What is the role of ribosomes in protein production?
What Is The Role Of Ribosomes In Protein Production? Protein synthesis takes place in ribosomes, which are located in cells. RRNA molecules are responsible for directing the catalytic steps of protein synthesis within the ribosome, which involves stitching together amino acids to form a protein molecule. ribozymes or catalytic RNAs are examples of the function of rRNA.
How do viruses make proteins without ribosomes?
How do viruses make proteins? Without a host cell, viruses cannot carry out their life-sustaining functions or reproduce. They cannot synthesize proteins , because they lack ribosomes and must use the ribosomes of their host cells to translate viral messenger RNA into viral proteins .
How do ribosomes use mRNA and tRNA to assemble proteins?
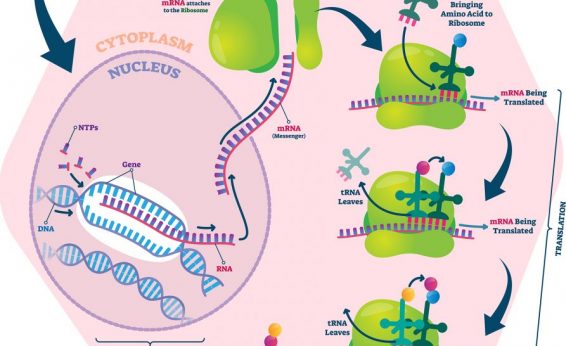
Ribosomes provide a structure in which translation can take place. They also catalyze the reaction that links amino acids to make a new protein. tRNAs ( transfer RNAs) carry amino acids to the ribosome. They act as "bridges," matching a codon in an mRNA with the amino acid it codes for. Here, we’ll take a closer look at ribosomes and tRNAs.
What are facts about ribosomes?
What are 3 facts about ribosomes?
- The “rib” in ribosome comes from ribonucleic acid (RNA) which provides the instructions on making proteins.
- They are made inside the nucleolus of the nucleus.
- Ribosomes are different from most organelles in that they are not surrounded by a protective membrane.

How are ribosomal proteins formed?
The ribosomal subunits are assembled at the nucleolus, where newly transcribed and processed rRNAs associate with the RPs acquired into the nucleus from the cytoplasm (Boisvert et al., 2007). These two ribosomal subunits are then exported to the cytoplasm through a nuclear pore.
Where is ribosomal proteins produced?
Ribosomal proteins, like other proteins, are synthesized in the cytoplasm.
How are ribosomes produced?
How do you make a ribosome? Some chromosomes have sections of DNA that encode ribosomal RNA, a type of structural RNA that combines with proteins to make the ribosome. In the nucleolus, new ribosomal RNA combines with proteins to form the subunits of the ribosome.
How is protein produced in the cell?
In order for a cell to manufacture these proteins, specific genes within its DNA must first be transcribed into molecules of mRNA; then, these transcripts must be translated into chains of amino acids, which later fold into fully functional proteins.
What process creates proteins?
Protein synthesis is the process in which cells make proteins. It occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. Transcription is the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus. It includes three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Where are proteins produced in the cell?
Ribosomes are the sites where proteins are synthesized. The transcription process where the code of the DNA is copied occurs in nucleus but the main process of translating that code to form the protein occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosomes with the help of tRNA.
Where ribosomal RNA is produced?
the nucleolusMolecules of rRNA are synthesized in a specialized region of the cell nucleus called the nucleolus, which appears as a dense area within the nucleus and contains the genes that encode rRNA.
Where is ribosomal DNA produced?
the nucleolus organizer regionIn most eukaryotes, ribosomal DNA consists of tandemly repeated arrays of four or five genes located at the nucleolus organizer region (NOR) of one or more chromosomes.
Where are ribosomes and rRNA produced?
In eukaryotes. As the building-blocks for the organelle, production of rRNA is ultimately the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of a ribosome. In the nucleolus, rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase I using the specialty genes (rDNA) that encode for it, which are found repeatedly throughout the genome.
Where in the cell is ribosomal RNA produced?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the most common form of RNA found in cells – it makes up around 50% of the structure of the ribosomes. It is produced in the nucleus, before moving out into the cytoplasm to bind with proteins and form a ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is found in the cytoplasm and has a complex shape.
Ribosomes
Ribosomal proteins are present in only one copy per ribosome, apart from one exception. This is the acidic protein L7/L12 in E. coli, which is found in four copies per ribosome.
Prothoracicotropic Hormone
Ribosomal protein S6 is a small (≈34kDa), basic protein present at one copy per 40S ribosome near the tRNA/mRNA binding site (see Fumagalli and Thomas, 2000; Meyuhas, 2008 ).
