
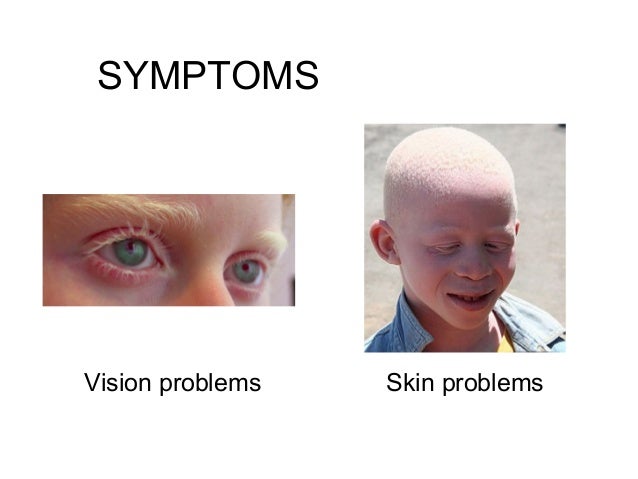
Symptoms
World and moreover the life expectancy of an albino in this society is said to be between 30 and 40 years. People with albinism may be limited in their activities because they cant tolerate the sun. Most forms of albinism dont affect a persons life expectancy. Albinism does not affect the lifespan of the person.
Causes
What are the abnormal eye findings of albinism?
- Nystagmus: involuntary eye movements or “shaking".
- Abnormal Head Position: the child develops a preferred head position to reduce the involuntary eye movements (nystagmus) and optimize vision.
- Strabismus: misalignment of the eyes.
- Photophobia: sensitivity to bright light and glare.
Prevention
Signs and symptoms include:
- pale skin
- hair that is very light blonde, brown, or reddish
- eyes that are pink, light blue, green, gray, or light brown
- eyes that are sensitive to light
- a “lazy eye” (called strabismus)
- back and forth movement of the eyes (called nystagmus)
- vision problems
Complications
The chance that each child will have two broken copies of the gene ( rr) and have albinism is 1 in 4. This is what happened in your wife’s aunts and uncle. The chance that each child will have at least one working copy of the gene ( RR or Rr) and not have albinism is 3 in 4. This is what happened to your wife’s mother.
What is the life expectancy with albinism?
How do doctors determine if a person has albinism?
How do you know if you have albinism?
What are the odds of having albinism?

How are albinos diagnosed?
Albinism Diagnosis Albinism is often obvious in newborns. A genetic test can confirm it. Your doctor probably will compare your baby's skin and hair to those of family members. An eye doctor, or ophthalmologist, may run a test called an electroretinography to check for vision problems linked to albinism.
How do you know if someone has albinism?
The most recognizable form of albinism results in white hair and very light-colored skin compared with siblings. Skin coloring (pigmentation) and hair color can range from white to brown, and may be nearly the same as that of parents or siblings without albinism.
What are 5 symptoms of albinism?
People with albinism may experience the following symptoms:Very pale skin, hair and eyes.Patches of missing skin pigment.Crossed eyes (strabismus).Rapid eye movements (nystagmus).Vision problems.Light sensitivity (photophobia).
Can you test for albinism gene?
Genetic testing offers the most accurate way to diagnose the specific type of albinism. Such testing is helpful if you have a family history of albinism. It is also useful for certain groups of people who are known to get the disease.
How early can albinism be detected?
Abstract. KIE: Albinism, a recessive genetic condition, can be diagnosed by fetoscopy between the 16th and 20th weeks of pregnancy, in time for subsequent abortion.
Can albinism be cured?
Because albinism is a genetic disorder, it can't be cured. Treatment focuses on getting proper eye care and monitoring skin for signs of abnormalities. Your care team may involve your primary care doctor and doctors specializing in eye care (ophthalmologist), skin care (dermatologist) and genetics.
What are the 4 types of albinism?
What are the types of albinism?oculocutaneous albinism (OCA)ocular albinism.Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.Chediak-Higashi syndrome.Griscelli syndrome.
