Common tests & procedures
Doctors often rely on lab tests, like microscopy, to confirm an African trypanosomiasis diagnosis, but screening tests and physical exams can also be helpful in determining who should be tested and how. 1 Certain tests can help health officials identify potential cases of African sleeping sickness out of a larger population.
What tests are used to diagnose African sleeping sickness?
African Trypanosomiasis, also known as “sleeping sickness”, is caused by microscopic parasites of the species Trypanosoma brucei. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly (Glossina species), which is found only in sub-Saharan Africa.
What is the cause of sleeping sickness in Africa?
Human African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness, is caused by infection with parasites of the genus Trypanosoma, transmitted by the tsetse fly. The disease has two forms, Trypanosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated. Despite a recent reduction i …
What causes trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)?
The current standard for diagnosing African trypanosomiasis is by looking for the parasite under a microscope using a body fluid or tissue sample. Samples are generally taken from blood, chancres (the sore that forms at the site of the fly bite), lymph nodes, or bone marrow. 17
How is African trypanosomiasis diagnosed?
See more

Which procedure uses for early diagnosis of African trypanosomiasis?
Blood Smear This technique is most sensitive in the early stages of the disease, when the number of circulating parasites is highest (≥5000/mL), particularly in T brucei rhodesiense (East African) trypanosomiasis. Trypanosoma brucei in a thin blood smear stained with Giemsa.
How is African sleeping sickness treated?
Antitrypanosomal treatment is indicated for all persons diagnosed with African trypanosomiasis. Choice of therapy depends on the infecting subspecies of the parasite and on the disease stage. The first line drugs for both first and second stage disease are highly effective. Pentamidine is used to treat first stage T.
How do humans get African sleeping sickness?
They are transmitted to humans by tsetse fly ( Glossina genus) bites which have acquired their infection from human beings or from animals harbouring human pathogenic parasites. Tsetse flies are found just in sub-Saharan Africa though only certain species transmit the disease.
How long does African sleeping sickness last?
West African sleeping sickness is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. This long-term (chronic) infection can last for years. East African sleeping sickness is caused by Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. It's a short-term (acute) illness that may last several weeks to months.
What part of the body does African sleeping sickness affect?
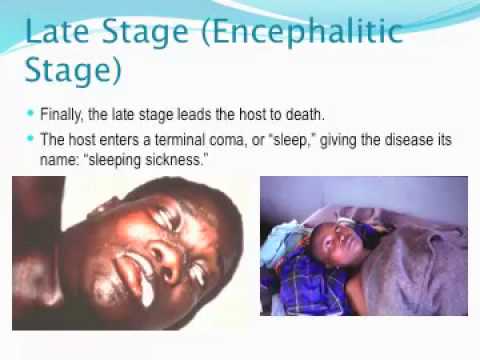
Fever, severe headaches, irritability, extreme fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and aching muscles and joints are common symptoms of sleeping sickness. Some people develop a skin rash. Progressive confusion, personality changes, and other neurologic problems occur after infection has invaded the central nervous system.
What do you do if a tsetse fly bites you?
Seek immediate medical attention if bitten by a tsetse fly (the bite is painful) and symptoms appear. If untreated, African Trypanosomiasis can lead to a coma and be fatal. Treatment includes taking antiparasitic drugs.
Can sleeping sickness be cured?
The oral therapy — called fexinidazole — cured 91% of people with severe sleeping sickness, compared with 98% who were treated with the combination therapy. It also cured 99% of people in an early stage of the disease who would typically undergo a spinal tap to determine whether they needed infusions.
Is sleeping sickness curable?
Sleeping sickness is curable with medication but is fatal if left untreated.
What do tsetse fly bites look like?
The tsetse fly bite is often painful and can cause red bumps or small red ulcers at the site of the bite. It can also transmit sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis) to animals and humans.
Is there a vaccine for African sleeping sickness?
There is no vaccine or medicine that prevents African trypanosomiasis. Travelers can protect themselves by preventing tsetse fly bites.
Is African sleeping sickness a virus or bacteria?
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. It is caused by the species Trypanosoma brucei....African trypanosomiasisSpecialtyInfectious disease12 more rows
Why is there no vaccine for African sleeping sickness?
Despite much research, no vaccine to prevent trypanosomiasis in animals or humans has been developed, and the prospects of developing one are very poor. The reason for this is that trypanosomes have evolved a system to evade the host's immune system by varying the structure of their surface coating (Vickerman, 1978).
Is there a vaccine for African sleeping sickness?
There is no vaccine or medicine that prevents African trypanosomiasis. Travelers can protect themselves by preventing tsetse fly bites.
Is sleeping sickness curable?
Sleeping sickness is curable with medication but is fatal if left untreated.
Why is there no vaccine for African sleeping sickness?
Despite much research, no vaccine to prevent trypanosomiasis in animals or humans has been developed, and the prospects of developing one are very poor. The reason for this is that trypanosomes have evolved a system to evade the host's immune system by varying the structure of their surface coating (Vickerman, 1978).
Who is most at risk for African sleeping sickness?
Who is at risk for African sleeping sickness? The only people at risk for African sleeping sickness are those who travel to Africa. That's where the tsetse fly is found. The parasites that cause the disease are passed on only by the tsetse fly.
How is African sleeping sickness diagnosed?
Tests can find the parasite. These tests may include blood samples and a spinal tap (lumbar puncture). Your provider may also take a sample of chancre fluid or tissue, or fluid from swollen lymph nodes.
