What increases the chance of trisomy?
Risk factors for trisomy conditions. The addition of an extra chromosome usually occurs spontaneously during conception. The cause of this is unknown and prevention is not possible. The most important risk factor for trisomy conditions is maternal age. Women in their late 30s and 40s have a higher chance of trisomy conditions occurring.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Trisomy 13 syndrome?
Children with trisomy 13 or 18 generally do not survive beyond their first year of life, and those who do are severely disabled and only live a short life.
How does trisomy 21 affect the body?
Trisomy 21 can affect health. Particularly frequent trisomy 21 features are heart defects. They occur in about half of all people with Down syndrome. A common heart defect is the so-called AV channel (atrioventricular channel). This is a defect of the septum between the atria and the ventricles.
What is the survival rate of trisomy 13?
The median survival time for live births with full trisomy 18 was 14 days and with full trisomy 13 was 10 days, the 3-month survival was 20% and 18%, respectively, and the 1-year survival for both syndromes was 8%.

Trisomy
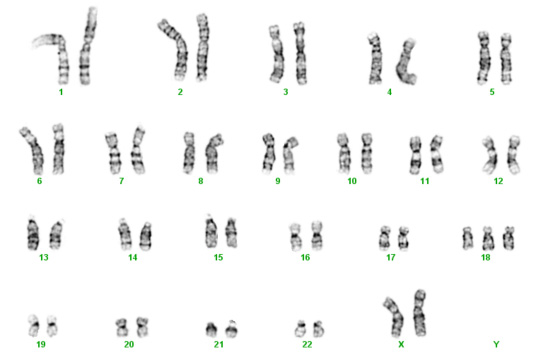
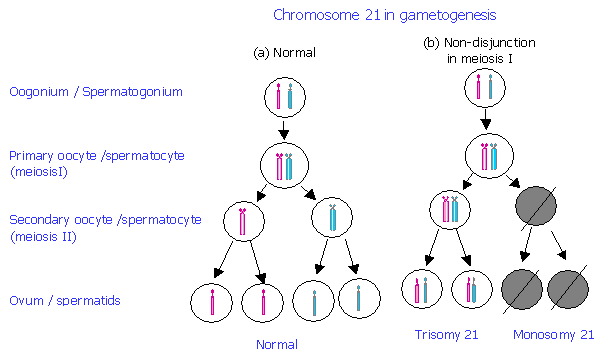
In a diploid organism, each cell normally has two copies of each chromosome - one from its mother and one from its father. But sometimes, a mistake can occur, and an embryo gets an extra copy of one of its chromosomes. Trisomy is when a diploid organism has three copies of one of its chromosomes instead of two.
How Does Trisomy Occur?
Trisomy often occurs because of errors during meiosis, which is the process by which gametes, or eggs and sperm, are formed. In meiosis, the replicated chromosomes are sorted into daughter cells in two steps, called meiosis I and meiosis II.
Symptoms of Trisomy
Our cells are optimized to function with the dosage or amount of proteins that is normally made from two copies of each chromosome. Trisomies and other aneuploidies disrupt the normal balance of gene products inside cells.
Beyond Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Kathleen Fergus, MS, LCGC, is a board-certified genetic counselor who has worked extensively with families affected by Down syndrome.
Understanding Trisomies
Genes that contain all of the DNA-coded information related to physiologic makeup and metabolic function are found on chromosomes. Each human cell nucleus typically contains 46 chromosomes, 23 of which we inherit from each genetic parent.
Causes and Consequences
Trisomies affecting the sex chromosomes—in which genetic females typically have two X chromosomes (XX) and genetic males have an X and Y chromosome (XY)—tend to be less severe. 2 Autosomal trisomies often cause serious physical and intellectual disabilities, particularly full autosomal trisomies, for which early death is common. 3
Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) is rare, affecting only one of every 5,000 births. Around 95% of cases are caused by an extra chromosome 18. The remaining 5% of cases are due to an error known as translocation in which the building blocks of one chromosome is inserted into another. 6
Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13) is the third most common autosomal disorder among newborns after Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome. Most cases are related to a full trisomy; a very small proportion is caused by translocation or a similar condition known as mosaicism in which the chromosomal building blocks are rearranged. 7
Warkany Syndrome (Trisomy 8)
Warkany syndrome (trisomy 8) is a common cause of miscarriage and usually results in newborn death within the first months. Babies born with Warkany syndrome typically have a cleft palate, distinctive facial features, heart defects, joint malformation, abnormal or missing kneecaps, and an abnormally curved spine (scoliosis). 8
Trisomy 16
Trisomy 16 is the most common autosomal trisomy seen in miscarriages, accounting for at least 15% of first-trimester pregnancy losses. Full trisomy 16 is incompatible with life. While most fetuses with this abnormality are spontaneously aborted by the 12th week of gestation, a few have survived into the second trimester. 4
Description and causes
Most organisms that reproduce sexually have pairs of chromosomes in each cell, with one chromosome inherited from each parent. In such organisms, a process called meiosis creates cells called gametes (eggs or sperm) that have only one set of chromosomes. The number of chromosomes is different for different species. Humans have 46 chromosomes (i.e.
