
What is the temperature range in the inner core?
The temperature of the inner core is estimated to be between 3,000 and 5,000 Kelvins (4,940 to 8,540 degrees Fahrenheit). The high temperature comes from three main sources. There is residual heat left from the Earth's formation, and heat is generated by gravitational forces from the sun and moon as they tug and pull on the inner core.
How hot is the inner core of Earth in Fahrenheit?
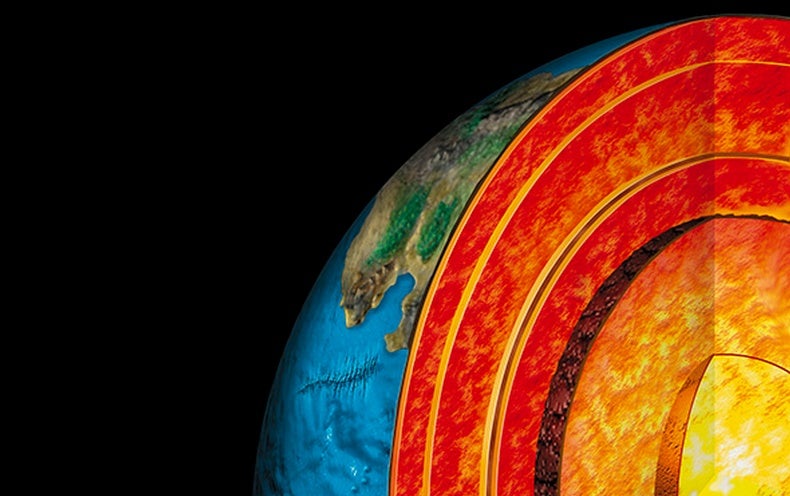
The inner core is a hot, dense ball of (mostly) iron. It has a radius of about 1,220 kilometers (758 miles). Temperature in the inner core is about 5,200° Celsius (9,392° Fahrenheit).The pressure is nearly 3.6 million atmosphere (atm).
How hot is the outer core in Fahrenheit?
The outer core, about 2,200 kilometers (1,367 miles) thick, is mostly composed of liquid iron and nickel. The NiFe alloy of the outer core is very hot, between 4,500° and 5,500° Celsius (8,132° and 9,932° Fahrenheit). What is the thickest layer of Earth?
Is the inner core hotter than the Sun?
The temperatures in the inner core are as hot as the surface of the sun, about 5505 °C. Earth’s inner core is 1,230 to 1,530 km thick. Why is the inner core made of iron? The iron-nickel alloy that composes the inner core is heavier than other elements in the mantle and outer core, causing it to sink to the center of earth. B.
How hot is the core?
How hot is the outer core?
What was the melting point of iron?
What material moved quickly during the iron catastrophe?
What is the core of Earth?
Where does the inner core grow?
Which hemispheres are divided into the inner core?
See 4 more
About this website
5 Facts About the Earth's Inner Core | Sciencing
The Earth's inner core is surprisingly large, measuring 2,440 km (1,516 miles) across. It makes up 19 percent of the Earth's total volume, which makes it just 30 percent smaller than the moon.
How much heat does the Earth get from the core?
Additionally, descent of the dense iron-rich material that makes up the core of the planet to the center would produce heating on the order of 2,000 kelvins (about 3,000 degrees F). The magnitude of the third main source of heat--radioactive heating--is uncertain. The precise abundances of radioactive elements (primarily potassium, uranium and thorium) are poorly known in the deep earth.
How deep is the Earth's core?
The earth's core is divided into two separate regions: the liquid outer core and the solid inner core, with the transition between the two lying at a depth of 5,156 kilometers (3,204 miles). Therefore, If we can measure the melting temperature of iron at the extreme pressure of the boundary between the inner and outer cores, ...
Why is the earth's core so hot? And how do scientists measure its temperature?
Quentin Williams, associate professor of earth sciences at the University of California at Santa Cruz offers this explanation
What is the melting temperature of iron?
Those experiments provide a stiff challenge, but our estimates for the melting temperature of iron at these conditions range from about 4,500 to 7,500 kelvins (about 7,600 to 13,000 degrees F). As the outer core is fluid and presumably convecting (and with an additional correction for the presence of impurities in the outer core), we can extrapolate this range of temperatures to a temperature at the base of Earth's mantle (the top of the outer core) of roughly 3,500 to 5,500 kelvins (5,800 to 9,400 degrees F) at the base of the earth's mantle.
How does heat move out of the Earth?
It takes a rather long time for heat to move out of the earth. This occurs through both "convective" transport of heat within the earth's liquid outer core and solid mantle and slower "conductive" transport of heat through nonconvecting boundary layers , such as the earth's plates at the surface. As a result, much of the planet's primordial heat, ...
How deep is the center of the Earth?
The center of the earth lies 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles) beneath our feet, but the deepest that it has ever been possible to drill to make direct measurements of temperature (or other physical quantities) is just about 10 kilometers (six miles). Sign up for Scientific American ’s free newsletters. Ironically, the core of the earth is by far less ...
What are the main sources of heat?
Advertisement. There are three main sources of heat in the deep earth: (1) heat from when the planet formed and accreted, which has not yet been lost; (2) frictional heating, caused by denser core material sinking to the center of the planet; and (3) heat from the decay of radioactive elements.
How hot is the core?
In general, temperatures range from about 4,400° Celsius (7,952° Fahrenheit) to about 6,000° Celsius (10,800° Fahrenheit).
How hot is the outer core?
The NiFe alloy of the outer core is very hot, between 4,500° and 5,500° Celsius (8,132° and 9,932° Fahrenheit).
What was the melting point of iron?
Eventually, after about 500 million years, our young planet’s temperature heated to the melting point of iron—about 1,538° Celsius (2,800° Fahrenheit). This pivotal moment in Earth’s history is called the iron catastrophe. The iron catastrophe allowed greater, more rapid movement of Earth’s molten, rocky material.
What material moved quickly during the iron catastrophe?
The iron catastrophe allowed greater, more rapid movement of Earth’s molten, rocky material. Relatively buoyant material, such as silicate s, water, and even air, stayed close to the planet’s exterior. These materials became the early mantle and crust. Droplets of iron, nickel, and other heavy metal s gravitate d to the center of Earth, becoming the early core. This important process is called planetary differentiation.
What is the core of Earth?
core. Earth’s core is the very hot, very dense center of our planet. The ball-shaped core lies beneath the cool, brittle crust and the mostly-solid mantle. The core is found about 2,900 kilometers (1,802 miles) below Earth’s surface, and has a radius of about 3,485 kilometers (2,165 miles).
Where does the inner core grow?
Growth is more concentrated around subduction zone s—regions where tectonic plate s are slipping from the lithosphere into the mantle, thousands of kilometers above the core.
Which hemispheres are divided into the inner core?
Just like the lithosphere, the inner core is divided into eastern and western hemisphere s. These hemispheres don’t melt evenly, and have distinct crystalline structures.