How is amniotic fluid embolism diagnosed?
- Blood tests, including those that evaluate clotting, heart enzymes, electrolytes and blood type, as well as a complete...
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to evaluate your heart’s rhythm.
- Pulse oximetry to check the amount of oxygen in your blood.
- Chest X-ray to look for fluid around your heart.
What are the tests for amniotic fluid embolism?
Your health care provider might order the following lab tests during your evaluation:
- Blood tests, including those that evaluate clotting, heart enzymes, electrolytes and blood type, as well as a complete blood count (CBC)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to evaluate your heart's rhythm
- Pulse oximetry to check the amount of oxygen in your blood
- Chest X-ray to look for fluid around your heart
What causes increased amniotic fluid?
- Birth defectsinvolving Baby's ability to swallow or kidney function: It's your baby's ability to swallow and process fluid through the kidneys that regulates the amount of fluid in the uterus.
- Diabetes: Some moms with diabetes might have increased levels of fluid.
- Rh Incompatibility: A mismatch between mom's blood and Baby's blood.
How to prevent amniotic fluid embolism?
- Advanced maternal age. If you're 35 or older at the time of your child's birth, you might be at increased risk of amniotic fluid embolism.
- Placenta problems. ...
- Preeclampsia. ...
- Medically induced labor. ...
- Operative delivery. ...
- Polyhydramnios. ...
What are the signs of leaking amniotic fluid?
You are leaking amniotic fluid if:
- The fluid is odourless
- It has a clear, watery colour, possibly tinged white-pink.
- It continues to leak and is out of your control, even if you bring your pelvic floor muscles into action
- The leak is steady, and you need to change your sanitary pad often You won’t have any doubt about whether to use a panty liner or a pad

How fast does amniotic fluid embolism happen?
Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery. There are several signs and phases of amniotic fluid embolism.
What is the survival rate of amniotic fluid embolism?
The prognosis after AFE is very poor, and most women do not survive. If patient survives the embolism, most survivors have neurologic deficits. The infant survival rate is 70%. Neurologic status of the infant is directly related to the time elapsed between maternal arrest and delivery.
How common is an amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a rare disorder. Rare disorders often go unrecognized or misdiagnosed, making it difficult to determine their true frequency in the general population. Estimates have ranged from 1 in 8,000 to 1 in 80,000 pregnancies.
How can you prevent amniotic fluid embolism?
To prevent amniotic fluid embolism, trauma to the uterus must be avoided during maneuvers such as insertion of a pressure catheter or rupture of membranes. Incision of the placenta during caesarean delivery should also be avoided if possible.
How can you tell the difference between amniotic fluid embolism and pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include tachycardia, tachypnea, and shortness of breath, all of which are common complaints in pregnancy. Heightened awareness leads to rapid diagnosis and institution of therapy. Amniotic fluid embolism is associated with maternal collapse.
Who is at risk for amniotic fluid embolism?
Age: Women ages 35 or older at the time of delivery may be at increased risk of amniotic fluid embolism. Delivery via operation: Operations like a cesarean section, forceps delivery, or vacuum extraction disturb the barriers between the mother and baby.
Should I be worried about amniotic fluid embolism?
An amniotic fluid embolism can cause potentially life-threatening breathing and heart issues, as well as uncontrolled bleeding. It is an often fatal emergency that requires immediate medical care for both the pregnant person and the baby.
Can amniotic embolism be prevented?
There is no known way to prevent the condition, but maternal risk factors include older age, having a pregnancy with more than one fetus, and having a cesarean delivery. AFE is considered an emergency, so people with any symptoms of the condition need immediate medical attention.
How do I know if I leaked amniotic fluid?
Signs of leaking amniotic fluid Leaking amniotic fluid might feel like a gush of warm fluid or a slow trickle from the vagina. It will usually be clear and odorless but may sometimes contain traces of blood or mucus. If the liquid is amniotic fluid, it is unlikely to stop leaking.
Can AFE happen during C section?
AFE is more common in vaginal delivery but can occur during a C-section as well. It can also happen shortly after birth while the placenta is still inside the mother's body.
When is an amniotic fluid embolism most likely to occur?
Amniotic fluid embolism is most likely to occur during delivery or in the immediate postpartum period. Amniotic fluid embolism is difficult to diagnose. If your doctor suspects you might have one, you'll need immediate treatment to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
How many cases of amniotic fluid embolism are there?
Risk factors. It's estimated that there are between one and 12 cases of amniotic fluid embolism for every 100,000 deliveries. Because amniotic fluid embolisms are rare, it's difficult to identify risk factors.
What is the condition where amniotic fluid enters the mother's bloodstream?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a rare but serious condition that occurs when amniotic fluid — the fluid that surrounds a baby in the uterus during pregnancy — or fetal material, such as fetal cells, enters the mother's bloodstream. Amniotic fluid embolism is most likely to occur during delivery or in the immediate postpartum period.
