Common tests & procedures
What causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)? CAH is caused by changes (mutations) in one of several genes. These changes lead to deficiencies in 21-hydroxylase or, less commonly, 11-hydroxylase. Both of these are chemicals called enzymes.
What is the cause of adrenal hyperplasia?
- The test will measure the levels of estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone in the blood.
- It will take several weeks for your vet to receive the test results. ...
- While waiting for the test results, your vet may want to perform other diagnostic tests, like ultrasound, that can help diagnose adrenal disease.
How to diagnose adrenal diseases?
With proper treatment, children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia can live normal lives and participate fully in school and other activities. Girls with CAH may also grow and develop normally, have regular menstrual cycles and have children.
What is the prognosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)?
The symptoms of nonclassic CAH include:
- Early signs of puberty, including acne and excess facial or body hair in females
- Rapid growth in childhood and as a teenager
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Male-pattern baldness
- Early puberty changes in a boy, for example early pubic hair and an enlarged penis but with small testicles
- Infertility
What are the symptoms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)?

How is non classic adrenal hyperplasia diagnosed?
How Is Nonclassical Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Diagnosed? Your doctor will test for hormone levels in the blood. If symptoms show up later in life, your doctor might conduct blood tests to check your adrenal steroid levels. You might also take an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test.
Can you see adrenal hyperplasia on ultrasound?
CAH can be diagnosed prenatally via amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, or after birth using serum blood tests and ultrasonography. Patients with CAH are closely monitored during glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement therapy to prevent salt wasting.
What is the most common reason hyperplasia of adrenal?
The most common cause of CAH is the lack of the enzyme known as 21-hydroxylase. CAH may sometimes be called 21-hydroxylase deficiency. This enzyme is required by the body to make proper amounts of hormones. There are other much rarer enzyme deficiencies that also cause CAH .
What is the treatment of adrenal hyperplasia?
Classic CAH is treated with steroids that replace the low hormones. Infants and children usually take a form of cortisol called hydrocortisone. Adults take hydrocortisone, prednisone, or dexamethasone, which also replace cortisol.
How do you test for hyperplasia?
An ACTH stimulation test is used to diagnose congenital adrenal hyperplasia and determine the type your child has. Blood samples are taken before and after giving your child an injection of synthetic ACTH, or adrenocorticotropic hormone, which signals the adrenal glands to release the hormone cortisol.
What causes thickening of the adrenal gland?
Hyperaldosteronism: This condition is caused by a small tumor in the adrenal gland that makes too much aldosterone or an enlargement (hyperplasia) of the adrenal glands. A high level of aldosterone plays a part in the body's salt and potassium balance, and may cause high blood pressure.
What is the prognosis for adrenal hyperplasia?
Outlook / Prognosis Most people with CAH have good health, but you may be shorter than other adults. In some cases, congenital adrenal hyperplasia can affect your fertility. If you were born with ambiguous genitalia, you may need psychological care.
What are the signs of adrenal gland problems in females?
Signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency may include:Fatigue.Body aches.Unexplained weight loss.Low blood pressure.Lightheadedness.Loss of body hair.Skin discoloration (hyperpigmentation)
What is female adrenal hyperplasia?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an inherited disorder that results in low levels of cortisol and high levels of male hormones, causing development of male characteristics in females, and early puberty in both boys and girls.
What happens if congenital adrenal hyperplasia is not treated?
If not found and treated, classic CAH can cause shock, coma, and death. Nonclassic CAH is a more common, less severe condition in which there is still some adrenal steroid 21-hydroxylase enzyme activity remaining. It is usually diagnosed in later childhood or adulthood.
What is the most common type of congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
The most common form of CAH, 21 hydroxylase deficiency, affects approximately 1:10,000 to 1:15,000 people in the United States and Europe. Among the Yupik Eskimos, the occurrence of the salt-wasting form of this disorder may be as high as 1 in 282 individuals.
What is hyperplasia of the adrenal gland?
Cortical hyperplasia is a benign enlargement of the gland. Normal adrenal gland size differs between two sides. They are characterized by signs and symptoms of Cushing syndrome due to increased cortisol secretion. This activity highlights the diagnosis and treatment of this condition by an interprofessional team.
