What’s the fertilizer manufacturing process?
- For example, if you want to make organic fertilizer, you should ferment the raw materials for several weeks. With a compost turner or fermentation tank, the fermentation period will be shorter. ...
- And then you should pulverize them into powders, and mix them. ...
- If there are some unqualified fertilizer pellets, you should select them out. ...
- Finally, it’s packing time. ...
Full Answer
How to make your own natural fertilizer?
Simple Weed Fertilizer Recipe
- Stuff a bucket about half-full with roughly chopped leaves, stems, and flowers of weeds or pruned herbs. ...
- Fill with water. ...
- Set aside to steep for a day in the sun. ...
- Strain out the herbs or weeds and fill up a spray bottle (or watering can) with the concoction.
- Pour it on the soil or fill a spray bottle to spray the leaves of your plants as a foliar feed.
What fertilizer has the highest nitrogen content?
- Ammonium Sulfate 21-0-0. -1st Commercial fertilizer produced.
- Calcium Cyanamide 22-0-0. -Discovered in 1909.
- Anhydrous Ammonium 82-0-0. Has the highest N content at 82%
- Aqua Ammonium 20-0-0.
- Ammonium Nitrate 34-0-0.
- Ammonium Nitrate-Lime, ANL 26-0-0.
- Calcium Nitrate 15.5-0-0.
- Sodium Nitrate 16-0-0.
What is a good homemade plant fertilizer?
Your garden will thrive with these DIY versions made from items around your pantry and backyard!
- Grass Clippings. If you have an organic lawn, make sure to collect your grass clippings to use on your gardens. ...
- Weeds. Just like grass clippings, many of the weeds that you’ll find in your gardens are very high in nitrogen and will make an excellent fertilizer.
- Kitchen Scraps. ...
- Manure. ...
- Tree Leaves. ...
- Coffee Grounds. ...
- Eggshells. ...
- Banana Peels. ...
What is the best high nitrogen fertilizer?
What Fertilizer Is High In Nitrogen?
- Sodium Nitrate. Sodium nitrate is a white solid that is water soluble. ...
- Feather Meal. Feather meal is made from poultry feathers. ...
- Blood Meal. Blood meal is a powder made from the dried blood of animals (often cattle or hogs). ...
- Hoof & Horn Meal. ...
- Hair. ...
- Fish Meal. ...
- Crab Meal. ...
- Animal Tankage. ...
- Bat Guano. ...
- Soybean Meal. ...

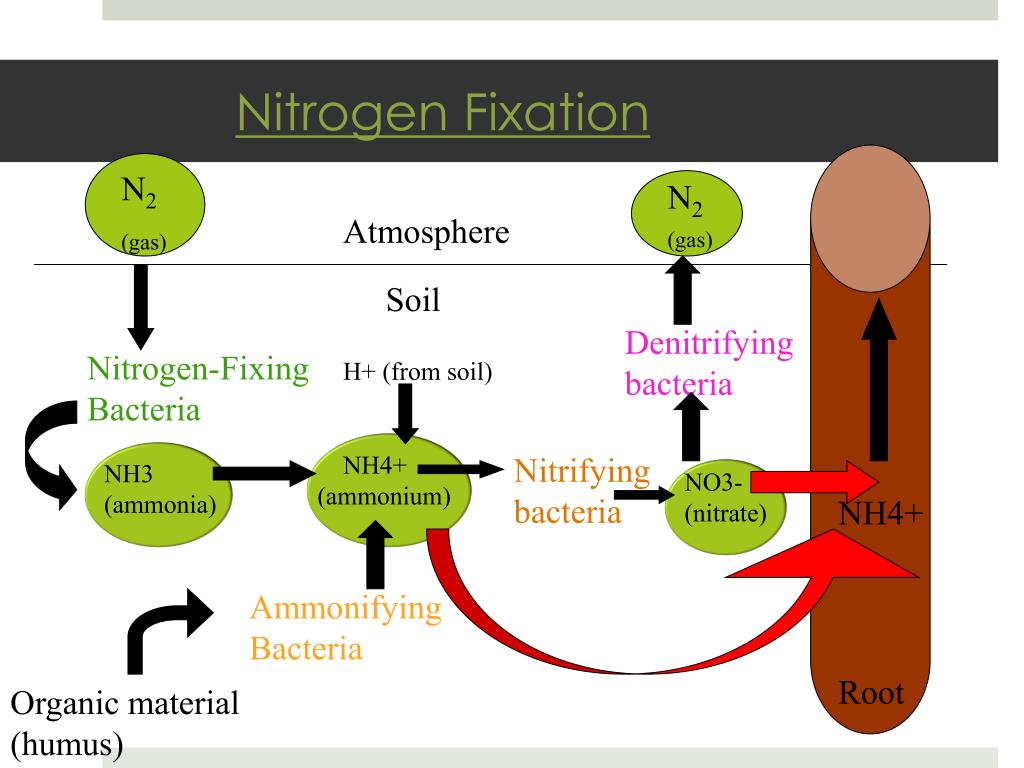
How is nitrogen fertilizer made?
