet high. When a tsunami comes ashore, areas less than 25 feet above sea level and within a mile of the sea will be in the greatest danger. However, tsunamis can surge up to 10 miles inland.
Will the Cascadia tsunami reach Portland?
Will a Tsunami hit Portland? No! Portland is too far from the Ocean to be in danger of a tsunami. Portland, like Salem and Eugene, is in the Willamette Valley, about 60 miles from the ocean.
How far inland would a tsunami go in Seattle?
There is evidence that an earthquake on the Seattle Fault that occurred around 900 AD produced a 16-foot tsunami. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recreated this tsunami using a model. The modelled tsunami would flood areas up to one mile inland with depths up to 5 meters.
How far inland will the Cascadia tsunami reach in California?
The shaking will be felt for hundreds of miles - from the coast all the way inland to Boise, Idaho, even to the southeast toward Sacramento in California. As one section of the sea floor drops, so will the ocean water above it creating a massive tsunami that will inundate low-lying coastal communities.
How far inland can a tsunami travel in Oregon?
That displaced water does not crest and fall; it simply rises, like an extremely high tide, until the entire water column is in motion, from seafloor to surface. Then it rolls inland, with ten or twenty or sixty miles of similar waves at its back, and demolishes everything in its path.
Where will the tsunami hit 2022?
Tonga Tsunami, January 15, 2022.
Could a tsunami take out Seattle?
A study by the Washington State Department of Natural Resources suggests that a major earthquake and ensuing tsunami from the Seattle fault could produce waves up to 40 feet high and inundate the area with 20 feet of water. A tsunami, resulting from a major earthquake, could inundate parts of Seattle.
How overdue is the Cascadia earthquake?
Jan. 26 marks 322 years since the last Cascadia Subduction Zone earthquake and tsunami struck the Pacific Northwest, the Oregon Office of Emergency Management reminds us.
Is Washington state in danger of a tsunami?
Washington is at a higher risk for tsunamis and earthquakes because of the Cascadia Subduction Zone, a 621-mile fault that runs from Vancouver Island, B.C. to northern California.
How far inland would a 200 foot tsunami travel?
20 miles inlandHowever, while there is no indication it could happen soon (but could), there are scientifically sound reasons for concern that at some point a mega-tsunami could engulf the entire East Coast with a wave almost 200 feet high sweeping everything and everybody up to 20 miles inland.
How far inland is safe from tsunami?
Pick shelters 100 feet or more above sea level, or at least one mile inland. Create a family emergency communication plan that has an out-of-state contact. Plan where to meet if you get separated.
What year will the Big One hit?
We know the San Andreas Fault will strike again and significantly impact all civilization within a 50-100 mile radius. According to USGS there is a 70% chance that one or more quakes of a magnitude 6.7 or larger will occur before the year 2030.
What cities will be affected by the Cascadia earthquake?
Coastal Pacific Northwest Called the Cascadia subduction zone, a big quake along this fault could affect the cities of Seattle, Tacoma, Portland, Eugene, Salem, and Olympia.
Is Portland Oregon on a fault line?
Nov. 27, 2020 6 a.m. Oregon doesn't see the same seismic activity associated with California and cities like San Francisco, but the city of Portland is surrounded by earthquake faults.
Will Oregon get a tsunami?
Oregon has the potential for a 9.0+ magnitude earthquake caused by the Cascadia Subduction Zone and a resulting tsunami of up to 100 feet in height that will impact the coastal area.
Where will the Cascadia earthquake hit?
Stresses have now been building along the Cascadia subduction zone for 320 years. The most likely scenario is a southern CSZ quake, with an 8 to 8.6 magnitude off the coast of southern Oregon and northern California according to the geologists. This is over 300 miles away from Portland.
How high would a tsunami wave be?
Tsunami waves would range from a high of about 13 feet at the Vashon Island ferry terminal and the town of Belfair at the tip of Hood Canal to a low of about 6 inches at the Port of Olympia, the study found.
How long did it take for the tsunami to reach Whidbey Island?
The first tsunami waves would reach Whidbey Island within one hour and 30 minutes after the earthquake, and strike more inland locations of Puget Sound some two to four hours after.
What magnitude earthquake would cause a tsunami?
OLYMPIA, Wash. – A 9.0 magnitude subduction earthquake off the Washington coast would generate a tsunami capable of submerging not only coastal areas but also most of the Puget Sound shoreline with churning waves of seawater several feet high for up to 14 hours, says a newly released study.
How high are the waves in Seattle?