How do you get Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia?
Cause. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disorder. In children with CAH, the gene (21-hydroxylase) that makes the enzyme needed to produce cortisol and aldosterone is not working properly. In order for a child to be born with CAH, both parents must be carriers of the mutated gene and pass it on to their baby.
Does CAH shorten life expectancy?
Deaths in patients with classic CAH in the context of an acute adrenal crisis (Addisonian crisis) are described in the literature. Mortality in CAH children is generally considered higher and assumed to be between 2 and 13% [17–19, 21].
What is congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency?
21-hydroxylase deficiency is one of a group of disorders known as congenital adrenal hyperplasias that impair hormone production and disrupt sexual development. 21-hydroxylase deficiency is responsible for about 95 percent of all cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
What is salt wasting congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
Salt-wasting CAH. Salt-wasting CAH is the severe form of classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. In this type of CAH, the adrenal glands make too little aldosterone, causing the body to be unable to retain enough sodium (salt). Too much sodium is lost in urine (thus the name, "salt-wasting").
How to tell if a baby has adrenal hyperplasia?
Infants with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia have the following signs and symptoms: Male-like genitalia in girls. Larger than normal penis in boys. Stunted growth. Loss of weight, dehydration, vomiting.
What to do if your child has congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
You may obtain certain prenatal treatments that reduce risk for the baby in your womb.
What is the name of the deficiency of 21-hydroxylase?
Therefore, congenital adrenal hyperplasia can also be called 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Lower the enzyme production, more severe are the signs and symptoms. Insufficient cortisol causes most of the symptoms of classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Cortisol, also called stress hormone, regulates your blood pressure, blood sugar and energy levels.
What is the disorder of the adrenal glands?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a disorder of your small hormone-secreting glands called adrenal glands. Faulty genes cause reduced production of a specific enzyme called 21-hydroxylase which results in decreased secretion of cortisol. Therefore, congenital adrenal hyperplasia can also be called 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
What is it called when your adrenal glands are insufficient?
The genetic disorders in which your adrenal glands produce insufficient adrenal hormones such as cortisol, mineralocorticoids and androgens are called congenital adrenal hyperplasia. These hormonal deficiencies result in stunted growth and development including that of the genitals.
How to treat Cushing's syndrome?
The doses can differ depending upon your child’s condition and in some cases, more than one drug may be used. Steroids commonly cause side effects like reduced bone mass and stunted growth which need regular monitoring to detect treatment effectiveness or dose adjustments. For girls with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a high dose of cortisone may be needed to suppress development of male-like characteristics but a high of the steroid can cause Cushing's syndrome. So maintaining the right dose is important.
What are the signs of adolescence?
Adolescent girls and women usually have the following signs and symptoms: Abnormal or missed menstruation. Male- like physical characteristics including facial hair, excessive body hair and a low-pitched voice. Fertility problems . While in females and males, following signs and symptoms may be observed:
What test is used to diagnose adrenal hyperplasia in an unborn child?
Prenatal tests, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, can be used to diagnose congenital adrenal hyperplasia in an unborn child. Your obstetrician may recommend these tests if the child has an older sibling with the condition or if a family member has congenital adrenal hyperplasia or carries a gene mutation that decreases production of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase.
When does adrenal hyperplasia start?
Both girls and boys with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia may experience early puberty, which can begin at around age eight for girls and nine for boys. Symptoms of the mildest type, called nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia, are not usually noticed unless girls and boys experience symptoms that mimic early puberty, ...
What is ACTH test?
An ACTH stimulation test is used to diagnose congenital adrenal hyperplasia and determine the type your child has. Blood samples are taken before and after giving your child an injection of synthetic ACTH, or adrenocorticotropic hormone, which signals the adrenal glands to release the hormone cortisol. The first blood test establishes ...
What is the purpose of amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling?
Both amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling are used to determine whether an unborn child carries gene mutations associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In amniocentesis, your doctor removes a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the unborn child. In chorionic villus sampling, your doctor removes a sample of tissue from the placenta, a temporary organ that delivers oxygen and nutrients to a baby in the womb.
What is the name of the condition in which the adrenal glands produce abnormal levels of certain hormones?
