
Factors and forces in the formation of coastal features
- Waves. The most obvious of all coastal processes is the continual motion of the waves moving toward the beach.
- Longshore currents. Waves usually approach the coast at some acute angle rather than exactly parallel to it. ...
- Rip currents. Learn how to escape a rip current. Displayed by permission of The Regents of the University of California.
How are coastlines formed?
The way coasts are formed depends a lot on what kind of material is in the land and water. The harder the material in the land, the harder it is to erode.
What are coastal landforms?
... (Show more) coastal landforms, any of the relief features present along any coast, the result of a combination of processes, sediments, and the geology of the coast itself.
How does the coast change over time?
Waves, tides, and currents help create coastlines. When waves crash onto shore, they wear away at, or erode, the land. But they also leave behind little parts of the sea, such as shells, sand dollars, seaweeds, and hermit crabs. Sometimes these objects end up as more permanent parts of the coastline. Coastal changes can take hundreds of years.
How were the oceans formed?
Scientists believe that the formation of the oceans did not occur until long after the earth was originally formed. On top of this, they do not believe that they formed all at once; rather, it took millions of years. Researchers think that the oceans formed as a result of a process known as “degassing.”
How are coasts formed ks2?
When the sea erodes the cliffs, large rocks fall away and into the sea. These rocks are tossed about by the action of the sea and they are eroded into smaller and smaller pebbles. The pebbles are eventually ground down into the tiny gains of sand that form a beach.
What causes coastal landforms?
The landforms that develop and persist along the coast are the result of a combination of processes acting upon the sediments and rocks present in the coastal zone. The most prominent of these processes involves waves and the currents that they generate, along with tides.
How coastal landforms are formed by deposition?
What landforms are created by deposition? Materials carried by the waves bump into each other and so are smoothed and broken down into smaller particles. This is the process by which the coast is worn down by material carried by the waves. Waves throw these particles against the rock, sometimes at high velocity.
How are coastal landforms formed by erosion?
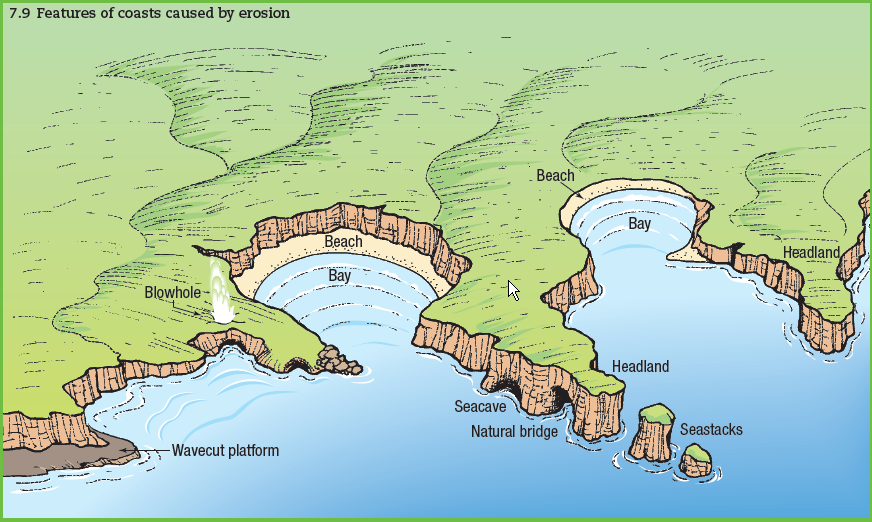
When the softer rock is eroded inwards, the hard rock sticks out into the sea, forming a headland . Erosional features such as wave-cut platforms and cliffs can be found on headlands, since they are more open to the waves. Bays are more sheltered with constructive waves which deposit sediment to form a beach.
How much of the ocean is coast?
Coasts make up a total of 7 percent of the Earth's oceans, with 95 percent of the world's marine productivity of aquaculture and the sustainability of marine habitats. Because of their importance to humanity, there are some coasts found in marine protected areas .
What is a flat coast?
A flat coast is one where the land gradually descends into the sea. A graded shoreline is one where wind and water action has produced a flat and straight coastline.
What are the environmental impacts of the coast?
principal among which are sea-level rise, and associated issues like coastal erosion and saltwater intrusion, and pollution, such as oil spills or marine debris contaminating coasts with plastic and other trash.
