The equilibrium price and quantity in the economy will change when either the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS In economics, aggregate supply (AS) or domestic final supply (DFS) is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing and able to sell at a given price level in an …Aggregate supply
Full Answer
How do aggregate demand and aggregate supply differ from regular demand and supply?
Differences between Aggregate demand and Aggregate supply Aggregate demand is the gross amount of services and goods demanded for all finished products in an economy. On the other hand, aggregate supply is the total supply of services and goods at a given price and in a given period.
What is the difference between aggregate demand and aggregate supply?
Aggregate Supply is the total quantity of all goods and services produced in an economy at all possible price levels at a given time. Aggregate Demand is the total quantity of all goods and services consumed in an economy at all possible price levels at a given time. The words total and price levels are important here.
How do aggregate demand and aggregate supply differ from regular demand and supply quizlet?
How do aggregate demand and aggregate supply differ from regular demand and supply? Regular demand and supply describe the market for a single good, while aggregate demand and aggregate supply describe the combined market for all final goods and services.
What is the difference between the long run aggregate supply and the short run aggregate supply curves?
Short-run aggregate supply curves illustrate supply in the near future or over a period in which capital is fixed. Long-run aggregate supply curves show supply in the long-term in which all inputs are variable. Aggregate supply is a function of total production within an economy and the price level.
What is the relationship of aggregate demand and aggregate supply?
Aggregate supply is the total quantity of output firms will produce and sell—in other words, the real GDP. Aggregate demand is the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services in an economy.
Where does the aggregate demand curve and the short run aggregate supply curve intersect?
the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves intersect at a point on the long-run aggregate supply curve.
What is aggregate demand and aggregate supply quizlet?
a schedule or curve that shows the total quantity of goods and services demanded (purchased) at different price levels. Real-balances effect.
What is the difference between demand and aggregate demand quizlet?
What is the difference between a market demand curve and the aggregate demand curve? A market demand shows the demand for one good/service at different prices. Aggregate demand shows the demand for all goods and services at different price levels.
What is the difference between demand and aggregate demand Why do we use aggregate demand not demand to measure the productivity of the economy?
Aggregate demand represents the total demand for these goods and services at any given price level during the specified period. Aggregate demand eventually equals gross domestic product (GDP) because the two metrics are calculated in the same way.
What makes aggregate supply different in the short-run and long run?
0:589:29Aggregate Supply in the Short Run and in the Long Run [AP ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd the reason why the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping is because in the short-MoreAnd the reason why the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping is because in the short-run. As prices. Increase aggregate output also increases. Just like in regular supply.
What is the short-run aggregate supply?
Definition. short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) a graphical model that shows the positive relationship between the aggregate price level and amount of aggregate output supplied in an economy.
What is the difference between short-run and long run?
"The short run is a period of time in which the quantity of at least one input is fixed and the quantities of the other inputs can be varied. The long run is a period of time in which the quantities of all inputs can be varied.
What is the difference between demand and aggregate?
Aggregate demand shows the total spending of the entire nation on all goods and services while demand is concerned with looking at the relationship between price and quantity demanded for each individual product.
What is an example of aggregate supply?
What is an example of aggregate supply? Aggregate supply represents the total amount of the goods and services that are being output in a given economy. An example of aggregate supply changing due a determinant would be if factor prices fell; then, aggregate supply would increase.
What is the difference between demand and aggregate demand quizlet?
What is the difference between a market demand curve and the aggregate demand curve? A market demand shows the demand for one good/service at different prices. Aggregate demand shows the demand for all goods and services at different price levels.
What do you mean by aggregate demand function and aggregate supply function?
An aggregate demand curve shows the total spending on domestic goods and services at each price level. You can see an example aggregate demand curve below. Just like in an aggregate supply curve, the horizontal axis shows real GDP and the vertical axis shows price level.
How to trace out short run aggregate supply curve?
