How is Voice Produced
- Power (Respiration) Our lungs provide the in and out air flow needed for voice. ...
- Source (Phonation) The air pushed up by our lungs travels through the windpipe to the voice box (larynx). ...
- Filter (Resonance) The sound then travels up to the filter which is made up of the bony spaces in our throat and head, such as the mouth and the nasal ...
How is voice produced in humans?
Jul 15, 2011 · The production of voice is complex, relying on many different nerves and organ systems to coordinate with one another. The production of voice, or sound, involves three major areas. The lungs to power voice production. The vocal folds to vibrate, producing sound.
How is speech produced?
Voice production involves a three-step process. A column of air pressure is moved towards the vocal folds. Air is moved out of the lungs and towards the vocal folds by coordinated action of the diaphragm, abdominal muscles, chest muscles, and rib cage. Vocal fold vibration – sequence of vibratory cycles:
What are the three steps of voice production?
Voice is produced by breath, vibrating the vocal folds in the larynx. The sound produced (phonation) is amplified or resonated by the area in, around and above the larynx, including the pharynx, and the mouth and nasal cavities.
What is a sound and how is it produced?
The vocal folds produce sound when they come together and then vibrate as air passes through them during exhalation of air from the lungs. This vibration produces the sound wave for your voice. In order for the sound to be clear and not raspy or hoarse, the vocal folds must vibrate together symmetrically and regularly.

How do vocal folds move?
Vocal folds are moved to midline by voice box muscles, nerves, and cartilages. The vibratory cycle occurs repeatedly; one vibratory cycle is as follows: Column of air pressure opens bottom of vocal folds. Column of air continues to move upwards, now towards the top of vocal folds, and opens the top.
What is the vocal fold?
Vocal Folds (also called Vocal Cords) “Fold-like” soft tissue that is the main vibratory component of the voice box; comprised of a cover (epithelium and superficial lamina propria), vocal ligament (intermediate and deep laminae propria), and body (thyroarytenoid muscle) Glottis (also called Rima Glottides)
How is voice produced?
Infants babble and coo; animals bark, moo, whinny, growl, and meow; and adult humans laugh, sing, and cry. Voice is generated by airflow from the lungs as the vocal folds are brought close together. When air is pushed past the vocal folds with sufficient pressure, the vocal folds vibrate. If the vocal folds in the larynx did not vibrate normally, speech could only be produced as a whisper. Your voice is as unique as your fingerprint. It helps define your personality, mood, and health.
How is voice generated?
Voice is generated by airflow from the lungs as the vocal folds are brought close together. When air is pushed past the vocal folds with sufficient pressure, the vocal folds vibrate. If the vocal folds in the larynx did not vibrate normally, speech could only be produced as a whisper. Your voice is as unique as your fingerprint.
What is the expression of human communication through which knowledge, belief, and behavior can be experienced, explained, and shared?
Language. Language is the expression of human communication through which knowledge, belief, and behavior can be experienced, explained, and shared. This sharing is based on systematic, conventionally used signs, sounds, gestures, or marks that convey understood meanings within a group or community.
Why do vocal folds vibrate?
If the vocal folds in the larynx did not vibrate normally, speech could only be produced as a whisper. Your voice is as unique as your fingerprint. It helps define your personality, mood, and health.
How many people have trouble using their voice?
Your voice is as unique as your fingerprint. It helps define your personality, mood, and health. Approximately 17.9 million adults in the United States have trouble using their voices. Disorders of the voice involve problems with pitch, loudness, and quality.
What is pitch in music?
Pitch is the highness or lowness of a sound based on the frequency of the sound waves. Loudness is the perceived volume (or amplitude) of the sound, while quality refers to the character or distinctive attributes of a sound.
What is the difference between loudness and quality?
Loudness is the perceived volume (or amplitude) of the sound, while quality refers to the character or distinctive attributes of a sound. Many people who have normal speaking skills have great difficulty communicating when their vocal apparatus fails.
What is the human voice?
The spectrogram of the human voice reveals its rich harmonic content. The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in ...
Why is the sound of each individual's voice unique?
