What are many amino acids joined by peptide bonds?
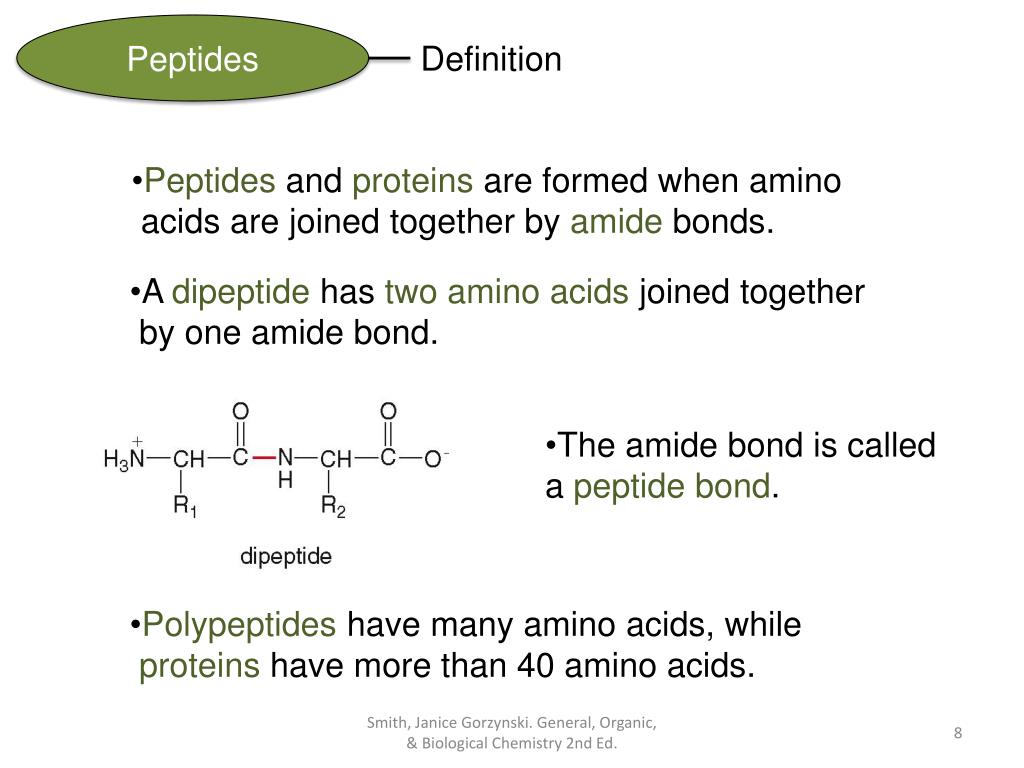
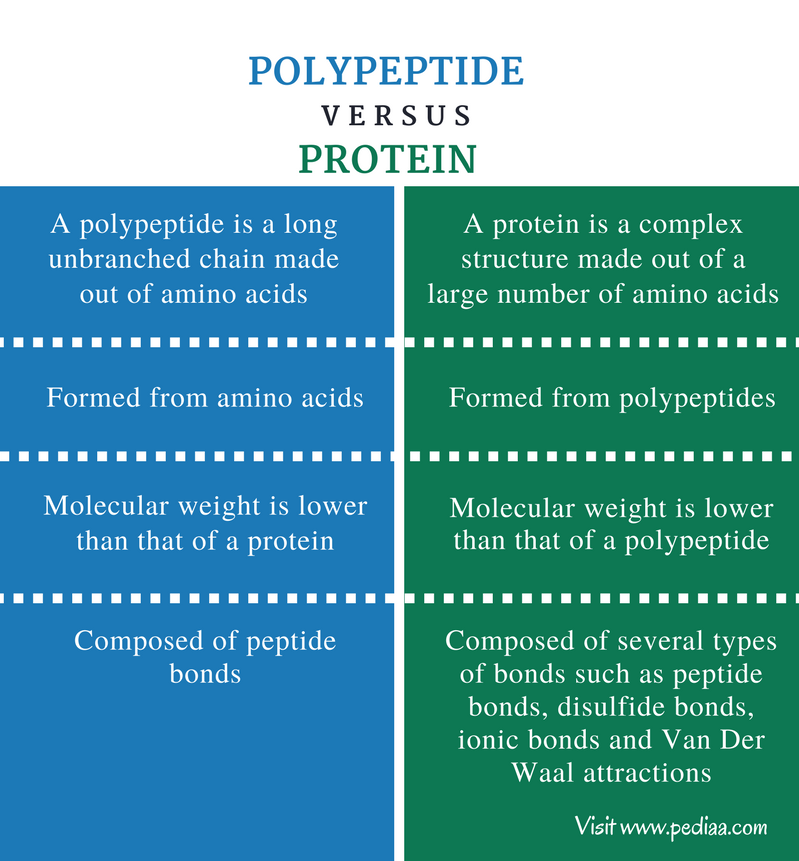
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. A protein contains one or more polypeptides. Therefore, proteins are long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.3 jan. 2021
When are two amino acids linked by the peptide bond?