What is the name of the area where land meets sea?
Southeast coast of Greenland. The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the sea or ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Earth has around 620,000 kilometres (390,000 mi) of coastline. Because coasts are constantly changing, ...
Why are caves made in the sea?
Sea caves are made when certain rock beds are more susceptible to erosion than the surrounding rock beds because of different areas of weakness. These areas are eroded at a faster pace creating a hole or crevice that, through time, by means of wave action and erosion, becomes a cave.
What are the animals that live on the coast?
Animals that live in coastal areas include puffins, sea turtles and rockhopper penguins, among many others. Sea snails and various kinds of barnacles live on the coast and scavenge on food deposited by the sea. Most coastal animals are used to humans in developed areas, such as dolphins and seagulls who eat food thrown for them by tourists. Since the coastal areas are all part of the littoral zone, there is a profusion of marine life found just off-coast, including sessile animals such as corals and sea anemones .
What is coastal zone?
The term coastal zone is used to refer to a region where interactions of sea and land processes occur. Both the terms coast and coastal are often used to describe a geographic location or region located on a coastline (e.g., New Zealand's West Coast, or the East, West, and Gulf Coast of the United States .)
What are the factors that contribute to the formation of coastal features?
The most prominent of these processes involves waves and the currents that they generate, along with tides.
What are coastal landforms?
Coastal landforms, any of the relief features present along any coast, the result of a combination of processes, sediments, and the geology of the coast itself. The coastal environment of the world is made up of a wide variety of landforms manifested in a spectrum of sizes and shapes ranging from gently sloping beaches to high cliffs, ...
How fast do longshore currents move?
Under rather quiescent conditions, longshore currents move only about 10–30 centimetres per second; however, under stormy conditions they may exceed one metre per second. The combination of waves and longshore current acts to transport large quantities of sediment along the shallow zone adjacent to the shoreline.
How do waves break up bedrock?
Waves erode the bedrock along the coast largely by abrasion. The suspended sediment particles in waves, especially pebbles and larger rock debris, have much the same effect on a surface as sandpaper does. Waves have considerable force and so may break up bedrock simply by impact.
What is the term for the current that extends from the shoreline out through the zone of breaking waves?
Such a current is called a longshore current , and it extends from the shoreline out through the zone of breaking waves.
How do waves affect the ocean?
Waves interact with the ocean bottom as they travel into shallow water; as a result, they cause sediment to become temporarily suspended and available for movement by coastal currents. The larger the wave, the deeper the water in which this process takes place and the larger the particle that can be moved.
How do waves move?
The most obvious of all coastal processes is the continual motion of the waves moving toward the beach. Waves vary considerably in size over time at any given location and also vary markedly from place to place. Waves interact with the ocean bottom as they travel into shallow water; as a result, they cause sediment to become temporarily suspended and available for movement by coastal currents. The larger the wave, the deeper the water in which this process takes place and the larger the particle that can be moved. Even small waves that are only a few tens of centimetres high can pick up sand as they reach the shore. Larger waves can move cobbles and rock material as large as boulders.
What are the forces that move the Earth's crust?
Glaciers, rivers, and streams deliver a steady supply of building material for nature's unending job. And not to be outdone, the tectonic forces that move giant pieces of Earth's crust will periodically bump the bedrock and squeeze fresh lava out.
What is the name of the wave that carries sand and gravel to the beach?
Built up by winds far out at sea, they unleash their energy and go to work when they break on the shore. The upward rush of water, called swash, delivers sand and gravel to the beach. On the return, backwash carries sand and gravel out to sea.
What is the line where land meets water?
Coastlines. The line where land meets water is constantly changing and reshaping. The coastline, that narrow strip of land that borders the sea along a continent or an island, is an ideal place to see a constantly-changing landscape. The nonstop wave action there means nothing ever stays the same.
What happens when waves chip away rocks?
Along much of the coastline, pounding waves slowly chip away the base of cliffs, forcing chunks of rock to crumble and slide into the sea. Where a band of solid rock gives way, waves claw at weaker clays behind to sculpt a cove or a bay.
Why do storm waves break rocks?
As the waves retreats, the pressure is released with explosive force and the rocks will weaken and will be shattered by the storm waves.
What are mangrove swamps?