Specialists at Hassenfeld Children’s Hospital at NYU Langone are experienced in diagnosing congenital adrenal hyperplasia, an inherited condition in which the adrenal glands produce abnormal levels of certain hormones, including cortisol and aldosterone. These hormones play an important role in many body functions, such as growth and blood pressure.
What happens if a child has adrenal hyperplasia?
It can cause vomiting, weight loss, and dehydration in the first few weeks of life.
What hormones are produced by the adrenal glands?
The adrenal glands also produce androgens, hormones that promote muscle growth and cause the development of underarm and pubic hair during puberty. Children who inherit two mutations in the gene that makes 21-hydroxylase, called CYP21A2, don’t have enough cortisol and aldosterone.
What is the rarest form of adrenal hyperplasia?
There are two major types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Classic CAH. This form is rarer and is usually detected in infancy. Approximately two-thirds of people who have classic CAH have what's known as the salt-losing form, while one-third have what's referred to as the simple-virilizing form. Nonclassic CAH.
What is the name of the disorder that affects the adrenal glands?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the adrenal glands, a pair of walnut-sized organs above the kidneys. The adrenal glands produce important hormones, including: Cortisol, which regulates the body's response to illness or stress. Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, ...
How is CAH detected?
Classic CAH is usually detected at birth through required newborn screening or when female babies have ambiguous genitalia. CAH may also be identified when male or female babies show signs of severe illness due to low levels of cortisol, aldosterone or both.
What are the signs of CAH?
Signs and symptoms of classic CAH in children and adults include: Appearance of pubic hair at a very early age. Rapid growth during childhood, but shorter than average final height.
When does CAH become evident?
Nonclassic CAH. This form is milder and more common, and may not become evident until childhood or early adulthood.
Does CAH cause adrenal crisis?
Aldosterone also may be low, which leads to dehydration and low sodium and high potassium levels. The nonclassic form of CAH doesn't cause adrenal crisis. Males and females who have either classic or nonclassic CAH may also experience fertility problems.
Can you have adrenal hyperplasia with a cure?
In people who have CAH, a genetic problem results in a lack of one of the enzymes needed to make these hormones. Although there is no cure, with proper treatment, most people who have congenital adrenal hyperplasia can lead normal lives . There are two major types of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Classic CAH.
What is the best treatment for adrenal crisis?
Adrenal crisis can present as hypotension or shock and serum electrolyte abnormalities (hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, acidosis). During adrenal crisis, an immediate bolus of hydrocortisone 50-100 mg can be given intravenously or intramuscularly followed by hydrocortisone 100 mg/m2/day given as either continuous infusion or divided at least every 6 hours. Rehydration can be started with 20ml/kg isotonic saline with D5 as rapid bolus followed by repeat boluses or continuous infusion guided by level of dehydration. Hypoglycemia may require dextrose bolus and an initial bolus of 0.5-1 gram/kg of dextrose can be given intravenously at 2-3 ml per minute. If hyperkalemia is present, cardiac monitoring should be done to monitor for EKG changes. If changes are present, hyperkalemia should be treated using insulin with glucose infusion with or without other measures.
When can you test for CAH in utero?
Prenatal testing for CAH in utero has historically utilized invasive techniques like amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling which cannot be done prior to 14 weeks of gestation. Prenatal dexamethasone treatment must begin prior to genital formation occurring at approximately 9 weeks, in order to avoid genital ambiguity in the affected female fetus. Massive parallel sequencing using hybridization probes on cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma indicated that the fetal CAH status was correctly deduced as early as 5 weeks 6 days of gestation. This is a noninvasive technique that accurately diagnoses CAH before the ninth week of gestation.
What is CAH in medical terms?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders that arise from defective steroidogenesis. The production of cortisol in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex occurs in five major enzyme-mediated steps.
What is the cause of CAH?
The production of cortisol in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex occurs in five major enzyme-mediated steps. CAH results from deficiency in any one of these enzymes. Impaired cortisol synthesis leads to chronic elevations of ACTH via the negative feedback system, causing overstimulation of the adrenal cortex and resulting in hyperplasia ...
How to treat CAH?