For nitrogen-based fertilizers, the largest product group, the process starts by mixing nitrogen from the air with hydrogen from natural gas at high temperature and pressure to create ammonia. Approximately 60% of the natural gas is used as raw material, with the remainder employed to power the synthesis process.
What is phosphate fertilizer?
Phosphate rock is primarily treated with sulphuric acid to produce phosphoric acid, which is either concentrated or mixed with ammonia to make a range of phosphate (P2O5) fertilizers.
What are the three essential nutrients in fertilizer?
Each year, the European fertilizer industry transforms millions of tons of air, natural gas and mined ores into products based on the three essential plant nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
What is the third major plant and crop nutrient?
POTASSIUM (K) Potassium is the third major plant and crop nutrient. Potassium-based fertilizers are also produced from mined ores. Several chemical processes can be used to convert the potash rock into plant food, including potassium chloride, sulphate and nitrate.
Organic fertilizer production method
The production of organic fertilizer is mainly composed of composting and granulation. Composting is the most important step in the production of organic fertilizer. The basic process of composting fermentation is usually divided into two stages: the first fermentation and the second fermentation.
Compound fertilizer production method
Granulation is the most important step in the production of compound fertilizer. First, it goes through raw material batching, raw material stirring, raw material granulation, granule drying, granule cooling, granule grading, finished product coating, and finally finished product packaging.
The first stage heating stage
After the compost raw materials are pre-mixed and the water is adjusted for inoculation, the temperature of the heap gradually rises from the ambient temperature to about 45 °C. At this time, mesophilic bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes begin to decompose the substrates in the compost, such as starch, sugar, etc.
Second stage high temperature stage
The temperature of the compost gradually rises to above 45 °C and enters the high-temperature period. At this time, the thermophilic bacteria begin to strongly decompose the complex organic matter in the compost, such as protein, hemicellulose, cellulose, lignin, and so on. When the temperature is above 50 °C, the microorganisms are very active.
The third stage cooling stage
The high temperature stage will inevitably lead to the death of microorganisms and the reduction of their activities. The explanation of the organic matter is that the heat gradually decreases, and mesophilic microorganisms gradually begin to dominate.
How is fertilizer made?
7 To produce fertilizer in the most usable form, each of the different compounds, ammonium nitrate, potassium chloride, ammonium phosphate, and triple superphosphate are granulated and blended together. One method of granulation involves putting the solid materials into a rotating drum which has an inclined axis. As the drum rotates, pieces of the solid fertilizer take on small spherical shapes. They are passed through a screen that separates out adequately sized particles. A coating of inert dust is then applied to the particles, keeping each one discrete and inhibiting moisture retention. Finally, the particles are dried, completing the granulation process.
What are synthetic fertilizers made of?
Modern synthetic fertilizers are composed mainly of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium compounds with secondary nutrients added . The use of synthetic fertilizers has significantly improved the quality and quantity of the food available today, although their long-term use is debated by environmentalists.
What is the nitrogen component in fertilizer?
Nitrogen fertilizer component. 1 Ammonia is one nitrogen fertilizer component that can be synthesized from in-expensive raw materials. Since nitrogen makes up a significant portion of the earth's atmosphere, a process was developed to produce ammonia from air.
How is nitric acid made?
Nitric acid is produced by first mixing ammonia and air in a tank. In the presence of a catalyst, a reaction occurs which converts the ammonia to nitric oxide. The nitric oxide is further reacted in the presence of water to produce nitric acid. 3 Nitric acid and ammonia are used to make ammonium nitrate.
What is fertilizer used for?
Fertilizer is a substance added to soil to improve plants' growth and yield. First used by ancient farmers, fertilizer technology developed significantly as the chemical needs of growing plants were discovered. Modern synthetic fertilizers are composed mainly of nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium compounds with secondary nutrients added.
How is ammonia stored?
Any impurities are removed from the ammonia, and it is stored in tanks until it is further processed. 2 While ammonia itself is sometimes used as a fertilizer, it is often converted to other substances for ease of handling. Nitric acid is produced by first mixing ammonia and air in a tank.
