
What are the four steps in aerobic respiration?
The steps of aerobic cellular respiration are:
- Glycolysis (the break down of glucose)
- Link reaction.
- Krebs cycle.
- Electron transport chain, or ETC.
What are the 4 stages of aerobic respiration?
what are the stages of aerobic respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- The stages of aerobic respiration
What are the different steps of aerobic respiration?
What are the 5 phases of respiration?
- Pulmonary Ventilation. …
- External Respiration. …
- Transport of gases through blood vessels. …
- Internal Respiration. …
- Cellular Respiration.
Is anerobic respiration better than aerobic respiration?
The energy yield of anaerobic respiration is very less than that of aerobic respiration. Only two ATP molecules are obtained from one glucose molecule. The NADH molecules obtained during glycolysis are not used to make TAP, rather they are used as reducing powers in fermentation.
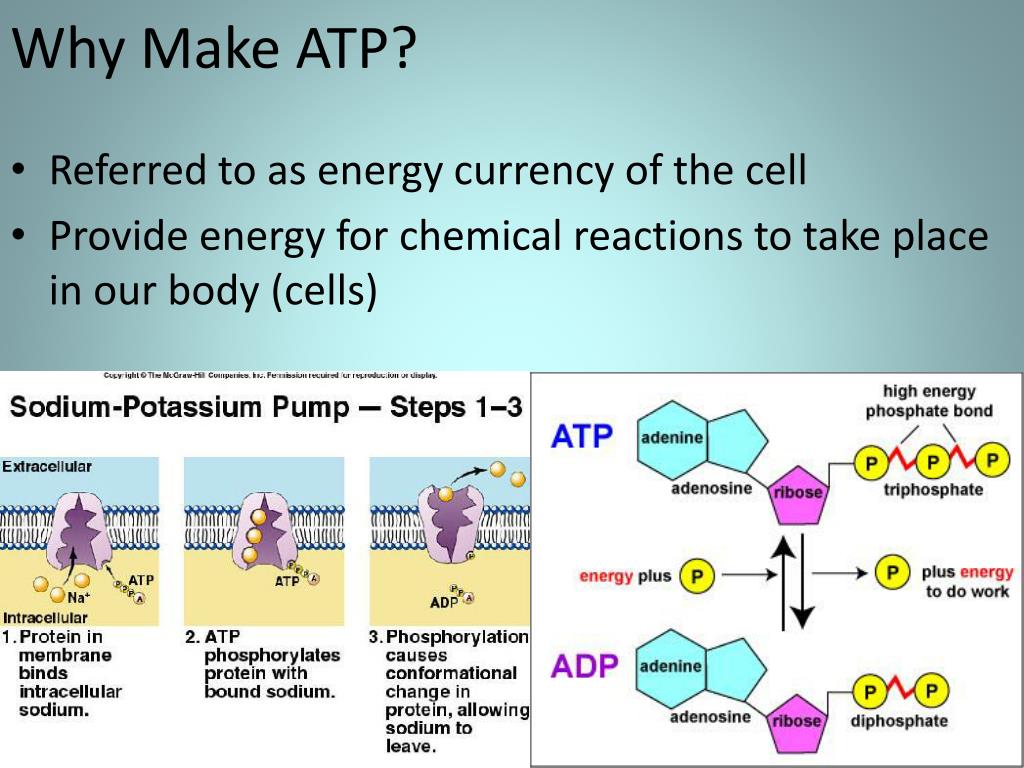
Do humans use aerobic respiration?
Inside the cell, the food, which contains glucose, is broken down into carbon dioxide and water with the help of oxygen. The process of breaking down the food particles releases energy, which is then utilized by our body. The energy released via aerobic respiration helps plants and animals, including us, grow.
Why aerobic respiration is important in our daily life?
All organisms respire to release energy to fuel their living processes. The respiration can be aerobic , which uses glucose and oxygen, or anaerobic which uses only glucose.
How important is aerobic and anaerobic respiration in our daily life?
Within the human body, both aerobic and anaerobic respiration are important to muscle function. Muscle cells specialized for aerobic respiration provide endurance, and those specialized for lactic acid fermentation support short but intense energy expenditures.
What is aerobic respiration give an example?