What are the symptoms of a fetal heart failure?
Signs and symptoms might include: Sudden failure of the heart to effectively pump blood (cardiovascular collapse) Life-threatening problems with blood clotting (disseminated intravascular coagulopathy) Fetal distress, such as a slow heart rate, or other fetal heart rate abnormalities.
What percentage of maternal deaths are due to amniotic fluid embolisms?
The numbers vary, but as many as 20 percent of maternal deaths in developed countries may be due to amniotic fluid embolisms. Infant death. Your baby is at risk of brain injury or death. Prompt evaluation and delivery of your baby improves survival. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What are the symptoms of a bleed from the uterus?
Bleeding from the uterus, cesarean incision or intravenous (IV) sites. Altered mental status, such as anxiety or a sense of doom. Chills. Rapid heart rate or disturbances in the rhythm of the heart rate. Fetal distress, such as a slow heart rate, or other fetal heart rate abnormalities. Seizures.
Why does my mother have a clot in her lungs?
When this breakdown happens, the immune system responds by releasing products that cause an inflammatory reaction, which activates abnormal clotting in the mother's lungs and blood vessels.
Why is it so difficult to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism?
Diagnosing amniotic fluid embolism is difficult because many of the symptoms can overlap with other serious medical conditions. Your doctor will rule out other possible causes while working to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery.
What is the amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic Fluid Embolism (Anaphylactic Syndrome of Pregnancy) A very rare condition, the exact cause of amniotic fluid embolism is unknown. This condition is a dangerous and fatal complication that can happen during labor or soon after childbirth.
What is it called when there is too much amniotic fluid surrounding the baby?
Polyhydramnios (this occurs when there is too much amniotic fluid surrounding the baby).
What happens when a baby floats in amniotic fluid?
When this fluid mixes with a mother’s blood, it can cause an allergic-like reaction that can be fatal. This is a medical emergency requiring expert medical care. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What are the signs of a C-section?
Additional signs can include: Acute low blood pressure (hypotension) or cardiac arrest. Respiratory arrest and lack of oxygen. Blood clotting or severe hemorrhage with no explanation. This can happen during labor, Cesarean birth (C-Section), dilation and evacuation within 30 minutes postpartum (after birth).
Can amniotic fluid cause an allergic reaction?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a very rare condition that can happen during childbirth or soon after birth. It’s unknown what causes amniotic fluid embolism, but some experts think it may be related to amniotic fluid entering the mother’s blood stream (circulatory system). Amniotic fluid is the liquid that the baby floats in while in the womb. When this fluid mixes with a mother’s blood, it can cause an allergic-like reaction that can be fatal. This is a medical emergency requiring expert medical care.
Can amniotic fluid be prevented?
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent amniotic fluid embolism. Healthcare providers are still unsure why this happens and what exactly causes this condition. One way to prepare for any kind of medical emergency is to develop a plan with your family and healthcare providers.
What are the symptoms of an amniotic fluid embolism?
Signs and symptoms. Amniotic fluid embolism is suspected when a woman giving birth experiences very sudden insufficient oxygen to body tissues, low blood pressure, and profuse bleeding due to defects in blood coagulation. Though symptoms and signs can be profound, they also can be entirely absent. There is much variation in how each instance ...
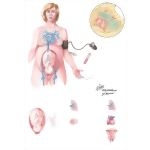
What is AFE in obstetrics?
Obstetrics. Pathophysiology of the amniotic fluid embolism. An amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a very uncommon childbirth ( obstetric) emergency in which amniotic fluid enters the blood stream of the mother to trigger a serious reaction.
How does AFE occur?
The disorder occurs during the last stages of labor when amniotic fluid enters the circulatory system of the mother via tears in the placental membrane or uterine vein rupture. Upon later analysis, fetal cells are found in the maternal circulation. When the fetal cells and amniotic fluid enter the bloodstream, reactions occur that cause severe changes in the mechanisms that affect blood clotting. Disseminated intravascular coagulation occurs and results in serious bleeding. The condition can also develop after elective abortion, amniocentesis, cesarean delivery or trauma. Small lacerations in the lower reproductive tract are associated with AFE.
Does induction of labor increase the risk of AFE?
According to one study, induction of labor may double the risk of AFE. However, other studies have refuted this claim. A maternal age of 35 years or older is associated with AFE.
Can milrinone be used immediately after amniotic fluid?
A case report on Amniotic Fluid Embolism published in the A & A Practice Journal in 2020 has revealed that when milrinone is administered as an aerosol, selective pulmonary vasodilation occurs without significant changes in mean arterial pressure or systemic vascular resistance; and if used immediately after Amniotic Fluid Embolism, inhaled milrinone may mitigate the pulmonary vasoconstriction.