RNA and Protein Synthesis
N.V. Bhagavan, Chung-Eun Ha, in Essentials of Medical Biochemistry (Second Edition), 2015
Ribosome Assembly
A. Sahasranaman, J.L. WoolfordJr., in Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry (Second Edition), 2013
New Approaches to Prokaryotic Systematics
Because ribosomal proteins dominate mass spectra (Ryzhov & Fenselau, 2001) and because structures of ribosomal components are conservative enough to mirror the phylogeny of organisms ( Winker & Woese, 1991 ), it can be assumed that MALDI-TOF mass spectra may contain information for inferring the phylogenetic relationship of bacteria.
Ribosomes
The database of ribosomal protein sequences is rapidly growing. From sequence comparisons, it is evident that about 50% of the bacterial ribosomal proteins are conserved and have corresponding proteins in chloroplasts, archaea, as well as eukaryotes (Table 2 ).
Mutational Analysis of 23S Ribosomal RNA Structure and Function in Escherichia coli
The L23 ribosomal protein binding site has been defined by a variety of biochemical methods (reviewed in Draper, 1996) to include the positions 1304–1416 and 1588–1613. Musters et al, (1991) demonstrated that substitution of the E. coli region 1371–1373 for the yeast sequences protected by L23 (V9) was tolerated by yeast 60S subunits. Liiv et al.
The Mechanism of Protein Synthesis
As with mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis can be divided into three phases: initiation, elongation, and termination. The process of translation is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Here we’ll explore how translation occurs in E. coli, a representative prokaryote, and specify any differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic translation.
Protein Folding, Modification, and Targeting
During and after translation, individual amino acids may be chemically modified, signal sequences may be appended, and the new protein “folds” into a distinct three-dimensional structure as a result of intramolecular interactions. A signal sequence is a short tail of amino acids that directs a protein to a specific cellular compartment.
Section Summary
The players in translation include the mRNA template, ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors. The small ribosomal subunit forms on the mRNA template either at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (prokaryotes) or the 5′ cap (eukaryotes). Translation begins at the initiating AUG on the mRNA, specifying methionine.
What is a ribosome? A quick definition
A ribosome is a particle-like cell organelle made of RNA (ribonucleic acid) and ribosomal proteins that serve as the site for protein synthesis in the cell. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits.
Ribosomes structure
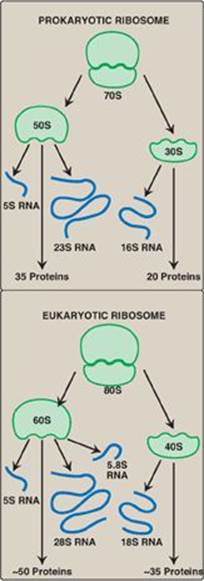
A ribosome is a complicated but elegant “micro-machine” for producing proteins. Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In prokaryotes, ribosomes consist of roughly 40 percent protein and 60 percent rRNA. A eukaryotic ribosome comprises three or four rRNA molecules and about 80 different proteins.
Do prokaryotes have ribosomes?
Yes, both prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotes (animals, plants, fungi) have ribosomes. Ribosomes in prokaryotes use a slightly different process to produce proteins than ribosomes do in eukaryotes. Fortunately, this difference presents a window of opportunity for attack by antibiotic drugs such as streptomycin.
The discovery of ribosomes
The small particles that are known as ribosomes were first described in 1955 by cell biologist George E. Palade, who found them using an electron microscope. He noticed that these particles are frequently associated with the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells.
Where are ribosomes located inside a cell?
Ribosomes can function in a “free” form in the cytoplasm, called free ribosomes. However, they can also “settle” on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to form “rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).” Ribosomes in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum can facilitate the further processing of newly made proteins.
How many ribosomes in a cell?
There are about 10 billion protein molecules in a mammalian cell, and ribosomes produce most of them. A rapidly growing mammalian cell can contain about 10 million ribosomes. This number is highly dependent on the cell types and the status of cells. Ribosomes are particularly abundant in cells that synthesize large amounts of protein.
Where are ribosomes made of?
The proteins and nucleic acids that form the ribosome subunits are made in the nucleolus (in the nuclei) and exported to the cytoplasm through nuclear pores. The two subunits stay apart until required for use. Ribosomes are not static organelles. When specific protein production is finished, two subunits separate and are usually broken down.
What are ribosomes made of?
Ribosomes are made up of the combination of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). That’s why ribosomes are also called riboprotein complexes.
How are ribosomes made in prokaryotic cells?
In prokaryotic cells, we all know that there isn’t any membrane-bound nucleus and so all the genetic materials that are included in the single circular chromosome floats freely in the center of the cytoplasm.
How are ribosomes made in eukaryotic cells?
In eukaryotic cell, there’s a well-defined nucleus located in the center of the cytoplasm. This well-defined nucleus is bounded by a double-layered nuclear membrane that has the nucleoplasm within it.
What is ribosome biogenesis?
Ribosome biogenesis is the biological process of production of rRNA from rDNA, and also the production of various ribosomal proteins by transcription and translation of the various ribosome gene operons.
What is so unique about ribosomes?
Ribosomes are those tiny organelles that are also considered as macromolecules that are composed of two macromolecules: ribosomal proteins and rRNA.