
- Organelle: Chloroplast during light dependent reaction
- Site of Electron transport chain: Thylakoid membrane of chloroplast
- Proton (H+) pumped into the thylakoid lumen or thylakoid space
- ATP synthesis occurs towards the stromal side (see the above figure)
- ATP produced during light reaction is used to fix carbon dioxide to carbohydrates in Calvin cycle
What are facts about chloroplasts?
Interesting Facts about Chloroplasts
- Simple cells, like those found in algae, may only have one or two chloroplasts. ...
- Chloroplasts will sometimes move around within the cell in order to position themselves to where they can best absorb sunlight.
- The "chloro" in chloroplast comes from the Greek word chloros (meaning green).
- The most abundant protein in chloroplasts is the protein Rubisco. ...
Does chlorophyll make ATP?
Results suggest chlorophyll type molecules modulate mitochondrial ATP by catalyzing the reduction of coenzyme Q, a slow step in mitochondrial ATP synthesis. We propose that through consumption of plant chlorophyll pigments, animals, too, are able to derive energy directly from sunlight.
What does chloroplast do for the plant to survive?
A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
Does chloroplast make cellular respiration?
Yes. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts, whereas cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria. Photosynthesis makes glucose and oxygen, which are then used as the starting products for cellular respiration. What type of cells contain chloroplasts?
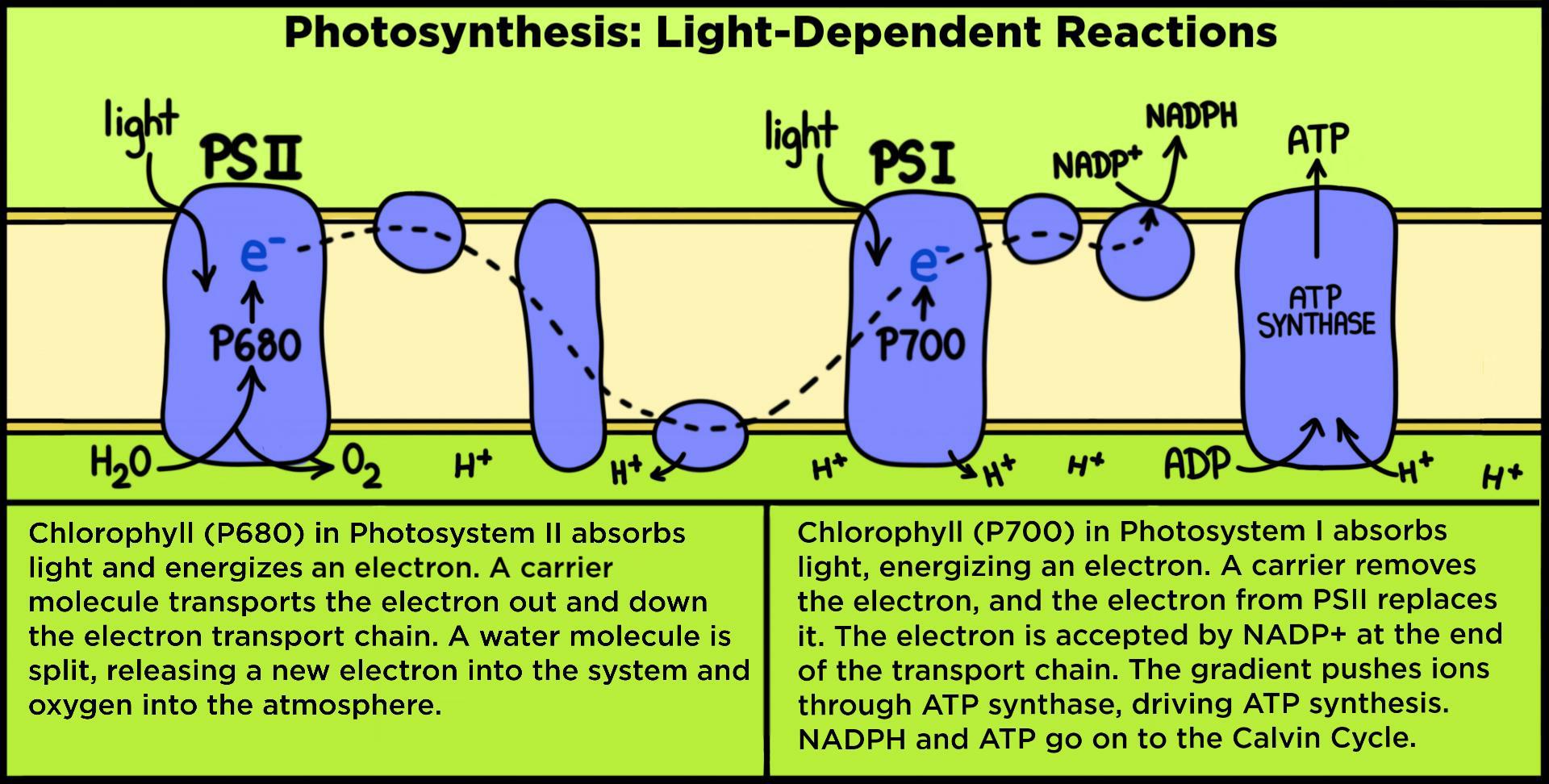
How is ATP synthesized in chloroplasts?
