
Precautions
The Dangers of Acetaminophen
- Liver Toxicity. ...
- Gut Health and Microbial Drug Metabolism. ...
- Cardiovascular Health, Kidney Disease, and Cancer. ...
- Blunted Emotions and Empathy. ...
- Autism, ADHD, and Brain Health. ...
- Severe Skin Reactions and Asthma. ...
- Altered Reproductive Function. ...
- Alternatives to Acetaminophen. ...
What are the harmful effects of acetaminophen?
DAILY LIMIT. Do not take more than 6 pills in 24 hours, unless directed by a doctor. ACETAMINOPHEN EXTENDED RELEASE for example Tylenol® 8HR Arthritis Pain 650 mg per pill. DOSE &. FREQUENCY. 2 pills every 8 hours. DAILY LIMIT. Do not take more than 6 pills in 24 hours. Acetaminophen dosage daily limit is 4,000 mg.
What is the maximum daily dose of acetaminophen?
acetaminophen/phenylephrine systemic. Brand names: Sudafed PE Sinus Pressure + Pain, Tylenol Sinus + Headache Day, Alka-Seltzer Plus Cold and Sinus, Contac Cold + Flu (Day Formula) Drug class (es): upper respiratory combinations. Acetaminophen/phenylephrine systemic is used in the treatment of: Nasal Congestion.
What medicines contain acetaminophen?
Yes, you can die from OD ing on Tylenol PM. It will be from the acetaminophen and it will cause indefinite liver damage. 6000 milligrams is the beginning toxic dose, but... usually people survive more then that.
Can Tylenol kill you?

Is acetaminophen given IV?
Approved by the FDA in 2010, the I.V. form of acetaminophen (ofirmev injection) is indicated to manage mild-to-moderate pain or moderate-to-severe pain with an adjunctive opioid. It can also be used to reduce fever.
Can acetaminophen be given intramuscularly?
Sometimes though, the oral route is not ideal and other routes are needed to administer acetaminophen. There are many methods to administer a drug to achieve systemic absorption, which include rectally, intramuscularly, subcu- taneously, intravenously, via intraosseus, as well as other less common routes.
How is acetaminophen prescribed?
Why is this medication prescribed? Acetaminophen is used to relieve mild to moderate pain from headaches, muscle aches, menstrual periods, colds and sore throats, toothaches, backaches, and reactions to vaccinations (shots), and to reduce fever.
How do you administer medication?
3:526:27How to give Medication - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSitting at the bottom if another medication is needed flush the feeding tube with a recommendedMoreSitting at the bottom if another medication is needed flush the feeding tube with a recommended amount of cool boiled water and repeat the process of giving the medication.
What are the 7 routes of medication administration?
Techniques involved in each route of medication administration are different, and some of the important points are summarized as follows:Intravenous Route. ... Intramuscular Route. ... Subcutaneous Route. ... Rectal Route. ... Vaginal Route. ... Inhaled Route.
How many acetaminophen 500mg can I take?
Each tablet, capsule, or gelcap contains 500 milligrams (mg) of acetaminophen. Extra Strength Tylenol can be used in adults and children 12 years and over. The recommended dose is two tablets, capsules, or gelcaps every six hours as needed. The maximum daily dose is six tablets, capsules, or gelcaps.
Whats stronger acetaminophen or ibuprofen?
Official answer. Acetaminophen is only effective at relieving pain and fever, while ibuprofen relieves inflammation in addition to pain and fever. Other key differences: Some research suggests NSAIDs such as ibuprofen are more effective than acetaminophen at relieving pain.
What is the most serious side effect of acetaminophen?
Liver damage is the most serious side effect of acetaminophen and it can be fatal. Liver damage can occur when a person exceeds the maximum daily dose of 4,000 milligrams — but it's also been known to occur in some people at even lower doses.
Is paracetamol injection IV or IM?
The paracetamol solution is administered as a 15-minute intravenous infusion.
