Explore
Treatment depends on the specific case. If the adnexal mass is benign and isn’t causing any pain, then your healthcare provider will likely monitor the situation with periodic imaging tests. However, if the tumor grows, if you have increased pain, internal bleeding, or if it is cancerous, surgery will be recommended.
Is surgery needed for an adnexal mass?
When symptoms are present, they often present as:
- Pelvic pain
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Difficulty urinating or the frequent urge to do so
- Constipation
- Gastrointestinal problems
What are the symptoms of adnexal mass?
An adnexal mass, or adnexal cyst, is a growth that occurs in or near the organs attached to the uterus in women. This is what is called the adnexa region and includes the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and the connecting tissues. Women of all ages may develop an adnexal mass, especially in the ovaries.
Where is adnexal cyst located?
What does adnexal tenderness indicate? Adnexal tenderness is a slight pain or tender feeling in the pelvic region, including your uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Adnexal tenderness that persists over a long period of time could be due to a cyst or other condition within your adnexal region.
What is adnexal tenderness?
How is adnexal cyst treated?
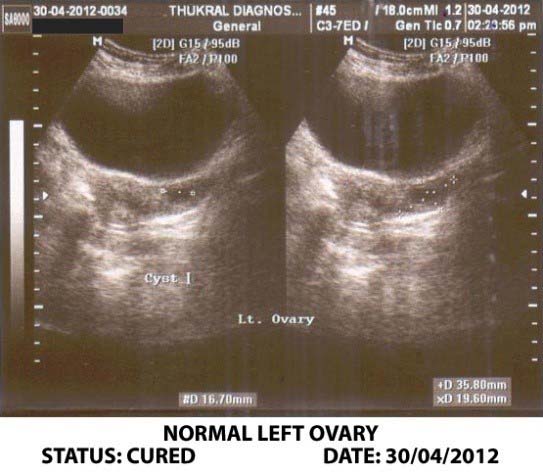
How Are Adnexal Cysts Treated? The majority of ovarian cysts (both fluid-filled and hemorrhagic) resolve spontaneously and require no intervention. Pelvic ultrasound is often repeated after 1-2 menstrual cycles to check for ovarian cyst resolution.
What is the most common adnexal mass?
In premenopausal women, physiologic follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts are the most common adnexal masses, but the possibility of ectopic pregnancy must always be considered. Other masses in this age group include endometriomas, polycystic ovaries, tubo-ovarian abscesses and benign neoplasms.
Is adnexal mass serious?
The majority of adnexal masses aren't harmful. They won't require treatment unless a woman is experiencing uncomfortable symptoms. Many adnexal masses will resolve themselves without any intervention. In a very small number of cases, the cause of the adnexal mass will be ovarian cancer.
How do you know if adnexal mass is cancerous?
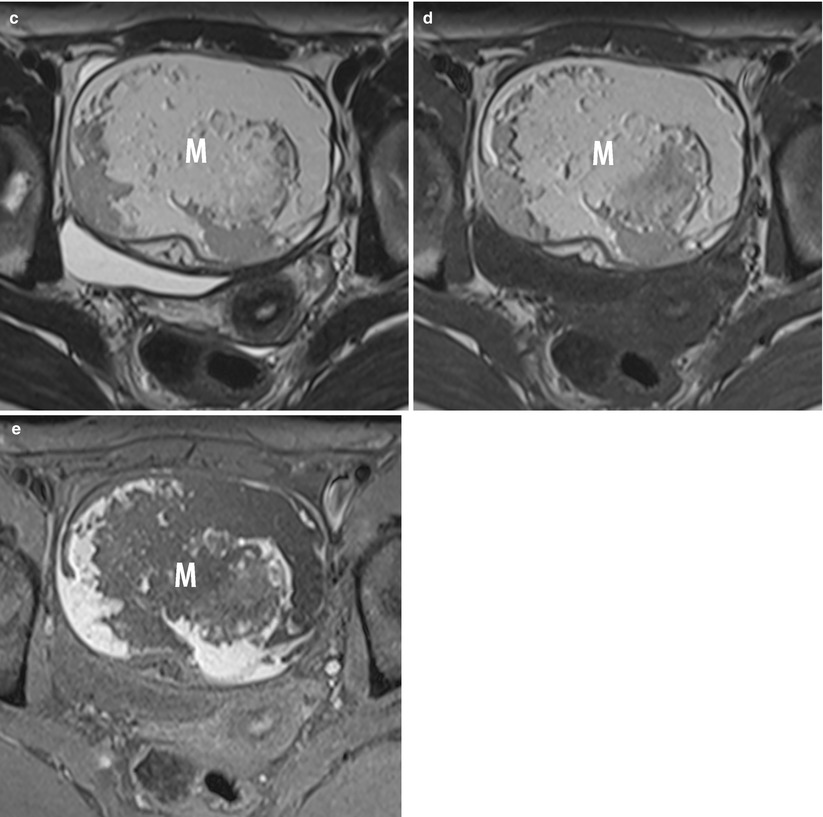
Transvaginal ultrasonography remains the standard for evaluation of adnexal masses. Findings suggestive of malignancy in an adnexal mass include a solid component, thick septations (greater than 2 to 3 mm), bilaterality, Doppler flow to the solid component of the mass, and presence of ascites.