The chloroplast adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase uses the electrochemical proton gradient generated by photosynthesis to produce ATP, the energy currency of all cells. Protons conducted through the membrane-embedded Fo motor drive ATP synthesis in the F1 head by rotary catalysis.
How is ATP produced in chloroplast quizlet?
In chloroplasts, ATP is produced as a result of harvesting energy from light. In chloroplasts, the ATP is used in the fixation of CO2 into sugars.
Can chloroplasts generate ATP?
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are the major ATP producing organelles in plant leaves.
Where is ATP generated in chloroplasts?
thylakoid membraneThe chloroplast adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase is located in the thylakoid membrane and synthesizes ATP from adenosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate at the expense of the electrochemical proton gradient formed by light-dependent electron flow.
How is ATP generated in the light reactions?
In a process called non-cyclic photophosphorylation (the "standard" form of the light-dependent reactions), electrons are removed from water and passed through PSII and PSI before ending up in NADPH. This process requires light to be absorbed twice, once in each photosystem, and it makes ATP .
How is ATP made during the light reactions quizlet?
How is ATP made during the light reactions? ATP synthase uses the energy to add a phosphate group to a molecule of ADP, which produces a molecule of ATP. absorption of sunlight, splitting of water, electrons flow down the electron transport chain, ATP is made.
How do chloroplasts and mitochondria produce ATP?
Introduction. In plant cells, chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy, and mitochondria consume the chemical energy to produce ATP. The optimal carbon fixation and plant growth require these two energy-transforming organelles to perform strictly coordinated actions.
How ATP is produced in plants?
Plants, through the process of photosynthesis, make use of the sunlight to energise and generate glucose through the available water and carbon dioxide. This glucose through pathways can be converted into pyruvate. Through cellular respiration, pyruvate in turn gives ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
How is ATP produced?
ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. This can be through aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. Aerobic respiration produces ATP (along with carbon dioxide and water) from glucose and oxygen.
Where is ATP produced in photosynthesis?
stroma sideATP and NADPH are produced on the stroma side of the thylakoid membrane, where they can be used by the Calvin cycle.
How is ATP produced in photosynthesis quizlet?
Explain how ATP is generated during photosynthesis. Sunlight energy is used to split water molecules into H+ and e-. The H+ goes into the thylakoid, creating a concentration difference. As the H+ diffuses out, it goes through the channel/enzymatic protein ATP synthase, providing the energy to synthesize ATP.
How is ATP produced quizlet?
ATP is produced during the process of cellular respiration.
In what process is ATP produced?
ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. This can be through aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. Aerobic respiration produces ATP (along with carbon dioxide and water) from glucose and oxygen.
Which is the most successful way to obtain ATP quizlet?
Aerobic cell respiration (glycolysis + the Krebs cycle + respiratory electron transport) produces 36 ATP/glucose consumed and is roughly 18 times more efficient than fermentation. Your cells require a lot of energy and are dependent on the high efficiency of aerobic respiration.
ATP Synthesis in Chloroplast Definition
Adenosine 5’ triphosphate (ATP) is an energy-rich molecule and is spent and generated by living cells by several cellular processes. It can be generated not only by metabolizing the organic and inorganic compounds but can also be generated by absorbing the sunlight and transforming it into a form of chemical energy.
Overview of ATP Synthesis In Chloroplast
The chloroplast is a unique cell structure found in the cells of most autotrophs. They serve as the kitchen of the cell and prepare food for the whole cell. ATP and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) are the products that are generated by the chloroplast’s cellular action.
Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation
In this type, both the photosystems operate together and produce ATP, NADPH, and also oxygen. This takes place in the membrane of the grana present in the chloroplast which possesses both the required photosystems. The PS II absorbs light of shorter wavelengths and passes it to its chlorophyll- reaction center P680 which becomes excited.
Cyclic Photophosphorylation
The dark reaction requires 3 ATP and 2 NADPH to reduce one molecule of carbon dioxide to one carbohydrate molecule. When two pairs of electron on undergoing non-cyclic photophosphorylation yields 2 ATP and 2 NADPH. But, one more ATP is required and this need is fulfilled by cyclic photophosphorylation.
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis
The chemiosmotic hypothesis puts forward the explanation of how ATP is synthesized in the chloroplast.ATP synthesis via photosynthesis reaction is connected with the generation of proton motive force (PMF) across the thylakoid membrane. The establishment of a proton gradient across the membranes occurs through the following reactions.