When the breakdown of glucose food occurs with the use of oxygen ,it is called aerobic respiration. Glucose___oxygen _____co2 +water + energy. For example -Human ,dogs ,cats and all the animals and birds ,insects ,grasshopper etc many more and most of the plants carry out aerobic respiration by using oxygen of air.
What do you understand by aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What are the different stages of aerobic respiration?
The different stages of aerobic respiration are: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Citric acid cycle Electron Transport Chain
What are the end products of aerobic respiration?
The end products of aerobic respiration include 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water and 30 molecules of ATP.
Where does aerobic and anaerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytop...
What is the importance of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is impo...
What are the different types of aerobes?
The different types of aerobes include: Obligate aerobes that strictly need oxygen to grow. Facultative aerobes can grow in the presence as well as...
What is aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form...
2. How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
Answer:Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of free oxygen and anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
3. How many ATP are produced in aerobic respiration?
Answer: 38 ATP molecules are produced during aerobic respiration.
4. Name the first product formed in the Krebs cycle.
Answer: The first product formed in the Krebs cycle is citric acid, hence it is also called the citric acid cycle.
5. What is the role of oxygen in aerobic respiration?
Answer: Oxygen is responsible for accepting electrons in the electron transport chain.
6. Name the pathway that is common between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: Glycolysis or EMP pathway is the common pathway between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
7. Which step of aerobic respiration produces maximum ATP?
Answer: Oxidative phosphorylation produces maximum ATP, i.e. 34 ATP molecules are formed in this step.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below-
What is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP?
Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP. The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What is the third step of aerobic respiration?
The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle , which is also called the Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a series of reactions and produces 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, ...
How many ATP molecules are produced in the last step of aerobic respiration?
In this phase, the large amounts of ATP molecules are produced by transferring the electrons from NADH and FADH. A single molecule of glucose creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.
What are the two types of respiration?
Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals.
What is the energy released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule?
The 2900 kJ of energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule and in turn, this energy is used to produce ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate molecules which are used by the system for various purposes. Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants and other living organisms.
What is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a process in which the cells utilize oxygen for the degradation of primary metabolites and release energy. It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
What are the two types of cellular respiration?
The cellular respiration is of two types, i.e. aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration . Aerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down to carbon dioxide in the presence of oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Anaerobic respiration: It is a process when glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP. Cellular respiration can take place in the presence or absence of molecular oxygen. Aerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration is a type ...
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration plays a significant role in releasing a lot of energy which helps in the survival of life. These are the following importance of aerobic respiration: It releases a large amount of energy in comparison to anaerobic respiration. It carries out a complete breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide.
How does the cell get ATP?
Cellular respiration is the process where a cell breaks down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
It takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell and produces ATP ( Adenosine Triphosphate ).
What is the process of breakdown of primary metabolites in the cell with the release of energy in the form of?
The process of breakdown of primary metabolites (like glucose, protein, fatty acids, etc.) in the cell with the release of energy in the form of ATP is called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in the living cells of organisms.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a series of biochemical reactions that convert oxygen and organic fuel into carbon dioxide, water and high-energy molecules. The process starts when organic fuel undergoes digestion in the stomach, intestines, and liver, which are then broken down and transferred into the blood. Oxygen is transferred to the bloodstream via gas exchange in the lungs.
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration is important because it is the primary way that your cells produce energy. Your cells can also use anaerobic respiration to generate energy without oxygen, but the cellular reactions are less efficient, generate a harmful byproduct called lactic acid and cannot sustain the long-term energy needs of a human cell.
Why is oxygen important for life?
Oxygen is essential because our cells use aerobic respiration to convert oxygen and food bits into the energy that we depend on for life . There are many biochemical reactions that create aerobic respiration, but for simplicity’s sake, this article will focus on a central concept: no oxygen = no energy. Organic fuel and other molecules are also required for energy, but oxygen is the only piece of this molecular puzzle that is restocked from outside your body every 4-5 seconds.
Why do we need gas exchange?
Almost every cell in your body needs a constant supply of oxygen and also needs to remove carbon dioxide to survive.
What is simplified science publishing?
Simplified Science Publishing offers graphic design services and data visualization classes. Click on the links below to learn more and contact if you want more information.
What happens to the energy stored in glucose during respiration?