How long is the average lifespan of a person with albinism?
Albinism is not associated with mortality. Lifespan is within normal limits. Because the reduction of melanin in the hair, skin, and eyes should have no systemic effects, the general health of a child and an adult with albinism is normal.
Who is most likely to albinism?
The condition affects people in many ethnic groups and geographical regions. Types 1 and 2 are the most common forms of this condition; types 3 and 4 are less common. Type 2 occurs more frequently in African Americans, some Native American groups, and people from sub-Saharan Africa.
Is albinism considered a disability?
Is Albinism a disability? Persons with Albinism are usually as healthy as the rest of the population, with growth and development occurring as normal, but can be classified as disabled because of the associated visual impairments.
Can 2 albinos have a normal child?
For most types of OCA, both parents must carry an albinism gene to have a child with albinism. Parents may have normal pigmentation but still carry the gene. When both parents carry the gene, and neither parent has albinism, there is a 25% chance at each pregnancy that the baby will be born with albinism.
Does albinism run in the family?
In all types of OCA and some types of OA, albinism is passed on in an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means a child has to get 2 copies of the gene that causes albinism (1 from each parent) to have the condition.
How do you know if your child is albino?
Doctors usually diagnose albinism when a child is noted to have skin, hair, or eyes that are much lighter than other family members. They'll also look for changes in the eyes to help make the diagnosis.
Can 2 albinos have a normal child?
For most types of OCA, both parents must carry an albinism gene to have a child with albinism. Parents may have normal pigmentation but still carry the gene. When both parents carry the gene, and neither parent has albinism, there is a 25% chance at each pregnancy that the baby will be born with albinism.
What are the 4 types of albinism?
What are the types of albinism?oculocutaneous albinism (OCA)ocular albinism.Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome.Chediak-Higashi syndrome.Griscelli syndrome.
Who is most likely to albinism?
The condition affects people in many ethnic groups and geographical regions. Types 1 and 2 are the most common forms of this condition; types 3 and 4 are less common. Type 2 occurs more frequently in African Americans, some Native American groups, and people from sub-Saharan Africa.
How to help someone with albinism?
Albinism is often very visible to other people. That may leave you feeling isolated or shunned. Talking to a mental health counselor or others who live with the condition may help. Support groups can offer you emotional support and practical tips. You can connect with a community online or through groups like the National Organization for Albinism and Hypopigmentation or Council of Citizens with Low Vision International.
What are the causes of albinism?
Albinism also can be linked to a few rare conditions caused by a problem with your genes: 1 Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. This is a rare form of albinism that also causes easy bruising and bleeding. 2 Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Another rare form of albinism, this can cause a low red blood cell count (anemia) and an enlarged liver and can make you more likely to get infections. 3 Griscelli syndrome type 2. Also called partial albinism and immunodeficiency syndrome, this is a rare condition that’s caused by a faulty gene. Symptoms include light skin, silver hair, and serious problems with your immune system that can eventually damage organs and tissues.
What Is Albinism?
Albinism is when you’re born with little or no pigment in your hair, eyes, and skin. The missing pigment is called melanin. Albinism usually makes your coloring lighter than is typical for your family or ethnic background.
What color are albinism's eyes?
Eye symptoms of albinism: Blue eyes are most common in people with albinism. But sometimes their iris, the colored part of the eye, can lack so much pigment that they appear pink or reddish from the blood vessels.
How to avoid albinism?
A few other simple steps can help you avoid or ease many common problems linked to albinism. Get checked for skin cancer every 6-12 months. Stay out of the sun if possible, and always wear sunscreen with SPF of 30 or higher, a hat, sunglasses, long-sleeved shirts, and long pants.
Can albinism be caused by genes?
Albinism also can be linked to a few rare conditions caused by a problem with your genes:
Can albinism be diagnosed?
Albinism Diagnosis. Albinism is often obvious in newborns. A genetic test can confirm it. Your doctor probably will compare your baby’s skin and hair to those of family members. An eye doctor, or ophthalmologist, may run a test called an electroretinography to check for vision problems linked to albinism.