Human trisomy
Trisomies can occur with any chromosome, but often result in miscarriage, rather than live birth. For example, Trisomy 16 is the most common trisomy in human pregnancies, occurring in more than 1% of pregnancies; only those pregnancies in which some normal cells occur in addition to the trisomic cells, or mosaic trisomy 16, survive.
What is Trisomy?
Genes are the blueprint for our bodies. Almost every cell in the body has a copy of the blueprint, stored inside a sac called the nucleus. Genes are beaded along chromosomes, which are tightly bundled strands of the chemical substance deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Trisomy Facts
Trisomy 18 syndrome (Edwards syndrome) is a disorder of human chromosomes which occurs in approximately 1 in 7,000 live born infants. Trisomy refers to three copies of a chromosome instead of the normal two and in trisomy 18 there is a presence of an extra #18 chromosome. (Select a .pdf download below)
Diagnosis & Screening
Prenatal diagnosis of a fetus with a trisomy condition generally results in a discussion with the obstetrician about termination or continuation of the pregnancy. Genetic counseling is recommended for those with a positive diagnosis.
Causes
Genetics
- Down syndrome, the most common genetic disorder in humans is referred to trisomy 21 because there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 in a gene. Other genetic disorders are similarly named.
Effects
- Trisomies affecting the sex chromosomesin which females typically have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have an X and Y chromosome (XY)tend to be less severe. Autosomal trisomies often cause serious physical and intellectual disabilities, particularly full autosomal trisomies for which early death is common. In addition to birth defects, trisomies can undermine the viability …
Epidemiology
- No one knows for sure why chromosome 21 is so vulnerable to trisomy. Of all the trisomies identified by researchers, Down syndrome is known to affect nearly one of every 1,000 births worldwide. Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) is rare, affecting only one of every 20,000 births. Around 95 percent of cases are caused by an extra chromosome 18. The remaining 5 percent o…
Symptoms
- Children with Patau syndrome will often have cleft lips and palates, extra fingers or toes, heart defects, severe brain abnormalities, and malformed or rotated internal organs. The severity of symptoms is such that a baby with Patau syndrome rarely lives past the first month. Warkany syndrome (trisomy 8) is a common cause of miscarriage and usually results in newborn death w…
Prognosis
- Babies with mosaic trisomy 9 have a far greater chance of surviving to adulthood. While some will have moderate intellectual deficits, others may have normal to above-normal intelligence. Mosaic trisomy 9 is also associated with an increased risk of myeloid leukemia. By contrast, the chances of survival of children with mosaic trisomy 16 used to be considered bleak with most deaths occ…
Signs and symptoms
- With that being said, more than half of babies with mosaic trisomy 16 will have fetal abnormalities, including musculoskeletal defects, distinctive facial features, undersized lungs, and an atrial septal defect (a hole between the upper chambers of the heart). Males will often have hypospadias in which the opening of the urethra develops on the shaft of the penis rather than a…
Overview
- Klinefelter syndrome, also known as XXY syndrome, is a condition affecting males caused by an additional X chromosome. Men with Klinefelter syndrome typically produce little testosterone, resulting in reduced muscle mass, facial hair, and body hair. Characteristic symptoms include small testicles, delayed development, breast enlargement (gynecomastia), and reduced fertility.
Treatment
- The severity of symptoms can vary dramatically. Some men may also have learning disabilities, which are typically language-oriented, although intelligence will usually be normal. Testosterone replacement therapy is often used to treat the disorder alongside assisted fertility treatments for men wanting to father children.