The goal of therapy in CAH is to both correct the deficiency in cortisol secretion and to suppress ACTH overproduction. Proper treatment with glucocorticoid reduces stimulation of the androgen pathway, thus preventing further virilization and allowing normal growth and development. The usual requirement of hydrocortisone (or its equivalent) for the treatment of classical 21-OHD form of CAH is about 10-15 mg/m2/day divided into 2 or 3 doses per day and for non-classical 21-OHD 5-8 mg/m2/day divided into 2 or 3 doses per day. Hydrocortisone is the glucocorticoid of choice in the pediatric age group. Prednisolone and dexamethasone are not used in growing children given growth suppressive effects. A small dose of dexamethasone at bedtime (0.25 to 0.5 mg) is usually adequate for androgen suppression in non-classical adult patients. Adequate biochemical control is assessed by measuring serum levels 17-OHP and androstenedione; serum testosterone can be used in females and prepubertal males (but not newborn males). We recommend that hormone levels are measured at a consistent time in relation to medication dosing, usually 1-2 hours after the morning corticosteroid. Titration of the dose should be aimed at maintaining 17-OHP concentrations below 1000 ng/dL and androstenedione concentrations below 200 ng/dl. Over-treatment should be avoided because it can lead to Cushing syndrome. Patients with salt wasting CAH have elevated plasma renin in response to the sodium-deficient state, and they require treatment with the salt-retaining 9α-fludrocortisone acetate. The average dose is 0.1 mg daily (0.05-0.2 mg daily). Infants should also be started on salt supplementation, as sodium chloride, at 1-2 g daily, divided into several feedings. Measurements of plasma renin and aldosterone are used to monitor the efficacy of mineralocorticoid therapy. Advancement of bone age is monitored by bone age x-rays. Growth hormone therapy, in conjunction with a GnRH analogue, has been shown to be effective in improving final adult height. Patients may also experience peripheral precocious puberty, which requires treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues. Aromatase inhibitors and growth hormone therapy should only be used in patients with a very short predicted final stature or in clinical trials. Use of aromatase inhibitors in CAH has been shown decrease bone maturation rates and some increase in adult height but the differences were not statistically significant.
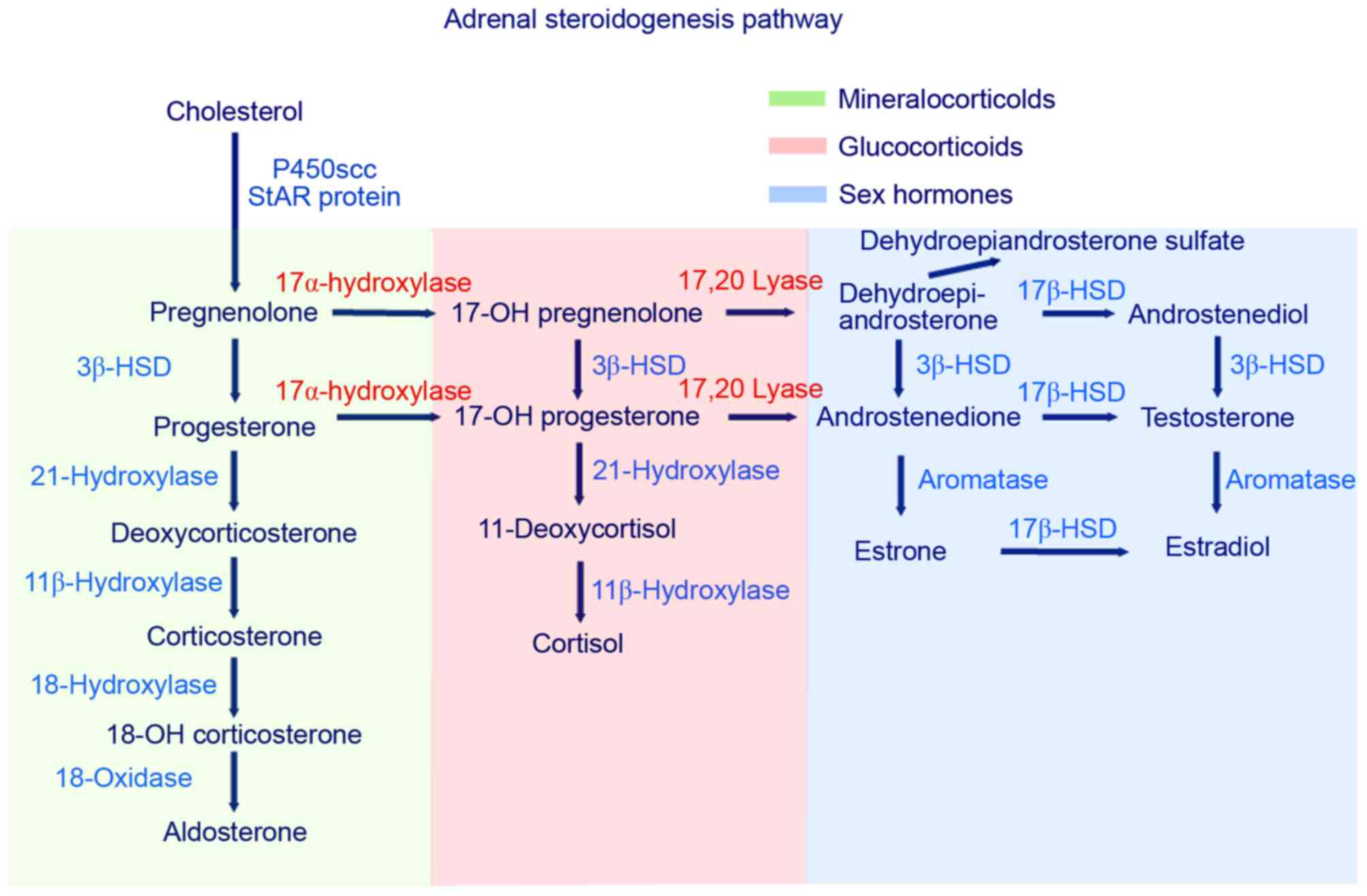
Which pathway is involved in adrenal steroidogenesis?
Adrenal steroidogenesis occurs in three major pathways: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and sex steroids as shown in Figure 1. Glucocorticoids (particularly cortisol), androgens, and estrogens are synthesized in the zona fasciculata and reticularis; and aldosterone in the zona glomerulosa.