The peptide bond is formed as a result of a condensation reaction between two amino acids when the carboxyl group of one reacts with the amino group of the other. The elimination of a water molecule occurs. This reaction also called dehydration leads to the formation of an amide.
What kind of bond connects two amino acids?
Two amino acids will be joined together by a PEPTIDE bond to form a molecule called a dipeptide. Each amino acid has one Carboxyl group (-COOH), one amine group (-NH2), a hydrogen atom and a variant (R) group attached to a main carbon atom called the alpha carbon.
What bonds are amino acids connected together by?
- The primary structure of a protein is its arrangement of amino acids.
- When it is the secondary structure, then it is the shape of the peptide chain.
- When a protein possesses several polypeptide chains, then the manner in which they are sequenced is called the quaternary structure.
How do peptide bonds form?
As mentioned earlier, the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids brings about the formation of a molecule of water. As a carboxyl group loses its hydroxyl (OH) and an amine group loses its hydrogen (H) atom, they combine to form one molecule of water for each peptide bond. This process is reversible; peptide bonds can be broken by the addition of a water molecule. The water molecule restores the hydroxyl (OH) to the carboxyl group and a hydrogen atom to the amine group, thus giving rise to two separate individual amino acids per peptide bond and releasing energy. This process is referred to as a hydrolysis reaction.
How do amino acids bind?
Two amino acids bind via a peptide bond. The formation of a peptide bond occurs between a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amine group of the other.
What is a Polymer of Amino Acids?
As explained earlier, a protein is made of a sequence of amino acids linked together via peptide bonds in a process titled polymerization. The order and sequence of amino acids are specific to each protein, which gives rise to the protein's primary structure.
What are proteins made of?
Proteins, which are vital to the functionality of all living organisms, are made up of multiple amino acid monomers linked together via peptide bonds. Peptide bonds are chemical covalent bonds linking one amino acid to the other, and they form between a carbon atom of one amino acid and a nitrogen atom of the other amino acid. The end of a protein with a free nitrogen atom is referred to as the N-terminus, while the other end of a protein with a free carbon atom is referred to as the C-terminus.
How many amino acids are in a protein?
A protein molecule is generally composed of a multitude of amino acids, or peptides, linked together via peptide bonds. The human body makes use of 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Proteins differ in the number and type of amino acids they possess.
What is the code for protein expression?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) serves as the code that dictates protein expression in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. DNA is made of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar and phosphate molecules together form what is called the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA, which anchors to the nitrogenous base and gives it the ability to form hydrogen bonds with nitrogenous bases of the complementary DNA strand. Recent scientific breakthroughs allowed the development of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs). PNAs are man-made DNA look-alike substances, in which the sugar-phosphate backbone is replaced with a peptide polymer. Because of their flexible and uncharged nature, they bind to complementary DNA strands in a very efficient manner. Therefore, PNAs are used in research and diagnostic settings, in which they are employed in hybridization assays.
What is an oligopeptide?
Oligopeptides: a protein structure composed of several amino acid residues organized in small chains. Oligopeptides are typically composed of two to forty amino acid residues. An example of an oligopeptide is Antipain, which is secreted by bacteria and acts as a protein inhibitor.
Where is the peptide bond formed?
The actual peptide bond is formed in a special protein macrostructure known as the ribosome, pictured below. The ribosome is a very large and complex cellular structure consisting of proteins, RNA and various other components that aid in catalyzing the formation of a peptide bond. This is known as the elongation stage of protein synthesis.
What is a peptide bond?
Peptide Bond Definition. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. Living organisms use peptide bonds to form long chains of amino acids, known as proteins. Proteins are used in many roles including structural support, catalyzing important reactions, and recognizing molecules in the environment.
What is the elongation stage of protein synthesis?
This is known as the elongation stage of protein synthesis. The ribosome helps match tRNA to the corresponding mRNA. In turn, the RNA changes shape slightly, which catalyzes the reaction between two amino acids and expels a water molecule. The chain that is formed exits the ribosome.
How many carbon bonds are there in an amino acid?
The carbons at the centers of each amino acid have 4 equal bonds, and can rotate freely. Thus, when many amino acids are linked together they form chains of rigid planes of atoms around the peptide bond, connected by flexible carbon bonds.
How many amino acids are there in life?
All life is based on bonds between about 20 different amino acids, which all organisms use and modify to their own purpose. The number of different combinations is limitless, while peptide groups in proteins form peptide backbones in all proteins.
Why is the acid nature of stomach acid important?