Is paracetamol injection given intramuscular?
Intramuscular route: Adults: 2 - ml 3 every 4 to 6 hours.
What routes can paracetamol be administered?
For increasing its beneficial effects on pain relief, paracetamol can be given as a rectal, oral, or intravenous preparation [13]; however, the route of administration can lead to different levels of effectiveness because of the differences in absorption and the time to reach peak plasma levels.
Where is paracetamol injection given?
Paracetamol injection, or acetaminophen, is one of the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Each mL contains 150mg of paracetamol. Paracetamol injection is given by injection into vein or muscle by a healthcare professional in a hospital or clinical setting.
Acetaminophen vs Ibuprofen: Which is better?
Acetaminophen is only effective at relieving pain and fever, while ibuprofen relieves inflammation in addition to pain and fever.
What is paracetamol / panadol called in the US?
Paracetamol is known as acetaminophen in the U.S. Acetaminophen relieves mild-to-moderate pain, headache and fever. It's available over-the-counter...
Is it safe to take ibuprofen (Advil) with acetaminophen (Tylenol)?
Yes, it is safe to take ibuprofen (Advil) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) together if you need to for extra pain relief, such as for a dental extractio...
How to give acetaminophen to a child?
Slowly give the medicine into your child's mouth (towards the inner cheek). Replace the cap back tightly. For patients using acetaminophen oral granules (e.g., Snaplets-FR): Just before the medicine is to be taken, open the number of packets needed for one dose.
How to take acetaminophen without a doctor?
If you are taking this medicine without the advice of your doctor, carefully read the package label and follow the dosing instructions. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions. Carefully check the labels of all other medicines you are using, because they may also contain acetaminophen.
How to store a syringe?
Keep the bottle closed when you are not using it. Store it at room temperature, away from light and heat. Do not freeze.
How to give medicine to a child?
Slowly give the medicine into your child's mouth (towards the inner cheek).
Can you take Micromedex more than once?
Proper Use. Drug information provided by: IBM Micromedex. Take this medicine only as directed by your doctor. Do not take more of it, do not take it more often, and do not take it for a longer time than your doctor ordered. Liver damage can occur if large amounts of acetaminophen are taken for a long time.
Can you drink liquid after taking a med?
Drink the medicine along with the liquid. You may drink more liquid after taking the medicine.
Can you use a syringe for AccuSafe?
Measure the dose with the provided dose syringe (e.g., AccuSafe™) that comes with the package. Do not use any other syringe, dropper, spoon, or dosing device when giving this medicine to your child.
What does acteminophen do and how does it work?
Acetaminophen is a pain reliever and fever reducer. It is thought to work to relieve minor aches and pains by elevating the body's overall pain threshold so you feel less pain, and lowers your fever by helping your body eliminate excess heat.
What is acetaminophen used for?
Acetaminophen is most commonly used to treat minor aches and pains, including headache, backache, minor pain of arthritis, toothache, muscular aches, premenstrual and menstrual cramps. It is also commonly used to temporarily reduce fever.
Is acetaminophen an NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug)?
Acetaminophen is not an NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug), the other main type of pain reliever. Ibuprofen, Aspirin, and Naproxen sodium are NSAIDS and different than Acetaminophen.
What forms is acetaminophen available in?
Acetaminophen is an active ingredient in TYLENOL ® products and in more than 600 other over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medicines. Do not take more than one medicine containing acetaminophen at the same time.
Acetaminophen warnings and acetaminophen side effects for adults
Liver warning : This product contains acetaminophen. Severe liver damage may occur if you take more than 4,000 mg of acetaminophen in 24 hours, with other drugs containing acetaminophen, and/or 3 or more alcoholic drinks every day while using this product. Ask a doctor before use if you have liver disease.
What is the most important aspect of acetaminophen toxicity?