Therefore, the energy stored in the glucose molecule is released gradually during respiration and used to form ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell.
What are the processes of respiration?
The process of respiration provides the energy required for these processes. It also provides energy for: 1 muscle contraction, required for movement 2 nerve impulses, required for sensitivity and responding 3 cell division and protein synthesis, required for growth
What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system in humans. Respiration is a chemical reaction which releases energy from food. The respiratory system exchanges the gases which are involved in respiration. Part of. Biology (Single Science) Cells, organ systems and ecosystems.
Where does aerobic respiration occur?
Aerobic respiration happens all the time in animals and plants. Note that respiration is different to breathing (ventilation). The oxygen dependent reactions involved in aerobic respiration happen inside mitochondria in cells.
Which process releases energy in the form of heat?
nerve impulses, required for sensitivity and responding. cell division and protein synthesis, required for growth. The process of respiration also releases energy in the form of heat.
Which membrane is folded inwards?
The inner membrane is folded inwards, providing a large surface area for the attachment of enzymes which catalyse the process of respiration.
Does aerobic respiration require oxygen?
Aerobicrespiration needs oxygen. It is the release of a relatively large amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the presence of oxygen.
Why is aerobic respiration important?
What is aerobic respiration and why is it important in the human body? Aerobic respiration is the process by which energy is released from glucose in the presence of oxygen ( as indicated by the word 'aerobic'). While in reality it is a complex, multi-step series of reactions controlled by enzymes (so called "biological catalysts") ...
Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient than aerobic respiration?
This is a less efficient method of energy release than aerobic respiration because oxygen is involved in a key, energy releasing step in the process of respiration.
What is the equation for glucose and oxygen?
While in reality it is a complex, multi-step series of reactions controlled by enzymes (so called "biological catalysts") it can be summarised in the following equation: glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) This process is occurring in the cells of your body right now - more specifically in the mitochondria.
What is the power house of a cell?
The mitochondria are organelles sometimes referred to as the 'power house' of the cell and, as you might expect, the number of mitochondria found inside a cell is proportional to the energy demands of the tissue that the cell is part of.
Why do all cells have mitochondria?
Almost all cells have mitochondria (a notable exception being Red Blood Cells) to provide them with the energy that they need to carry out basic cellular functions such as protein production and active transport (the movement of a substance against its concentration gradient using energy).
How does exercise affect the body?
When we exercise, our muscles become more efficient at consuming oxygen and converting it to useable energy. One of the body’s natural reactions to aerobic stimulation is an increase in oxygen-transporting enzymes, which carry oxygen out of the bloodstream and into the muscle.
What is the energy produced by mitochondria?
Here are the basics of energy production in the mitochondria: Your cells are already storing fuel, in the form of fats and carbohydrates that you’ve eaten. Once oxygen is introduced into a cell, it causes a chain of chemical reactions that lead the mitochondria to burn the fat/carbohydrate fuel stored in your muscles.
How does aerobic exercise work?
For humans the aerobic process begins with breathing. When you exercise, the body demands more oxygen than it would while resting. As a result, your breathing must increase to keep up with demand. At rest, adults typically inhale about 12 liters of air per minute. That number can jump to over 100 liters per minute when exercising. Our atmosphere is approximately 20% oxygen, so the oxygen that we need to function must be processed by our bodies first. When you take a breath, the lungs fill with air. That air is filtered through small tubes called bronchioles. The filtered air passes the bronchioles, eventually reaching thousands of microscopic sacs called alveoli. Inside the alveoli, Oxygen is diffused and begins to enter the bloodstream. The freshly-oxygenated blood travels to the heart, where some is used and the rest is sent along for reassignment.
How are mitochondria similar to cars?
Muscle s are similar to cars, in that they need fuel to run. The mitochondria is an organelle (a specialized structure within a cell), where the processes of respiration and energy production take place. The mitochondria is the ‘power plant’ that I referenced earlier, where oxygen is used in a chemical reaction to burn the body’s primary fuel sources, fats and carbohydrates. Think of mitochondria as tiny engines that use fats or carbohydrates as fuel, like a car uses gas. Here are the basics of energy production in the mitochondria:
How does the aerobic system work?