The sound of each individual's voice is entirely unique not only because of the actual shape and size of an individual's vocal cords but also due to the size and shape of the rest of that person's body, especially the vocal tract, and the manner in which the speech sounds are habitually formed and articulated.
What is voice modulation?
Voice modulation in spoken language. Human spoken language makes use of the ability of almost all people in a given society to dynamically modulate certain parameters of the laryngeal voice source in a consistent manner.
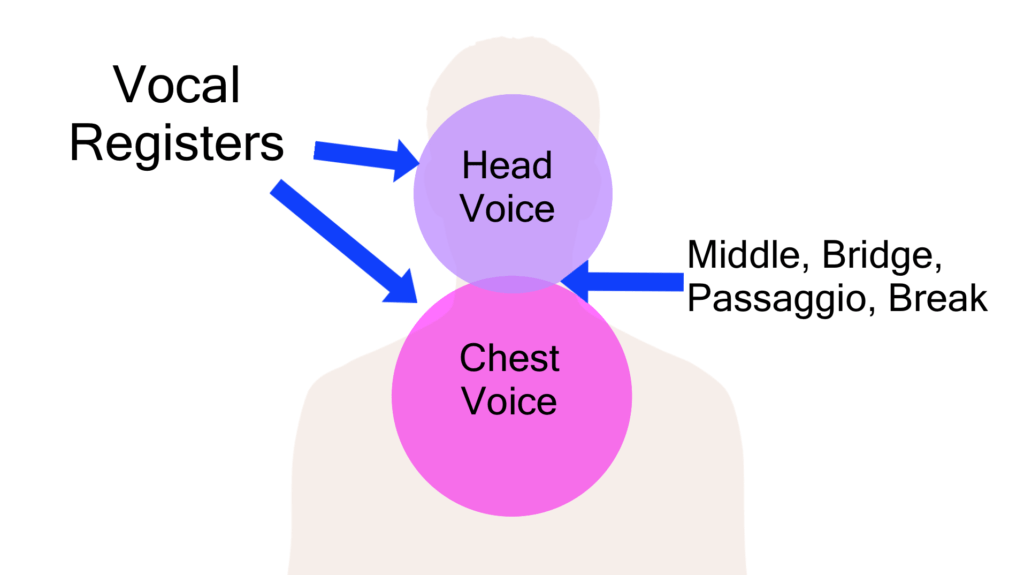
What is the register of the voice?
A register in the human voice is a particular series of tones, produced in the same vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, and possessing the same quality. Registers originate in laryngeal functioning. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns.
What are the disorders that affect the voice?
There are many disorders that affect the human voice; these include speech impediments, and growths and lesions on the vocal folds. Talking improperly for long periods of time causes vocal loading, which is stress inflicted on the speech organs.
Where are vocal folds located?
The female vocal folds are between 12.5 mm and 17.5 mm in length. The folds are within the larynx. They are attached at the back (side nearest the spinal cord) to the arytenoids cartilages, and at the front (side under the chin) to the thyroid cartilage.
What is the function of vocal folds?
The ability to vary the ab/adduction of the vocal folds quickly has a strong genetic component, since vocal fold adduction has a life-preserving function in keeping food from passing into the lungs, in addition to the covering action of the epiglottis.
Why is voice important?
As the primary means of communication, voice plays an important role in daily life. Voice also conveys personal information such as social status, personal traits, and the emotional state of the speaker. Mechanically, voice production involves complex fluid-structure interaction within the glottis and its control by laryngeal muscle activation.
What are vocal folds?
The vocal folds are layered structures, consisting of an inner muscular layer (the thyroarytenoid muscle) with muscle fibers aligned primarily along the anterior-posterior direction, a soft tissue layer of the lamina propria, and an outmost epithelium layer [Figs. 1(a)and 1(b)].
What is the lamina propria?
The lamina propria consists of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and interstitial substances. The two primary ECM proteins are the collagen and elastin fibers, which are aligned mostly along the length of the vocal folds in the anterior-posterior direction (Gray et al., 2000).
What is the body layer?
The body layer includes the muscular layer and the deep layer of the lamina propria, and the cover layer includes the intermediate and superficial lamina propria and the epithelium layer. This body-cover concept of vocal fold structure will be adopted in the discussions below.