How do you know if you have albinism?
Signs of albinism are usually apparent in a person's skin, hair and eye color, but sometimes differences are slight. People with albinism are also sensitive to the effects of the sun, so they're at increased risk of developing skin cancer.
When to see a doctor for albinism?
When to see a doctor. At your child's birth, if the doctor notices a lack of pigment in hair or skin that affects the eyelashes and eyebrows , the doctor will likely order an eye exam and closely follow any changes in your child's pigmentation and vision. If you observe signs of albinism in your baby, talk to your doctor.
How is albinism inherited?
The most common form is type 1, inherited by a gene mutation on the X chromosome. X-linked ocular albinism can be passed on by a mother who carries one mutated X gene to her son (X-linked recessive inheritance). Ocular albinism occurs almost exclusively in males and is much less common than OCA.
What are the symptoms of albinism?
Contact your doctor if your child with albinism experiences frequent nosebleeds, easy bruising or chronic infections. These signs and symptoms may indicate the presence of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome or Chediak-Higashi syndrome, which are rare but serious disorders that include albinism.
How are albinisms classified?
Types of albinism are classified based on how they're inherited and on the gene that is affected.
What color is albinism?
The most recognizable form of albinism results in white hair and very light-colored skin compared with siblings. Skin coloring (pigmentation) and hair color can range from white to brown, and may be nearly the same as that of parents or siblings without albinism.
Why do people with albinism use the term "Albinism"?
Using the term "person with albinism" is preferred to avoid the stigma of other terms.
How do you know if you have albinism?
People with albinism will have the following symptoms: an absence of color in the hair, skin, or eyes. lighter than normal coloring of the hair, skin, or eyes. patches of skin that have an absence of color.
What is the cause of albinism?
The cause of albinism is a defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin, the pigment that gives skin, eyes, and hair their coloring. The defect may result in the absence of melanin production or a reduced amount of melanin production.
What causes albinism in children?
A defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin causes albinism . The defect may result in the absence of melanin production, or a reduced amount of melanin production. The defective gene passes down from both parents to the child and leads to albinism.
What is it called when you have no color?
What is albinism ? Albinism is a rare group of genetic disorders that cause the skin, hair, or eyes to have little or no color. Albinism is also associated with vision problems.
Why do people with albinism have to limit their outdoor activities?
People with albinism may have to limit their outdoor activities because their skin and eyes are sensitive to the sun. UV rays from the sun can cause skin cancer and vision loss in some people with albinism. Last medically reviewed on March 29, 2018.
What is the name of the condition that causes albinism?
Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Chediak-Higashi syndrome is another rare form of albinism that’s the result of a defect in the LYST gene. It produces symptoms similar to OCA, but may not affect all areas of the skin. Hair is usually brown or blond with a silvery sheen. The skin is usually creamy white to grayish.
What is the rarest form of albinism?
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. This syndrome is a rare form of albinism that’s due to a defect in one of eight genes. It produces symptoms similar to OCA. The syndrome occurs with lung, bowel, and bleeding disorders.
How to diagnose albinism?
Albinism can be diagnosed merely by observation of major or total absence of pigmentation of the skin, hair and eyes.
What is the test for albinism?
Chemical testing of hair also provides an easy confirmation of the diagnosis of albinism. Hairbulb pigmentation test - It can be used to identify carriers. It is done by incubating a piece of the person's hair in a solution of tyrosine, an amino acid the body uses to make melanin. If the hair turns dark, it means the hair is making melanin.
What is the most accurate test for albinism?
Genetic Testing -. Genetic testing is the most accurate way to diagnose albinism and its specific type. This is helpful in families with albinism and is useful for specific, isolated populations who carry the trait in them.
What test is done to determine vision problems in albinism?
An ophthalmologist should perform a complete examination of the eyeof an affected individual. An electroretinogram testshould be done to determine vision problems in albinism.