Mangrove swamps are the areas of vegetation found along sheltered tropical coastlines and estuaries between 32 °N and 38 °S where there is a large area between high and low watermark. They are made up of different species of evergreen mangrove trees and other plants. Mangroves need to live in salty water as they are halophytes. They only grow in areas where the temperature remains above 20 °C and the seasonal temperature range should not exceed 5 °C. The areas where they grow should be calm with no strong waves or tidal currents. Mangrove trees are able to withstand being covered twice a day by saltwater. They have specially adapted aerial and salt filtering roots and salt excreting leaves that enable them to occupy the wetlands where other plants cannot survive. They prop the tree up with their prop roots and take in oxygen at low tide with their aerial roots. Mangroves are the home to a diverse number of species including fish, birds, frogs, snakes, insects and crocodiles. Mammals also live in these areas, ranging from small animals like swamp rats and monkeys to large carnivores like tigers. (Mangroves protect coastlines from erosion by acting as a natural barrier and flood defence).
Do mangroves need clam water?
Mangrove needs clam water and can not grow in areas of strong tidal currents. Ideal location are tropical salt marshes and sheltered bays. Develop Aerial and Prop roots to support growth in muddy-tidal water and to take oxygen directly from the air at low tide. Have unique ecosystem with diverse number of species.
Where does the net movement of sand along both coasts of the United States occur?
The net movement of sand along both coasts of the United States is to the south. The explanation is that most of North America's big waves come from the North Pacific on the West Coast or from the North Atlantic on the East Coast. So, swells coming from north hit the beach and push the sand from north to south.
Why does sand move south along the ocean?
Then, it ends up moving south along the beach because of the longshore drift. When the sand reaches the head of one of these submarine canyons, it ends up draining down the canyon out onto the ocean floor.
How does sand move from north to south?
So, swells coming from north hit the beach and push the sand from north to south. In Southern California, the sand moves south along the coast by longshore drift. However, it doesn't just travel south along the coast forever. Here and there, it leaves the beaches where it drains off down areas called submarine canyons.
How does sand move on a beach?
The Longshore Drift. Now that the sand has descended from the mountains, it's time to understand how it moves up, down, and along a beach. Rather than just moving toward the beach and away from the beach according to the size of the waves, sand also moves along the beach, parallel to the beach. When wind and waves are hitting ...
Why is the age of sand important?
First, the age of the sand is important because older quartz sand grains have had more time to roll and slide around, making them lighter in color, " notes the coastal geomorphologist. "The second reason is that there are other types of minerals found on beaches.
What is sand made of?
On most beaches, sand is made of quartz minerals. "There's a good reason for this," note Rob Brander, author of "Dr. Rip's Essential Beach Book.". "The most common type of rock on the Earth's surface is granite, which just happens to contain a lot of minerals, including quartz.". "When granite rocks are broken down and eroded, ...
What colors are in beach sand?
Nevertheless, the palette of colors of beach sand is vast and sometimes surprising. They range from shades of grey and brown to red, black, and even green.
What are beaches made of?
Beaches are composed of deposited sediments including sand, rocks, shells, algae, or pebbles. A beach is a geologic formation that is located along a large body of water, including lakes, rivers, and oceans. Beaches are characterized by the presence of tiny pieces of organic sediment. The sediments may be composed of sand, rock, shell, algae, ...
What are the characteristics of a beach?
Characteristics of Beaches. Beaches are typically divided into 4 zones (known as the beach profile): swash, beach face, wrack line, and berm. The particles found within each of these zones are different. For example, finer sediment is found closer to the water. This is partially because the moving water constantly breaks down ...
How does urban development affect the amount of erodible land found near bodies of water?
Urban development, dam projects, and rerouting rivers may reduce the amount of erodible land found near bodies of water. As these human activities progress, the sediment found suspended in the waves is reduced. With less sediment in the water, fewer particles are deposited along the beach, resulting in recession.
How does human activity contribute to beach recession?
This means that waves require access to material that can be eroded and turned into sediment that can later be deposited along coastlines.
Why are sandy beaches different from rocky beaches?
Sandy beaches are often characterized by their slowly sloping profile, whereas rocky beaches tend to exhibit more extreme slope angles. This difference in slope is because of the difference in particle size. The larger particles on rocky beaches, for example, cause the waves to lose their power more quickly.
Why is sediment found closer to the water?
For example, finer sediment is found closer to the water. This is partially because the moving water constantly breaks down the particles located here. As the beach moves further inland, the particles along its surface grow in size.