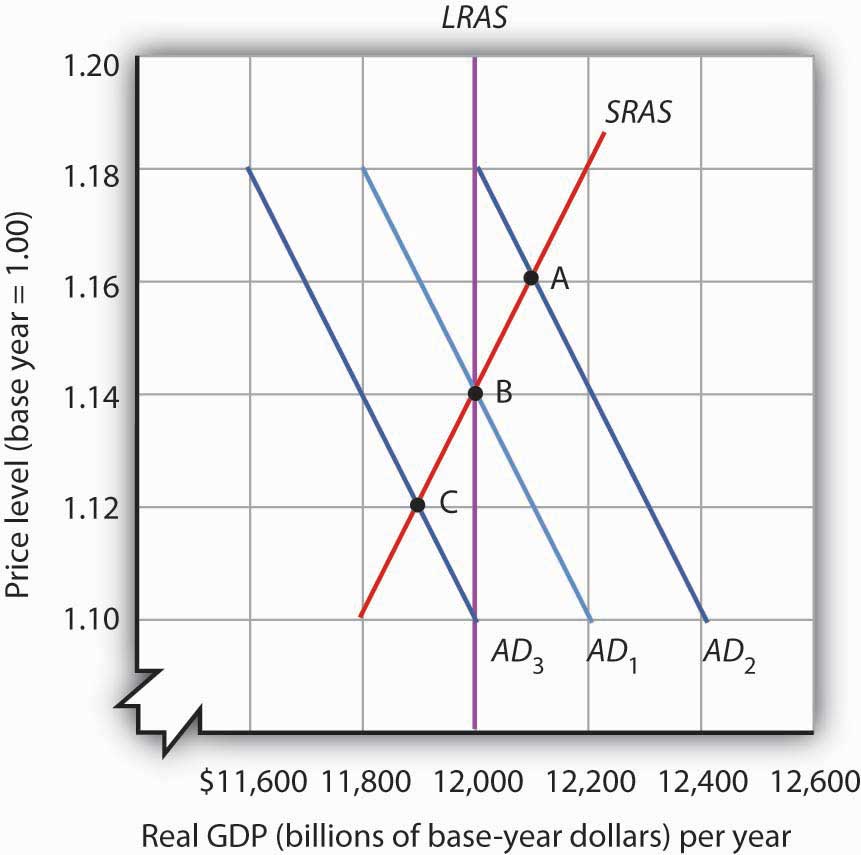
By examining what happens as aggregate demand shifts over a period when price adjustment is incomplete, we can trace out the short-run aggregate supply curve by drawing a line through points A, B, and C . The short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between production and the price level in the short run. Among the factors held constant in drawing a short-run aggregate supply curve are the capital stock, the stock of natural resources, the level of technology, and the prices of factors of production.
What is the effect of a reduction in aggregate demand?
Consider next the effect of a reduction in aggregate demand (to AD3 ), possibly due to a reduction in investment. As the price level starts to fall, output also falls. The economy finds itself at a price level–output combination at which real GDP is below potential, at point C. Again, price stickiness is to blame. The prices firms receive are falling with the reduction in demand. Without corresponding reductions in nominal wages, there will be an increase in the real wage. Firms will employ less labor and produce less output.
Why is aggregate price adjustment incomplete?
Taken together, these reasons for wage and price stickiness explain why aggregate price adjustment may be incomplete in the sense that the change in the price level is insufficient to maintain real GDP at its potential level. These reasons do not lead to the conclusion that no price adjustments occur. But the adjustments require some time. During this time, the economy may remain above or below its potential level of output.
What is the analysis of the macroeconomy in the short run?
Analysis of the macroeconomy in the short run—a period in which stickiness of wages and prices may prevent the economy from operating at potential output—helps explain how deviations of real GDP from potential output can and do occur. We will explore the effects of changes in aggregate demand and in short-run aggregate supply in this section.
How does rigidity affect output price?
Since wages are a major component of the overall cost of doing business, wage stickiness may lead to output price stickiness. With nominal wages stable, at least some firms can adopt a “wait and see” attitude before adjusting their prices. During this time, they can evaluate information about why sales are rising or falling (Is the change in demand temporary or permanent?) and try to assess likely reactions by consumers or competing firms in the industry to any price changes they might make (Will consumers be angered by a price increase, for example? Will competing firms match price changes?).
Where does long run equilibrium occur?
Long-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the long-run aggregate supply curve. For the three aggregate demand curves shown, long-run equilibrium occurs at three different price levels, but always at an output level of $12,000 billion per year, which corresponds to potential output.
How long do wage contracts last?
The length of wage contracts varies from one week or one month for temporary employees, to one year (teachers and professors often have such contracts), to three years (for most union workers employed under major collective bargaining agreements). The existence of such explicit contracts means that both workers and firms accept some wage at the time of negotiating, even though economic conditions could change while the agreement is still in force.
Why does aggregate supply differ from potential output in the short run?
To sum up, aggregate supply will differ from potential output in the short run because of inflexible elements of costs. In the short run, firms will respond to higher demand by raising both production and prices. In the long run, as cost respond to the higher level of prices, most or all of the responses to increased demand takes the form ...
How does aggregate demand affect prices?
This gets reflected in the behaviour of firms. Firms raise both prices and output in the short run as aggregate demand increases. In contrast, increases in aggregate demand lead to price changes with little, if any, change in output in the long run.
Why are some elements of business costs inflexible or sticky in the short run?
For this reason, firms can make profit from higher levels of aggregate demand by expanding their output levels. In the long run, a different type of behaviour is observed.
Why is the LRAS curve vertical?
Whereas the SRAS curve is upward sloping, the LRAS curve is vertical because, given sufficient time, all costs adjust.
What happens to firms once costs increase?
Once costs have increase as much as prices, firms will be unable to profit from the higher level of aggregate demand. In the long run, after all elements of cost have fully adjusted, firms will face the same ratio of price to costs as they did before the increase in aggregate demand. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What happens when the aggregate price level rises by x%?
Ultimately all costs get adjusted to the higher output prices. If the aggregate price level rises by x% because of higher demand, then, nominal wages, rents, regulated prices and other costs items will — in ...
Is the LRAS vertical or horizontal?
ADVERTISEMENTS: So they will have hardly any incentive to increase their output. The LRAS, therefore, tends to be vertical. This simply means that output supply has no relation to the level of prices and costs.