Why are manures not used in fertilizer?
The first fertilizers were manures, however, they are not utilized on a large scale because their handling has proven too expensive. When technology improves and costs are reduced, this material will be a viable new fertilizer. — Perry Romanowski.

Background
History
- The process of adding substances to soil to improve its growing capacity was developed in the early days of agriculture. Ancient farmers knew that the first yields on a plot of land were much better than those of subsequent years. This caused them to move to new, uncultivated areas, which again showed the same pattern of reduced yields over time. Eventually it was discovered t…
Raw Materials
- The fertilizers outlined here are compound fertilizers composed of primary fertilizers and secondary nutrients. These represent only one type of fertilizer, and other single nutrient types are also made. The raw materials, in solid form, can be supplied to fertilizer manufacturers in bulk quantities of thousands of tons, drum quantities, or in meta...
The Manufacturing Process
- Fully integrated factories have been designed to produce compound fertilizers. Depending on the actual composition of the end product, the production process will differ from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Quality Control
- To ensure the quality of the fertilizer that is produced, manufacturers monitor the product at each stage of production. The raw materials and the finished products are all subjected to a battery of physical and chemical tests to show that they meet the specifications previously developed. Some of the characteristics that are tested include pH, appearance, density, and melting point. S…
Byproducts/Waste
- A relatively small amount of the nitrogen contained in fertilizers applied to the soil is actually assimilated into the plants. Much is washed into surrounding bodies of water or filters into the groundwater. This has added significant amounts of nitrates to the water that is consumed by the public. Some medical studies have suggested that certain disorders of the urinary and kidney sy…
The Future
- Fertilizer research is currently focusing on reducing the harnful environmental impacts of fertilizer use and finding new, less expensive sources of fertilizers. Such things that are being investigated to make fertilizers more environmentally friendly are improved methods of application, supplying fertilizer in a form which is less susceptible to runoff, and making more concentrated mixtures. …
Overview
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and P…
History
Management of soil fertility has preoccupied farmers for thousands of years. Egyptians, Romans, Babylonians, and early Germans are all recorded as using minerals or manure to enhance the productivity of their farms. The science of plant nutrition started well before the work of German chemist Justus von Liebig although his name is most mentioned. Nicolas Théodore de Saussure and scientific colleagues at the time were quick to disprove the simplifications of Justus von Lie…
Mechanism
Fertilizers enhance the growth of plants. This goal is met in two ways, the traditional one being additives that provide nutrients. The second mode by which some fertilizers act is to enhance the effectiveness of the soil by modifying its water retention and aeration. This article, like many on fertilizers, emphasises the nutritional aspect. Fertilizers typically provide, in varying proportions:
• three main macronutrients:
Classification
Fertilizers are classified in several ways. They are classified according to whether they provide a single nutrient (e.g., K, P, or N), in which case they are classified as "straight fertilizers." "Multinutrient fertilizers" (or "complex fertilizers") provide two or more nutrients, for example N and P. Fertilizers are also sometimes classified as inorganic (the topic of most of this article) versus organic. Inorganic fertilizers exclude carbon-containing materials except ureas. Organic fertilizer…
Environment
Synthetic fertilizer used in agriculture has wide-reaching environmental consequences. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land, production of these fertilizers and associated land use practices are drivers of global warming. The use of fertilizer has also led to a number of direct environmental consequences: agricultural runoff which leads to downstream effects like ocean dead zones and waterway conta…
Production
The production of synthetic, or inorganic, fertilizers requires prepared chemicals, whereas organic fertilizers are derived from the organic processes of plants and animals in biological processes using biochemicals.
Nitrogen fertilizers are made from ammonia (NH3) produced by the Haber-Bosch process. In this energy-intensive process, natural gas (CH4) usually supplies the hydrogen, and the nitrogen (N2) is derived …
Application
Fertilizers are commonly used for growing all crops, with application rates depending on the soil fertility, usually as measured by a soil test and according to the particular crop. Legumes, for example, fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and generally do not require nitrogen fertilizer.
Fertilizers are applied to crops both as solids and as liquid. About 90% of fertilizers are applied as solids. The most widely used solid inorganic fertilizers are urea, diammonium phosphate and pot…
Statistics
Recently nitrogen fertilizers have plateaued in most developed countries. China although has become the largest producer and consumer of nitrogen fertilizers. Africa has little reliance on nitrogen fertilizers. Agricultural and chemical minerals are very important in industrial use of fertilizers, which is valued at approximately $200 billion. Nitrogen has a significant impact in the global mineral use, followed by potash and phosphate. The production of nitrogen has drasticall…