What are the two types of waves that prevent erosion?
Constructive waves, which are those that allow the water to recede and the beach particles to stop moving between waves, result in compacted sediment. This firm beach surface prevents future erosion. Destructive waves, which are fast forming and do not allow the water to recede between waves, result in a near-constant state ...
How long did it take for the oceans to form?
On top of this, they do not believe that they formed all at once; rather, it took millions of years.
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by oceans?
In fact, oceans cover 71% of the earth’s surface, and with global warming causing the ocean to rise, it could cover even more in future centuries! We know the ocean is big and mysterious, and many of us love it for that!
What is the ocean floor?
The continental shelf is the structure of the ocean that surrounds landmasses (the continents). Sometimes the shelf is very small, and sometimes it extends for miles.
What is the name of the meteorite that holds water?
Another theory that some researchers have is that carbonaceous chondrites, which is essentially a meteorite that holds a lot of water, kept pelting into the surface of the earth after it cooled down. This distributed water in large amounts to the earth, which eventually made up the oceans.
Why is there no liquid water on Earth?
When the earth was first formed, its temperature was well above the boiling point for water. Because of this, there was no liquid water on earth. Instead, all water was in the form of a gas. A side note: this water was believed to be squeezed out of the molten minerals that would someday form solid earth! Anyway, this gas stayed in the earth’s ...
Why are trenches important to the ocean floor?
Trenches are also an ocean floor attraction. The shape of the ocean floor is known as bathymetry, which is caused by plate tectonic shifts . As the plates of the earth move , it creates the features of the ocean floor. The actual “holes” that make up the ocean are believed to just be how the earth’s crust formed.
Is the ocean flat or flat?
The plains are not necessarily flat, however. They may have hills and valleys, just like land masses! The ocean also has mountain ranges, such as the mid-ocean ridge, the longest mountain range on earth. Trenches are also an ocean floor attraction.

Overview
In geology
The identification of bodies of rock formed from sediments deposited in shoreline and nearshore environments (shoreline and nearshore facies) is extremely important to geologists. These provide vital clues for reconstructing the geography of ancient continents (paleogeography). The locations of these beds show the extent of ancient seas at particular points in geological time, and provide clues to the magnitudes of tides in the distant past.
Size
The Earth has around 620,000 kilometres (390,000 mi) of coastline. Coastal habitats, which extend to the margins of the continental shelves, make up about 7 percent of the Earth's oceans, but at least 85% of commercially harvested fish depend on coastal environments during at least part of their life cycle. As of October 2010, about 2.86% of exclusive economic zones were part of marine pr…
Formation
Tides often determine the range over which sediment is deposited or eroded. Areas with high tidal ranges allow waves to reach farther up the shore, and areas with lower tidal ranges produce deposition at a smaller elevation interval. The tidal range is influenced by the size and shape of the coastline. Tides do not typically cause erosion by themselves; however, tidal bores can erode as the waves surge up the river estuaries from the ocean.
Importance for humans and ecosystems
More and more of the world's people live in coastal regions. According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 150 km (93 mi) of the sea. Many major cities are on or near good harbors and have port facilities. Some landlocked places have achieved port status by building canals.
Nations defend their coasts against military invaders, smugglers and illegal mi…
More and more of the world's people live in coastal regions. According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 150 km (93 mi) of the sea. Many major cities are on or near good harbors and have port facilities. Some landlocked places have achieved port status by building canals.
Nations defend their coasts against military invaders, smugglers and illegal mi…
Types
According to one principle of classification, an emergent coastline is a coastline that has experienced a fall in sea level, because of either a global sea-level change, or local uplift. Emergent coastlines are identifiable by the coastal landforms, which are above the high tide mark, such as raised beaches. In contrast, a submergent coastline is one where the sea level has risen, due to a global sea-level change, local subsidence, or isostatic rebound. Submergent coastlines a…
Landforms
The following articles describe some coastal landforms:
• Bay
• Headland
• Cove
• Peninsula
Wildlife
Larger animals that live in coastal areas include puffins, sea turtles and rockhopper penguins, among many others. Sea snails and various kinds of barnacles live on rocky coasts and scavenge on food deposited by the sea. Some coastal animals are used to humans in developed areas, such as dolphins and seagulls who eat food thrown for them by tourists. Since the coastal areas …