Answer to Question #1. B is correct. While the acid nature of stomach acid helps denature proteins and unfold them, the peptide bonds are broken in the opposite way in which they were formed. Because a water molecule was lost when the bond was created, a water molecule must be used to separate the two amino acid residues.
How are peptides formed?
Peptide Bond Formation. At the molecular level, a peptide bond is formed through a dehydration reaction. As seen in the image below, two amino acids are able to bond together when two hydrogens and an oxygen are removed from the molecules. One amino acid presents a carboxyl group to the reaction, and loses a hydroxyl group in the reaction ...
What type of bonds are amide and peptide?
The Amide Bond: Peptide bonds are amide bonds, characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group attached to an amine.
What is a peptide?
Peptides. A peptide is a molecule composed of two or more amino acids. The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond, or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds (in this case, two amino acids). It occurs when the carboxylic group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, ...
What are higher order structures such as peptide chains and proteins?
Higher-ordered structures such as peptide chains and proteins are formed when amino acids bond to each other. The Peptide Bond: The peptide bond (circled) links two amino acids together. The blue balls represent the nitrogen that connect from the amine terminus of one amino acid to the carboxylate of another. ...
How are long chain polypeptides formed?
Long chain polypeptides can be formed by linking many amino acids to each other via peptide bonds. The amide bond can only be broken by amide hydrolysis, where the bonds are cleaved with the addition of a water molecule. The peptide bonds of proteins are metastable, and will break spontaneously in a slow process.
What is the chemical compound that bonds to an amine group?
Amino acids are chemical compounds consisting of a carbon atom bonded to an amine group, a hydrogen atom, a carboxylic group, and a varying side-chain (R group); it is this side chain that distinguishes each amino acid from another. Higher-ordered structures such as peptide chains and proteins are formed when amino acids bond to each other.
How are proteins formed?
Large proteins are formed by linking amino acids with peptide bonds. The amide bond is formed through a condensation reaction, whereby the carbonyl and the amine group link together with the release of water.
What are the key points of an amide bond?
Key Points. An amide bond has various resonance forms which allow for extra stabilization and extra versatility in various environments. Amino acids is the basic building block of proteins; they are composed of a carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, a carbonyl group, an amine group, and an R group. Large proteins are formed by linking amino acids ...
How do peptide bonds form?
Peptide Bond Formation. In order to form a peptide bond, the molecules of the amino acids in question must be orientated so that the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid is able to react with the amine group of another amino acid. At its most basic, this can be illustrated by two lone amino acids combining through the formation ...
What is a Peptide Bond?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids. To form a peptide bond, a carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid. As a result, a molecule of water is also released. This is referred to as a condensation reaction. The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and is henceforth referred to as a peptide bond. Additionally, the resulting molecule is termed an amide.
How many amino acids are in a peptide?
Further, any number of amino acids can be joined together in chains to form new peptides: as a general guideline, 50 or less amino acids are referred to as peptides, 50 – 100 are termed polypeptides, and peptides with over 100 amino acids are generally referred to as proteins.
What wavelength of absorbance is a peptide bond?
The wavelength of absorbance for a peptide bond is 190-230 nm. In the biological realm, enzymes inside living organisms can both form and break down peptide bonds. A number of hormones, antibiotics, antitumor agents and neurotransmitters are peptides, most of which are referred to as proteins (due to the number of amino acids contained).
What is the bond that releases water?
As a result, a molecule of water is also released. This is referred to as a condensation reaction. The resulting bond is a CO-NH bond and is henceforth referred to as a peptide bond. Additionally, the resulting molecule is termed an amide.
Which bond is longer, N-C or C-O?
This resonance directly affects the structure of the peptide bond. Indeed, the N–C bond of the peptide bond is actually shorter than the N–Cα bond, and the C=O bond is longer than normal carbonyl bonds.
What breaks down peptide bonds?
Hydrolysis (a chemical breakdown of a compound resulting from a reaction with water) can break down a peptide bond. Though the reaction itself is quite slow, the peptide bonds formed within peptides, polypeptides, and proteins are susceptible to breakage when they come into contact with water (metastable bonds).
What happens when you have more than one polypeptide chain?
1. If more than one polypeptide chain, the chains are separated and purified.
Which amino acid is found in bacteriorhodopsin?
The free amino group of glutamic acid or glutamine cyclizes to form lactam. This amino acid is found in bacteriorhodopsin.
What is a post-translationally modified amino acid?
A post-translationally modified amino acid, where the glutamic acids residues undergo carboxylation; observed in the blood coagulation cascade, in clotting factors II, VII, IX, X and protein Z.
Is lysine a side chain?
Side chain is similar to Lysine, and is positively charged at neutral pH. Synthesized from two molecules of L-lysine.