They use the food you eat, combined with the oxygen you breathe, to produce the energy you need to move. Although you may not realize it, your aerobic system is hard at work- powering the body forward as efficiently as possible.
What are some examples of aerobic exercise?
Running, cycling, swimming, and walking are a few classic examples. This article will explain how the aerobic system functions, adapts with exercise, and helps power your movement. Aerobic Exercise is broadly defined as “any type of exercise performed at moderate levels of intensity, for extended periods of time, ...
Why is it important to train your heart?
This is good news for folks that haven’t been as active as they’d like, but want to get moving again. Aerobic training increases the diameter and mass of the heart, allowing it to pump faster and more efficiently. As a result, there is an increase in the amount of blood that the heart pumps with each beat. The amount of blood pumped per beat is called the ‘stroke volume’. A higher stroke volume means that the heart won’t need to pump as quickly to meet the demands of exercise. This is why well-trained athletes have lower resting heart rates than their non-trained peers.
How does aerobic respiration produce ATP?
Aerobic respiration can also use fatty acids from fat reserves in muscle and the body to produce ATP. In extreme cases (like starvation), proteins can also be broken down into amino acids and used to make ATP. Aerobic respiration would use carbohydrates first, then fats and finally proteins, if necessary. Aerobic respiration takes even more chemical reactions to produce ATP than either of the above systems. Aerobic respiration produces ATP at the slowest rate of the three systems, but it can continue to supply ATP for several hours or longer, so long as the fuel supply lasts.
How does the body respond to glucose?
By two minutes of exercise, the body responds to supply working muscles with oxygen. When oxygen is present, glucose can be completely broken down into carbon dioxide and water in a process called aerobic respiration. The glucose can come from three different places: 1 remaining glycogen supplies in the muscles 2 breakdown of the liver's glycogen into glucose, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream 3 absorption of glucose from food in the intestine, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream
How does glycogen get to muscles?
remaining glycogen supplies in the muscles. breakdown of the liver's glycogen into glucose, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream. absorption of glucose from food in the intestine, which gets to working muscle through the bloodstream. Aerobic respiration can also use fatty acids from fat reserves in muscle and the body to produce ATP.
Which process uses carbohydrates first, fats and proteins?
Aerobic respiration would use carbohydrates first, then fats and finally proteins, if necessary. Aerobic respiration takes even more chemical reactions to produce ATP than either of the above systems.
How often and for how long should I do these exercises?
The American Heart Association recommends that everyone reach a minimum of 30 minutes of some form of cardiovascular exercise 5 to 7 days per week. This can be broken up into 10-minute time periods. This means that taking 3 walks of 10 minutes each would let you reach the recommended minimum guideline for reducing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol. You would also burn the same number of calories as you would if you walked for the full 30 minutes at 1 time.
What is upper body ergometer?
Using an upper body ergometer (a piece of equipment that provides a cardiovascular workout that targets the upper body only). Higher impact aerobic exercise includes: Running. Jumping rope. Performing high impact routines or step aerobics.
What is aerobic exercise?
Aerobic exercise provides cardiovascular conditioning. The term aerobic actually means "with oxygen," which means that breathing controls the amount of oxygen that can make it to the muscles to help them burn fuel and move.
How long should an aerobic workout last?
This allows the body to increase blood flow to the muscles and decreases the likelihood of a muscle or joint injury. The warm-up should last between 5 and 10 minutes. The cool-down session should last a similar amount of time as the warm-up, with the pace gradually decreasing. Stretching exercises would be appropriate after aerobic exercise.
How does heart rate affect exercise?
Your heart rate increases in direct correlation with the intensity of the exercise. Heart rate levels can vary significantly from one person to another based on fitness level, genetics, environment, and exercise tolerance. If you wish to train based on heart rate, contact your health care provider to determine what the appropriate range is for you. Some medications, most often blood pressure drugs, control heart rate, making it impossible to determine exercise intensity in this way. Ask your physician to determine if you are on any of these medications.
How is intensity determined?
The intensity is determined by how hard you are working. The intensity of the exercise is determined by what your goals are, what limitations you have, and your current fitness level.
How long should a warm up last?
The warm-up should last between 5 and 10 minutes. The cool-down session should last a similar amount of time as the warm-up, with the pace gradually decreasing. Stretching exercises would be appropriate after aerobic exercise.