The most crucial aspect of acetaminophen toxicity is prevention. Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists all share in this responsibility. Pharmacists and nurses need to emphasize the maximum dose permitted daily. Patients also need to understand how to look for acetaminophen in various medications they take and how to calculate the dose they receive when they combine products. Pharmacists need to perform medication reconciliation to look for drug interactions, as well as verify that there are not too many acetaminophen-containing drugs in the regimen. If there are concerns, the pharmacist should report them to the nurse and physician.
How does acetaminophen affect the liver?
Acetaminophen is responsible for an estimated 500 deaths and 50000 emergency department visits in the United States each year.[9] It is the most common drug-related cause of acute liver failure. The mechanism of hepatic injury is due to the drug metabolism properties of acetaminophen.[10] Following therapeutic concentrations of oral acetaminophen, 60% to 90% of the drug gets metabolized in the liver to glucuronic acid- and sulfate-conjugate metabolites. A smaller fraction (approximately 5% to 15%) undergoes metabolism by the cytochrome P450 system (CYP450). Metabolism primarily via CYP2E1 results in the formation of the toxic intermediate N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). Normally, NAPQI is neutralized by glutathione to nontoxic metabolites. However, with excessive doses of acetaminophen, the normal phase II drug metabolism pathways become depleted, and the CYP450 pathway metabolizes a higher portion of the acetaminophen taken, resulting in high concentrations of NAPQI formation, and the limited glutathione stores can become depleted. Without glutathione, NAPQI concentrations build-up, and NAPQI, as a reactive intermediate, can react with cellular macromolecules, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. This phenomenon can lead to centrilobular (Zone 3) hepatic injury and hepatocellular death. There can also be nephrotoxicity.
What is the best antidote for acetaminophen overdose?
The only approved antidote for acetaminophen overdose and toxicity is N-acetylcysteine (NAC).[11] NAC is a precursor to glutathione synthesis and helps to restore the intracellular stores of glutathione to neutralize the NAPQI compound, and it can inactivate NAPQI directly. N-acetyl cysteine can be administered orally or by IV. IV N-acetyl cysteine is typically preferred because vomiting is common with acetaminophen overdose. It is effective when administered within the first few hours (up to 8 to 10 hours) of a toxic ingestion of acetaminophen. N-acetyl cysteine administration has a 20-hour IV protocol or 72-hour oral protocol, and the clinician must monitor the AST/ALT during treatment.[12] One important thing to keep in mind is that most patients do not have symptoms in the first few hours of ingestion of toxic doses of acetaminophen and may only have abdominal pain and nausea as symptoms for the first 12 to 24 hours. Between 24 and 72 hours, these symptoms may dissipate, although AST/ALT concentrations may be abnormal. Patients who present more than 24 hours following ingestion of toxic doses of acetaminophen may have symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, jaundice, abdominal pain, and hypotension. These patients may require airway management, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, hemodialysis, or management of cerebral edema or other symptoms as they arise.
Is acetaminophen a contraindication?
Contraindications to the use of acetaminophen include hypersensitivity to acetaminophen, severe hepatic impairment, or severe active hepatic disease. However, there is a general debate among experts whether hepatic impairment is truly a limiting factor, as it would likely be associated with decreased production of the toxic metabolite, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI).
Does acetaminophen cross the placental barrier?
Acetamino phen can cross the placental barrier, but there is no evidence of increased teratogenic effects due to the use of normal doses of acetaminophen during pregnancy.[8] Acetaminophen also is excreted into breast milk, but there have not been many observations of adverse reactions in nursing infants.
Does acetaminophen cause liver failure?
Acetaminophen use has been linked to liver failure and sometimes has led to liver transplant or death. The hepatotoxicity occurring with acetaminophen use typically correlates with high doses of acetaminophen that exceed the recommended maximum dose.[6] This effect may involve the intake of more than one drug product that contains acetaminophen as an ingredient. Liver damage also has been seen in patients with chronic dosing of acetaminophen.
Can acetaminophen be administered intravenously?