Can a blood test identify albinism?
Recently, a blood testhas been developed that can identify carriers of the gene for some types of albinism.
What does it mean when you have albinism?
When someone has albinism, their body has trouble creating pigment. Pigment is the material in the body that produces color. Albinism is a hereditary condition, which means it's passed from parent to child. People with albinism have a reduced amount or absence of pigment in their eyes, hair and skin. There are two basic types of albinism, both of ...
Who is at risk for albinism?
Albinism is an inherited genetic disorder. Usually, both parents must carry the albinism gene to have a child with albinism. The albinism gene is a recessive gene, meaning that a child has to receive a copy from both parents to have the disorder. If the child gets a copy of the gene from just one parent, he or she will not have symptoms of albinism. If both parents carry the gene, there is a one-in-four chance with each pregnancy that the baby will be born with albinism.
How is Albinism Treated?
Glasses can be prescribed to improve vision and reduce light sensitivity. Magnifying glasses for reading and low vision aids for distance vision can also be helpful . Eye misalignment can be treated with glasses or surgery. Abnormal head postures and nystagmus can be improved with surgery. Genetic counseling of affected individuals and their families is recommended. Counselors can provide a detailed explanation of the disorder including the chances of future children being affected. The American College of Medical Genetics and the National Society of Genetic Counselors maintain a referral list.
What causes albinism?
Albinism is passed from parents to their children through genes. For most types of OCA, both parents must carry an albinism gene to have a child with albinism. Parents may have normal pigmentation but still carry the gene. When both parents carry the gene, and neither parent has albinism, there is a 25% chance at each pregnancy that the baby will be born with albinism. This type of inheritance is called autosomal recessive inheritance. For OA, the gene for albinism is located on an X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. X-linked ocular albinism appears almost exclusively in males. The gene for it is passed from mothers (who carry it without developing the condition) to their sons. The mothers have subtle eye changes that an ophthalmologist could identify, but they generally have normal vision. For each son born to a mother who carries the gene, there is a 50% chance of having X-linked ocular albinism.
How common is albinism?
One person in 17,000 has some type of albinism. Albinism affects people from all races. Most children with albinism are born to parents who have normal hair and eye color for their ethnic backgrounds. Some patients with albinism have white hair and very light blue eyes, others have blonde hair and blue eyes, and some even have brown hair and eyes. The findings may be subtle, and a person may not even know that he or she has albinism.
What lifestyle adjustments does albinism usually require?
It may also result in the inability to drive and place limitations on vocational choice. Student, parents, and teachers should work as a team to consider seating, lighting, optical aids, and social and emotional growth. Albinism does not typically cause intellectual disabilities and children with albinism usually have normal intelligence . In addition, individuals with albinism are more susceptible to sunburn and skin cancer, so sunscreen and wide brim hats, as well as sunglasses and/or prescription lens tint are strongly encouraged.
What optical aids are useful in albinism?
Some children may do well with ordinary glasses. Some people do well with bifocals which have a strong reading lens. Some may benefit more from contact lenses. Others use hand-held magnifiers or special small telescopes, and some prefer to use screen magnification products on computers. For older children and adults, glasses with small telescopes mounted on the lenses may help with both close and distant vision.
Are there any other medical conditions associated with albinism?
There are two systemic conditions that are (rarely) present in patients with albinism. HermanskyPudlak Syndrome (HPS) is associated with bleeding problems and bruising. Some forms are also associated with lung and bowel disease. HPS is a less common form of albinism but should be suspected if a person with albinism shows unusual bruising or bleeding. Chédiak-Higashi syndrome is a rare disorder that affects multiple systems of the body. The disease is characterized a susceptibility to infections, anemia (low blood count), and hepatomegaly (enlarged liver).
What is albinism in biology?
What is albinism? Albinism is an inherited condition present at birth, characterized by a reduced or lack of pigment that normally gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes [figure 1]. Fig. 1: People with albinism have inherited genes that code for hypo-production of melanin.
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support