What is African sleeping sickness?
African sleeping sickness (African trypanosomiasis) is a disease caused by a parasite. It is passed on by the bite of the infected tsetse fly.
What are the complications of African sleeping sickness?
If the disease is not treated, the symptoms can worsen to a severe illness. Death will occur.
How long does sleeping sickness last in Africa?
East African sleeping sickness is caused by Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. It’s a short-term (acute) illness that may last several weeks to months. People from the U.S. who travel to Africa are rarely infected.
Where do African sleeping sickness flies live?
The parasites that cause the disease are passed on only by the tsetse fly. The tsetse flies live only in rural areas. They live in woodland thickets of the savanna ...
What is the parasite that causes sleep sickness?
Parasites - African Trypanosomiasis (also known as Sleeping Sickness) minus. Related Pages. African Trypanosomiasis, also known as “sleeping sickness”, is caused by microscopic parasites of the species Trypanosoma brucei. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly ( Glossina species), which is found only in sub-Saharan Africa.
Where is trypanosomiasis transmitted?
b. gambiense causes a slowly progressing African trypanosomiasis in western and central Africa and T. b.
What causes sleep sickness?
Sleeping sickness is caused by parasites transmitted by infected tsetse flies and is endemic in 36 sub-Saharan African countries where there are tsetse flies that transmit the disease. Without treatment, the disease is considered fatal.
What is African trypanosomiasis?
Human African trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness, is a vector-borne parasitic disease. It is caused by infection with protozoan parasites belonging to the genus Trypanosoma. They are transmitted to humans by tsetse fly ( Glossina genus) bites which have acquired their infection from human beings or from animals harbouring human ...
How many cases of African trypanosomiasis in 2019?
In 2009 the number reported dropped below 10 000 for the first time in 50 years, and in 2019 there were 992 cases recorded. Diagnosis and treatment of the disease is complex and requires specifically skilled staff. Human African trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness, is a vector-borne parasitic disease.
Why is it important to make a diagnosis early?
Diagnosis must be made as early as possible to avoid progressing to the neurological stage in order to elude complicated and risky treatment procedures
When will trypanosomiasis be eliminated?
Since the number of new human African trypanosomiasis cases reported between 2000 and 2012 dropped significantly as a result of international coordinated efforts, the WHO neglected tropical diseases road map targeted its elimination as a public health problem by 2020 and interruption of transmission (zero cases) for 2030.
Where does trypanosomiasis occur?
Only Uganda presents both forms of the disease, but in separate zones. Another form of trypanosomiasis occurs mainly in Latin America. It is known as American trypanosomiasis or Chagas disease.
Who provides anti-trypanosome medicines free of charge to endemic countries?
WHO provides the anti-trypanosome medicines free of charge to endemic countries thanks to public-private partnerships with Sanofi (pentamidine, melarsoprol, eflornithine and fexinidazole) and with Bayer HealthCare (suramin and nifurtimox). The conditioning and shipment of medicines is done in collaboration with MSF-Logistics.
How is African sleeping sickness diagnosed?
Tests can find the parasite. These tests may include blood samples and a spinal tap (lumbar puncture). Your provider may also take a sample of chancre fluid or tissue, or fluid from swollen lymph nodes.
What is African sleeping sickness?
African sleeping sickness (African trypanosomiasis) is a disease caused by a parasite. It is passed on by the bite of the infected tsetse fly.
What are possible complications of African sleeping sickness?
If the disease is not treated, the symptoms can worsen to a severe illness. Death will occur.
How long does sleeping sickness last in Africa?
East African sleeping sickness is caused by Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. It’s a short-term (acute) illness that may last several weeks to months. People from the U.S. who travel to Africa are rarely infected.
How is tsetse fly disease passed on?
It is passed on by the bite of the infected tsetse fly. The only risk factor is travel to parts of Africa where the tsetse fly is found. The only way to prevent the disease is to prevent insect bites. Medicine is available to treat it.
What is the cause of African trypanosomiasis?
Human African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness, is caused by infection with parasites of the genus Trypanosoma, transmitted by the tsetse fly. The disease has two forms, Trypanosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated.
What is the best treatment for T B rhodesiense?
Melarsoprol is the only available treatment for late-stage T b rhodesiense infection, but can be lethal to 5% of patients owing to post-treatment reactive encephalopathy. Eflornithine combined with nifurtimox is the first-line treatment for late-stage T b gambiense.
Is trypanosomiasis fatal?
The disease has two forms, Try panosoma brucei (T b) rhodesiense and T b gambiense; and is almost always fatal if untreated. Despite a recent reduction in the number of reported cases, patients with African trypanosomiasis continue to present major challenges to clinicians.
How is African sleeping sickness diagnosed?
Tests can find the parasite. These tests may include blood samples and a spinal tap (lumbar puncture). Your provider may also take a sample of chancre fluid or tissue, or fluid from swollen lymph nodes.
What is African sleeping sickness?
African sleeping sickness (African trypanosomiasis) is a disease caused by a parasite. It is passed on by the bite of the infected tsetse fly.
How long does sleeping sickness last in Africa?
West African sleeping sickness is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. This long-term (chronic) infection can last for years. East African sleeping sickness is caused by Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. It’s a short-term (acute) illness that may last several weeks to months.
What are possible complications of African sleeping sickness?
If the disease is not treated, the symptoms can worsen to a severe illness. Death will occur.