Can adnexal mass be cured?
Most adnexal tumors are benign (noncancerous), but they can be malignant (cancerous). Many adnexal masses go away on their own, but some require treatment, which may include surgery.
What is the normal size of adnexal mass?
Results: One hundred and eighty-six women underwent laparoscopic evaluation for an adnexal mass of 10 cm or larger in size. The average preoperative mass size was 12.1 +/- 4.9 cm.
When should an adnexal cyst be removed?
Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous.
Where is an adnexal mass located?
A lump in tissue near the uterus, usually in the ovary or fallopian tube. Adnexal masses include ovarian cysts, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, and benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) tumors.
What does Adnexa mean on an ultrasound?
INTRODUCTION. Adnexa refer to the anatomical area adjacent to the uterus, and contains the fallopian tube, ovary, and associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue.
Can an adnexal mass be a fibroid?
Some of the causes of adnexal masses include: Ectopic pregnancy: A pregnancy where the fertilized egg implants somewhere outside the uterus. Endometrioma: A benign cyst on the ovary that contains thick, old blood that appears brown. Leiomyoma: A benign gynecological tumor, also known as a fibroid.
Do adnexal cysts cause pain?
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst An ovarian cyst usually only causes symptoms if it splits (ruptures), is very large or blocks the blood supply to the ovaries. In these cases, you may have: pelvic pain – this can range from a dull, heavy sensation to a sudden, severe and sharp pain. pain during sex.
Is Adnexa and ovary the same?
Adnexa is a Latin word meaning attachment or appendages. It refers to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and ligaments that hold the reproductive organs in place. These are all located in your lower abdomen near your pelvic bone.
What is right adnexal mass?
Listen to pronunciation. (ad-NEK-sul…) A lump in tissue near the uterus, usually in the ovary or fallopian tube. Adnexal masses include ovarian cysts, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, and benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) tumors.
When should an adnexal cyst be removed?
Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous.
What are adnexal masses?
Adnexal tumors are growths near the uterus. They're also known as adnexal masses. They usually form in the ovaries, which make eggs and hormones, or the fallopian tubes, which connect your uterus and ovaries. The tumors can form in the connective tissue around this part of your body.
Can an adnexal mass be a fibroid?
Some of the causes of adnexal masses include: Ectopic pregnancy: A pregnancy where the fertilized egg implants somewhere outside the uterus. Endometrioma: A benign cyst on the ovary that contains thick, old blood that appears brown. Leiomyoma: A benign gynecological tumor, also known as a fibroid.
What is an adnexal mass?
An adnexal mass refers to a growth that develops in the female pelvic region. Adnexal masses occur near the uterus, usually in the ovaries, fallopi...
What causes an adnexal mass?
There are multiple causes of adnexal mass development. Gynecologic causes, meaning that masses originate from the reproductive system, are the most...
Does having an adnexal mass mean cancer?
Adnexal masses are not necessarily cancerous. They may be malignant in some cases, but most commonly, adnexal masses are benign, or not cancerous.
What are the symptoms of having an adnexal mass?
Symptoms associated with adnexal masses often differ depending on what caused the mass to form. Pelvic pain is a common symptom, and it can suggest...
How is an adnexal mass diagnosed?
When evaluating adnexal masses, a review of medical history, with a detailed gynecologic and family history, and a careful review of symptoms are o...
How is an adnexal mass treated?
Treatment options for adnexal masses vary depending on the specific diagnosis. Some masses can be treated conservatively, and others may require su...
What are the most important facts to know about adnexal masses?
Adnexal masses include different types of growths near the uterus, in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or connecting tissues. In most cases, they are...
What is an adnexal mass?