Does cortisol increase ACTH?
Therefore, a decrease in cortisol secretion leads to increased ACTH production, which in turn stimulates (1) excessive synthesis of adrenal products in those pathways unimpaired by the enzyme deficiency and (2) an increase of precursor molecules in pathways blocked by the enzyme deficiency. Figure 1.
When is CAH diagnosed?
This screening determines whether a child has classic CAH. In almost all cases, doctors diagnose classic CAH in infants and young children. Diagnosis of nonclassic CAH may not occur until a person begins to show symptoms of the disease. In some cases, this may not happen until early adulthood.
How many adrenal glands are there in the kidney?
You have one adrenal gland on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands produce several important hormones your body needs. In CAH, genetic mutations (changes) cause shortages of certain enzymes, such as 21-hydroxylase, that help your body produce needed hormones.
What is CAH in medical terms?
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a genetic condition you are born with. It impacts your adrenal glands. With treatment, many people find symptom relief and lead healthy lives.
What enzyme is needed for CAH?
For people living with classic CAH, symptoms occur due to a lack of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase. Doctors group classic CAH into 2 subcategories: salt-wasting CAH and simple virilizing (non-salt-wasting) CAH.
Why do people with CAH have genetic testing?
Some couples at higher risk, including those with family members diagnosed with CAH, may have genetic testing to determine the risk of passing on genetic mutations to their children.
Can adrenal hyperplasia be prevented?
There is no way to prevent congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Can you get treatment for CAH?
People living with nonclassic CAH who have very mild or no symptoms may not need treatment. For some, medications like steroids or fertility drugs improve symptoms.
How to diagnose adrenal hyperplasia?
Laboratory diagnostics of adrenal hyperplasia involves two methods - enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) and radioimmunoassay (RIA). In the first case, the amount of hormones in the blood serum is detected, and in the second case, the presence of free cortisol in urine and cortisol in the blood. RIA by studying the blood plasma allows you to determine the number of aldosterone and the presence of renin. The inclusions of 11-oxycorticosteroids give information on the glucocorticoid function of the adrenal glands. It is possible to evaluate the functioning of the androgenic and partially glucocorticoid component by releasing free dehydroepiandrosterone in the urine. As for functional tests, dexamethasone samples are used that help differentiate hyperplasia or adrenal tumor processes from similar in clinical signs.