Acetaminophen can be administered orally, rectally, or intravenously (IV). [5]
What is acetaminophen used for?
Acetaminophen is used to relieve pain. Experts aren't sure exactly how acetaminophen works, but suspect it blocks a specific type of cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzyme, located mainly in the brain. Acetaminophen belongs to the class of medicines called analgesics (pain relievers); it is specifically a non-narcotic analgesic.
How long does acetaminophen last?
The pain-relieving effects of acetaminophen occur within 30-60 minutes of administration of the oral tablets. The effects last for three to four hours. 7. Interactions.
What medications interact with acetaminophen?
Common medications that may have a moderate interaction with acetaminophen include: anticonvulsants, such as carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, or phenytoin (may increase the conversion of acetaminophen to hepatotoxic metabolites) barbiturates. busulfan. carbamazepine.
Can you take acetaminophen and paracetamol at the same time?
Be careful not to administer other products containing acetaminophen or paracetamol at the same time. Acetaminophen is often an ingredient in combination cold and flu remedies.
Is acetaminophen generic?
Generic acetaminophen is available. 3. Downsides. If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: Rarely, may cause itchiness, constipation, nausea, vomiting, headache, insomnia, and agitation.
Can you use a kitchen teaspoon to dissolve acetaminophen?
Do NOT use a kitchen teaspoon. Shake liquid acetaminophen before use. Chewable tablets should be properly chewed before swallowing. Hands should be dry before handling the acetaminophen disintegrating tablet, then the tablet should be placed on the tongue and allowed to fully dissolve before swallowing.
Does acetaminophen cause liver damage?
Acetaminophen is an effective mild pain reliever with a low risk of side effects. It carries a risk of liver damage even at recommended dosages, but the risk is increased with higher dosages, a shorter interval between doses, in people who drink three or more alcoholic drinks per day, when taken with other medications that also contain acetaminophen, and in patients with pre-existing liver disease
Can you take paracetamol with liver disease?
Can paracetamol (acetaminophen) be administered to patients with liver impairment? Although 60 years have passed since it became widely available on the therapeutic market, paracetamol dosage in patients with liver disease remains a controversial subject. Fulminant hepatic failure has been a well documented consequence of paracetamol overdose ...
Is paracetamol safe for liver disease?
Although 60 years have passed since it became widely available on the therapeutic market, paracetamol dos age in patients with liver disease remains a controversial subject. Fulminant hepatic failure has been a well documented consequence of paracetamol overdose since its introduction, while short and long term use have both been associated ...
How long does it take for acetaminophen to raise serum levels?
Chronic therapy with acetaminophen in doses of 4 grams daily has been found to lead to transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels in a proportion of subjects, generally starting after 3 to 7 days, and with peak values rising above 3-fold elevated in 39% of persons. These elevations are generally asymptomatic and resolve rapidly with stopping therapy or reducing the dosage, and in some instances resolve even with continuation at full dose (Case 1).
How does acetaminophen cause hepatoxicity?
The injury is due to a direct, toxic effect of the high doses of acetaminophen. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity most commonly arises after a suicide attempt using more than 7.5 grams (generally more than 15 grams) as a single overdose (Case 2). Hepatic injury generally starts 24 to 72 hours after the ingestion with marked elevations in serum ALTand AST(often to above 2000 U/L), followed at 48 to 96 hours by clinical symptoms: jaundice, confusion, hepatic failure and in some instances death. Evidence of renal insufficiency is also common. Serum aminotransferase levels fall promptly and recovery is rapid if the injury is not too severe. Similar injury can occur with high therapeutic or supratherapeutic doses of acetaminophen given over several days for treatment of pain and not as a purposeful suicidal overdose (Case 3). This form of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity is referred to as accidental or unintentional overdose, and usually occurs in patients who have been fasting, or are critically ill with a concurrent illness, alcoholism or malnutrition, or have preexisting chronic liver disease. Some cases of unintentional overdose occur in patients taking acetaminophen in combinations with controlled substances (oxycodone, codeine), who take more than recommended amounts over several days in attempts to control pain or withdrawal symptoms. Instances of unintentional overdose in children are often due to errors in calculating the correct dosage or use of adult sized tablets instead of child or infant formulations. Because acetaminophen is present in many products, both by prescription and over-the-counter, another problem occurs when a patient ingests full or high doses of several products unaware that several contain acetaminophen.