An adnexal mass refers to a growth that develops in the female pelvic region. Adnexal masses occur near the uterus, usually in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or connecting tissues. These growths can originate from either the reproductive system or nearby pelvic organs, such as the intestines or the urinary bladder. Adnexal masses usually are not cancerous (i.e., benign), but they can be cancerous (i.e., malignant) in some cases.
How is an adnexal mass diagnosed?
When evaluating adnexal masses, a review of medical history, with a detailed gynecologic and family history, and a careful review of symptoms are often necessary.
What are the most important facts to know about adnexal masses?
The causes of adnexal masses vary and can be either gynecologic or non-gynecologic. Common symptoms associated with adnexal masses include irregular vaginal bleeding, bloating, dyspareunia, urinary symptoms, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis of adnexal masses involves medical history review and physical examination. Blood tests and imaging may be necessary for diagnosis in rare cases. Treatment for adnexal masses largely depends on the underlying cause and can be either conservative or surgical.
What causes adnexal masses?
Common symptoms associated with adnexal masses include irregular vaginal bleeding, bloating, dyspareunia, urinary symptoms, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis of adnexal masses involves medical history review and physical examination.
What is the procedure for a benign cyst?
For benign masses, minimally invasive techniques are the preferred method of intervention. One such method is laparoscopy, which allows the surgeon to access the inside of the abdomen through small incisions in the skin. In cases of larger or malignant cysts that cannot be extracted laparoscopically, open surgery may be required.
Can adnexal masses cause genital pain?
Lastly, dyspareunia, or genital pain during sexual intercourse, may be experienced by individuals with adnexal masses.
How Are Adnexal Tumors Treated?
The treatment for an adnexal tumor will depend on several factors, including what's causing it and where it's located. Generally, there are three options for treating adnexal masses:
Where do adnexal tumors form?
Adnexal tumors are growths near the uterus. They're also known as adnexal masses. They usually form in the ovaries, which make eggs and hormones, or the fallopian tubes, which connect your uterus and ovaries. The tumors can form in the connective tissue around this part of your body. Many conditions can cause an adnexal tumor and they can happen at any age.
What to do if you have a mass on your thigh?
Surgery. You may need to have surgery to remove the mass or take a sample of it if your doctor thinks it's cancer or if it's causing you problems.
Does adnexal mass go away on its own?
Expectant management. If your adnexal mass is not cancerous and your doctor thinks it will go away on its own, you may not need any treatment or follow-up care. This may be the case if you have a small cyst that will probably go away.
How to diagnose adnexal mass?
Adnexal masses are usually diagnosed by a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or both. Often, in cases when the woman isn’t showing any symptoms, the growth is detected during routine exams. Once diagnosed, your doctor will decide if your case is an emergency. Usually it’s not, and your doctor will have time to investigate what’s causing the mass and ...
Where does an adnexal mass occur?
An adnexal mass is a growth that occurs in or near the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the connecting tissues. They’re usually benign, but are sometimes cancerous. Some of them are filled with fluid, and some are solid.
What tests can be used to determine the cause of adnexal mass?
Imaging and lab tests can be used to determine the underlying cause of the adnexal mass. Your doctor will also probably have you take a pregnancy test to rule out an ectopic pregnancy, since this will need immediate treatment.
When should adnexal masses be discovered?
However, adnexal masses are sometimes discovered during a pregnancy when having routine ultrasounds or pelvic exams.
Can you have surgery for a small adnexal mass?
If the adnexal mass is small and you have no symptoms, then it may not require treatment at all. However, your doctor will likely want to monitor you with regular pelvic exams and ultrasounds. Surgery will be needed if: the mass begins to grow. you develop symptoms.
Is adnexal mass malignant?
your doctor suspects that the adnexal mass is malignant. the mass is so big that it’s likely to cause a problem with the pregnancy. About 10 percent of adnexal masses discovered in pregnancy are malignant, according to one 2007 clinical review. Even in these cases, the cancer is usually in its early stages.
Is it safe to monitor adnexal mass during pregnancy?
Since the majority of adnexal masses aren’t harmful and mostly resolve on their own, it’s usually considered appropriate to monitor the mass closely during pregnancy without treatment.
What is an adnexal mass?
Adnexal masses are lumps that occur in the adnexa of the uterus, which includes the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. They have several possible causes, which can be gynecological or nongynecological.
Why do doctors need to pinpoint the location and cause of an adnexal mass?
Doctors need to pinpoint the location and cause of an adnexal mass to determine the appropriate management and treatment.
What are the symptoms of adnexal mass?
People with an adnexal mass may report: severe lower abdominal or pelvic pain that is usually on one side. abdominal symptoms, including a feeling of fullness, bloating, constipation, difficulty eating, increased abdominal size, indigestion, nausea, and vomiting.