When is adrenal hyperplasia diagnosed?
Adrenal hyperplasia is differentiated immediately after birth or in the first years of life, more often pathology is found in female infants. An important role is assigned to the early diagnosis of the disease, since the neglected process most unfavorably affects all body systems - digestive, nervous, vascular, and the like.
What causes hyperplasia of the adrenal glands?
The causes of hyperplasia of the adrenal glands depend on the type of disease. The emergence of a congenital form of pathology common in clinical practice is preceded by severe functional disorders of the pregnant woman's body.
How to detect diffuse hyperplasia of the left adrenal gland?
Diffuse hyperplasia of the left adrenal is differentiated by computer or magnetic resonance imaging. Through these survey methods, it is possible to detect changes in the gland with a certainty of 70 to 98%. The purpose of selective phlebography is to determine the functional activity of the adrenal gland with obtaining data on the amount of cortisol and aldosterone in the blood.
How to treat congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex?
Often, the treatment of congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex is performed by intramuscular injections of cortisone. The initial dosage is chosen to suppress adrenocorticotropic function of the pituitary:
How to treat adrenal hyperplasia on the right side?
Treatment of adrenal hyperplasia on the right is based on diagnostic data and the type of disease. In most cases, surgical resection is shown, which allows to normalize blood pressure and return the patient to a full life.
What is the phenomenon of hyperplasia?
The phenomenon of hyperplasia is an active increase in cell tissue. The organ that undergoes such changes increases in volume, retaining its original shape. The adrenal glands include the bark and the brain substance. The processes of hyperplasia affect the adrenal cortex more often, and tumors are detected primarily in the brain substance.
How to diagnose adrenal gland disorders?
For example, the severe form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is most commonly identified during newborn screening.1 But pheochromocytoma is diagnosed using blood and urine tests.2
What test can detect a tumor in the adrenal gland?
Blood and urine tests help measure the amount of adrenal hormones, which can detect a functional tumor. A computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be useful in diagnosing an adrenal gland tumor and determining whether it is cancerous. A metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scan can detect a neuroendocrine tumor.
How to identify CAH in infants?
The most common way health care providers identify CAH in infants is through newborn screening. If the first screening test indicates that the infant may have CAH, the health care provider will order another blood test to confirm the diagnosis.
How to diagnose pituitary tumor?
The first step in diagnosing pituitary tumors is a physical exam that includes checking neurologic responses, like reflexes and strength, and evaluation for signs of high hormone secretion, such as acne or unusual hair growth . A health care provider may also conduct a vision test to determine whether the growth of a pituitary tumor has affected ...
What test is used to diagnose Addison's disease?
Addison's disease. Typically, a blood test to measure cortisol levels and levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is used to diagnose Addison's disease. A health care provider may also use an ACTH stimulation test, an hour-long test during which a person receives a synthetic (man-made) version of ACTH through an intravenous (IV) line.
What tests are done to check for high aldosterone levels?
Hyperaldosteronism. If a health care provider suspects hyperaldosteronism, he or she may order blood and urine tests to check for high levels of aldosterone and low levels of potassium. The health care provider also may order a computed tomography (called a CT or "cat") scan to determine whether there is a non-cancerous tumor or other abnormal ...
What test is used to determine if you have pheochromocytoma?
If a health care provider suspects a pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma, he or she may administer a blood or urine test . The test measures the levels of: Catecholamines (pronounced kat-i-KOL-uh-meens ), hormones that increase the heart rate, blood pressure, rate of breathing, and amount of energy available to the body.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect the adrenal glands, a pair of walnut-sized organs above the kidneys. The adrenal glands produce important hormones, including: 1. Cortisol, which regulates the body's response to illness or stress 2. Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, which regulate sodium...
Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of CAHvary, depending on which gene is affected and the level of enzyme deficiency. The imbalance of hormones the body needs to function may mean too little cortisol, too little aldosterone, excess androgens or a combination of these imbalances.