How much acetaminophen is in a single overdose?
Acetaminophen (~10 g as a single overdose)
Is acetaminophen a hepatotoxic drug?
Acetaminophen is a widely used nonprescription analgesic and antipyretic medication for mild-to-moderate pain and fever. Harmless at low doses, acetaminophen has direct hepatotoxic potential when taken as an overdose and can cause acute liver injury and death from acute liver failure. Even in therapeutic doses, acetaminophen can cause transient serum aminotransferase elevations.
Is acetaminophen dangerous for liver?
Miller AL. Liver damage from chronic acetaminophen dosing is dangerous, but not the only risk. Altern Med Rev 2009; 14: 322-3. [PubMed: 20030459]
Does acetaminophen cause liver damage?
While acetaminophen has few side effects when used in therapeutic doses, recent reports suggest that its standard use can result in severe hypersensitivity reactions including Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Both of these syndromes can be life-threatening and both may be accompanied by evidence of liver injury. However, the hepatic involvement is usually mild and marked only by asymptomatic mild-to-moderate elevations in serum aminotransferase levels.
Who has the responsibility to determine the maximum acetaminophen dose?
Physicians, nurses, and pharmacists all share in this responsibility. Pharmacists and nurses need to emphasize the maximum dose permitted daily. Patients also need to understand how to look for acetaminophen in various medications they take and how to calculate the dose they receive when they combine products.
How long does it take for acetaminophen to dissipate?
Between 24 and 72 hours, these symptoms may dissipate, although AST/ALT concentrations may be abnormal. Patients who present more than 24 hours following ingestion of toxic doses of acetaminophen may have symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, jaundice, abdominal pain, and hypotension.
What is APAP in medical terms?
Acetaminophen (APAP) is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat pain and fever. It is used as a single agent for mild ...
What is the antidote for acetaminophen overdose?
The only approved antidote for acetaminophen overdose and toxicity is N-acetylcysteine (NAC). [11] . NAC is a precursor to glutathione synthesis and helps to restore the intracellular stores of glutathione to neutralize the NAPQI compound, and it can inactivate NAPQI directly.
How does acetaminophen affect the liver?
[9] It is the most common drug-related cause of acute liver failure. The mechanism of hepatic injury is due to the drug metabolism properties of acetaminophen. [10] Following therapeutic concentrations of oral acetaminophen, 60% to 90% of the drug gets metabolized in the liver to glucuronic acid- and sulfate-conjugate metabolites. A smaller fraction (approximately 5% to 15%) undergoes metabolism by the cytochrome P450 system (CYP450). Metabolism primarily via CYP2E1 results in the formation of the toxic intermediate N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). Normally, NAPQI is neutralized by glutathione to nontoxic metabolites. However, with excessive doses of acetaminophen, the normal phase II drug metabolism pathways become depleted, and the CYP450 pathway metabolizes a higher portion of the acetaminophen taken, resulting in high concentrations of NAPQI formation, and the limited glutathione stores can become depleted. Without glutathione, NAPQI concentrations build-up, and NAPQI, as a reactive intermediate, can react with cellular macromolecules, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. This phenomenon can lead to centrilobular (Zone 3) hepatic injury and hepatocellular death. There can also be nephrotoxicity.
How long does it take for N-acetyl cysteine to work?
It is effective when administered within the first few hours (up to 8 to 10 hours) of a toxic ingestion of acetaminophen.
Does acetaminophen inhibit the COX pathway?