Elsewhere, waves would reach an estimated height of about 10 feet in the Port of Bellingham, 3.7 feet at Seattle's Harbor Island, about 5.7 feet at the Snohomish River delta, and about 3.5 feet at the Port of Tacoma. No part of the Puget Sound shoreline would be unaffected.
Is it a matter of time before a quake hits Washington?
The study, by the state Department of Natural Resources' Washington Geological Survey division, found that it's only a matter of time before such a huge quake strikes the region.
What would happen if a 9.0 earthquake hit the Cascadia subduction zone?
The Washington Department of Natural Resources recently released simulations that show how a powerful tsunami would overwhelm the state's coastal and shoreline communities if a magnitude 9.0 earthquake struck along the Cascadia subduction zone.
How long does it take for a tsunami to hit Washington state?
(Washington Department of Natural Resources) In the videos, the initial wave could hit the state's outer coast in 15 to 20 minutes after the ground starts shaking and the quake generates a tsunami.
How long does a tsunami last?
But the DNR notes that tsunamis are "multi-wave events" that can impact areas for "many hours to potentially days" after the initial quake happens.
Where was the 2016 tsunami?
In 2016, federal officials ran a massive earthquake and tsunami drill in the Pacific Northwest around the premise of a 9.0 magnitude earthquake 95 miles off of the coast of Oregon that resulted in a tsunami.
How many feet did the tsunami cover?
The tsunami that struck Japan swept over eighteen-foot protective barriers, rushed through towns and cities, and tore them apart, so that those towns and cities became part of the wave, cars and trucks and warehouses and real houses swirling in the water.
How fast will the tsunami move in Oregon?
When the tsunami hits the Oregon coast, it will be, at its lowest reaches, twenty feet high, and moving somewhere between ten and twenty miles per hour.
What is the area that will be completely underwater when the tsunami arrives?
That region is known as the tsunami-inundation zone, which is exactly what it sounds like: the area that, according to seismologists, will be completely underwater when the wave arrives.
How many square miles of the West Coast will be affected by a quake?
When that fault line next unleashes a full-scale quake, it will affect some hundred and forty thousand square miles of the West Coast.
How many feet can a rogue wave sink?
A rogue wave — one that is more than twice the height of those around it — can sink a nine-hundred-foot ship.
What are the secondary disasters that an earthquake can trigger?
In that condition, they will need to escape damaged or destroyed buildings and make their way to higher ground, despite crumpled roads, collapsed bridges, downed electrical lines, and all the secondary disasters an earthquake can trigger, from power outages and fires to landslides and liquefaction.
Is Oregon going to have a tsunami?
An option is simply to start moving citizens and infrastructure out of harm’s way. Because, in the next fifty years, Oregon faces a one-in-three chance of experiencing a tsunami comparable to those that recently devastated Japan and Indonesia. But Oregon’s message to its residents seems clear: we are turning our backs on danger;
What are the tsunami maps in California?
California Tsunami Hazard Area Maps and data are prepared to assist cities and counties in identifying their tsunami hazard for tsunami response planning. The maps and data are compiled with the best currently available scientific information and represent areas that could be exposed to tsunami hazards during a tsunami event. They are primarily based on inundation limits corresponding to a 975-year average return period tsunami event model. These limits have been extended to reflect potential local tsunami sources not considered in probabilistic analysis and are also modified to reflect the practical need to define limits that coincide with geographic features or city streets. The following documents explain the methodology for determining inundation and evacuation areas.
What are tsunami maps?
California Official Tsunami Hazard Area Maps are prepared to assist cities and counties in identifying their tsunami hazard. They are intended for local jurisdictional, coastal evacuation planning uses only. They are not legal documents and do not meet disclosure requirements for real estate transactions nor for any other regulatory purpose. The California Governor's Office of Emergency Services (Cal OES), the University of Southern California (USC), AECOM Technical Services, and the California Geological Survey (CGS) make no representation or warranties regarding the accuracy of the maps nor the data from which the maps were derived. The State of California shall not be liable under any circumstances for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages with respect to any claim by any user or any third party on account of or arising from the use of these maps.
Is California tsunami data updated in 2021?
These are statewide data sets; however, the 2021 data cover only the counties updated in 2021. Similarly, the 2009 data cover only the counties not updated in 2021. Therefore, to get the most complete tsunami data coverage for California's coast, you must utilize the 2021 and 2009 data together.
Does California have tsunami maps?
Tsunami Hazard Area Maps for California cover much of the state's populated coastal areas and will one day cover the entire California coast. Explore your area of interest in the map—zoom in, pan, and click (or tap) a coastal location to invoke a pop-up window that provides additional information and links. NOTE: there may be many results in the pop-up, depending on where you click. We recommend you zoom in to a specific area of interest before using the pop-up feature.