What is a gynecological emergency involving a complete or partial rotation of the tissue that?
Ovarian torsion: A gynecological emergency involving a complete or partial rotation of the tissue that supports the ovary, which cuts off blood flow to the ovary.
Can you get antibiotics for a tubo ovarian abscess?
However, doctors can now prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics. A person with a ruptured tubo-ovarian abscess may still require surgery.
Can endometrioma be managed?
Doctors have not yet determined the optimal management of an endometrioma, according to a study that featured in Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey.
Can a family doctor treat a benign adnexal mass?
A family doctor can usually manage benign masses. However, prepubescent and postmenopausal individuals will need to see a gynecologist or oncologist. Malignant adnexal masses require treatment from a specialist. In this article, we discuss the characteristics of adnexal masses.
What is the adnexal mass?
An adnexal mass, or adnexal cyst, is a growth that occurs in or near the organs attached to the uterus in women. This is what is called the adnexa region and includes the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and the connecting tissues. Women of all ages may develop an adnexal mass, especially in the ovaries.
Where does adnexal mass originate?
Usually, an adnexal mass or cyst affects the adnexa, but when it is metastatic in nature, it may originate somewhere else, such as in the breast or stomach. An adnexal cyst can be found in women of all ages. A malignant adnexal cyst may develop in females as young as 15, but more often, the mass is a functional cyst that will likely disappear on ...
What is a complex adnexal mass?
A complex adnexal mass or cyst can be further classified into categories of dermoid cysts, endometriomas, and low malignant tumors. There are thought to be hundreds of adnexal mass causes. Adnexal cyst symptoms are often similar ...
What causes adnexal cysts?
Causes of Adnexal Cyst and Mass Growth . There are a variety of different adnexal cysts and masses. Some fluid-filled growths arise in the woman’s ovaries; others have both solid and liquid matter (called septated) and are especially dangerous.
What are the symptoms of a cyst in the adnexal region?
It is important to consult your doctor if you experience any of the following adnexal cyst symptoms, since they may also be present in other conditions and further investigation is likely required. Pain or pressure in the pelvic region. Abdominal distension. Constipation and gastrointestinal disorders.
How to diagnose adnexal cyst?
Diagnosing Adnexal Cyst and Mass. A physical pelvic exam will help the doctor diagnose an adnexal cyst or mass. The doctor will feel the woman’s ovaries, uterus, vagina, bladder, and rectum, and make note of a lump or anything else unusual.
Can ovarian cysts cause adnexal cysts?
Ovarian Cysts. Ovarian cysts will also cause adnexal cysts. These liquid-filled sacs will develop on the ovaries; however, ovarian cysts are often painless and don’t produce symptoms. When it contains tissue from the endometrium or uterine lining, this type of ovarian cyst is called an endometrioma.
Why is a cystadenoma removed?
Cystadenoma – Surgical removal is recommended to prevent growth, torsion, rupture, and rule out malignancy. Other benign tumors of the ovary – Surgical removal is recommended to prevent growth, torsion, rupture, and rule out malignancy.
Can a tumor spread to the adnexal region?
Other cancers, especially from breast and the gastrointestinal tract, may spread to the adnexal region as well. Fibroid – This is a benign tumor of the uterine muscle that may grow adjacent to the uterus, presenting itself in the adnexal region. See website link Fibroids. If the ovarian mass is large, ovarian torsion can occur.
What is an adnexal mass?
Management/Treatment. An adnexal mass is an abnormal growth that develops near the uterus, most commonly arising from the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or connective tissues. The lump-like mass can be cystic (fluid-filled) or solid.
What is the best doctor for adnexal mass?
If an adnexal mass is found and cancer is suspected, it is always best to get a second option from a gynecologic oncologist who will be more experienced in the diagnosis, staging, and of treatment of endometrial and ovarian cancers.
Can adnexal masses be benign?
While most adnexal masses will be benign (noncancerous), they can sometimes be malignant (cancerous). 1. Adnexal masses may occur at any age, although they are more typically seen in women of reproductive age. skaman306 / Getty Images.
Is an adnexal mass a cause for alarm?
In most cases, an adnexal mass will not be a cause for alarm and may never present any health problems to the woman.
Can an adnexal mass be alarming?
In most cases, an adnexal mass will not be a cause for alarm and may never present any health problems to the woman. With that being said, doctors will pay particular attention to any masses or lesions that appear in or around the ovaries or in fallopian tubes. Studies have shown that growths in the fallopian tubes often serve as precursors ...