It may be that acetaminophen inhibits the COX pathway in the central nervous system but not peripheral tissues. Additionally, acetaminophen does not appear to bind to the active site of either the COX-1 or COX-2 enzyme, instead of reducing the activity of COX by a different mechanism.
How It Works
This drug is used to treat mild to moderate pain (from headaches, menstrual periods, toothaches, backaches, osteoarthritis, or cold/flu aches and pains) and to reduce fever.
May Treat: Back pain · Arthritic pain · Dysmenorrhea · Fever · Headache disorder and more
Brand Names: Tylenol · Acephen · Ofirmev · Children's Non-Aspirin · Non-Aspirin Children's and more
Drug Class: Analgesic or Antipyretic Non-Opioid
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
May Treat: Back pain · Arthritic pain · Dysmenorrhea · Fever · Headache disorder and more
Brand Names: Tylenol · Acephen · Ofirmev · Children's Non-Aspirin · Non-Aspirin Children's and more
Drug Class: Analgesic or Antipyretic Non-Opioid
Availability: Prescription sometimes needed
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Does not adversely affect lactation
Alcohol: Limit intake while taking this medication
Upsides
Downsides
Bottom Line
Tips
Response and Effectiveness
- Effective for the temporary relief of minor aches, pains, and headache. May be used in the treatment of many conditions such as arthritis, backache, colds, menstruation pain, and toothache.
- Lowers a fever but does not control inflammation.
- First choice for mild-to-moderate pain due to its efficacy, minimal toxicity, and low cost.
- Effective for the temporary relief of minor aches, pains, and headache. May be used in the treatment of many conditions such as arthritis, backache, colds, menstruation pain, and toothache.
- Lowers a fever but does not control inflammation.
- First choice for mild-to-moderate pain due to its efficacy, minimal toxicity, and low cost.
- At low dosages, it lacks the gastrointestinal side effects associated with NSAID pain relievers (does not cause ulcerations, bleeding, or perforations).
Interactions
- If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: 1. Rarely, may cause itchiness, constipation, nausea, vomiting, headache, insomnia, and agitation. May cause gastrointestinal side effects at high dosages. 2. The potential for liver damage exists, even at recommended dos…
References
- Acetaminophen is an effective mild pain reliever with a low risk of side effects. It carries a risk of liver damage even at recommended dosages, but the risk is increased with higher dosages, a sho...
Further Information
- May be administered without regard to food; although food may decrease any reported stomach upset.
- Do not exceed the recommended dosage, because this may put you at risk of liver toxicity. Adults and teenagers who weigh at least 110 pounds (50kg) should not take more than 1000mg of acetaminophen...
- May be administered without regard to food; although food may decrease any reported stomach upset.
- Do not exceed the recommended dosage, because this may put you at risk of liver toxicity. Adults and teenagers who weigh at least 110 pounds (50kg) should not take more than 1000mg of acetaminophen...
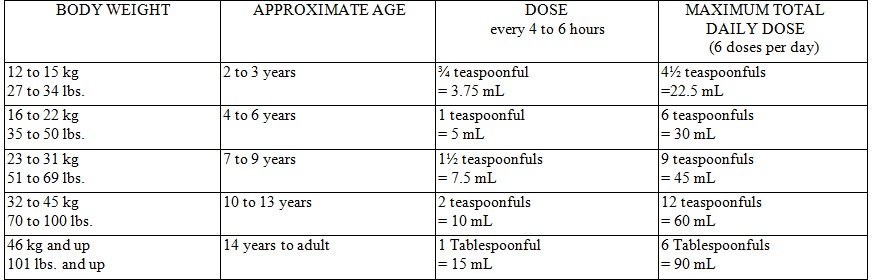
- Always seek your doctor's advice before administering acetaminophen to children aged less than two. If you are giving pediatric acetaminophen, always use the dosing syringe provided, or another sui...
- Shake liquid acetaminophen before use. Chewable tablets should be properly chewed before swallowing. Hands should be dry before handling the acetaminophen disintegrating tablet, th…