Is glycolysis probably the oldest known way of producing ATP?
The latter pathway, anaerobic glycolysis, is believed to be the first process to have evolved in nature to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In some cells—notably in mature red blood cells—glycolysis is the only means of ATP production because of the lack of mitochondria.
How is ATP made in the Krebs cycle?
Simply so, how is ATP made in Krebs cycle? In eukaryotes, the Krebs cycle uses a molecule of acetyl CoA to generate 1 ATP, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, and 3 H+. Both the NADH and FADH2 molecules made in the Krebs cycle are sent to the electron transport chain, the last stage of cellular respiration.
How much total ATP is produced in the Krebs cycle?
Two molecules of acetyl-CoA are produced from each glucose molecule so two turns of the Krebs cycle are required which yields four CO 2, six NADH, two FADH 2 and two ATPs. Cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction taking place in the cells.
What process makes ATP?
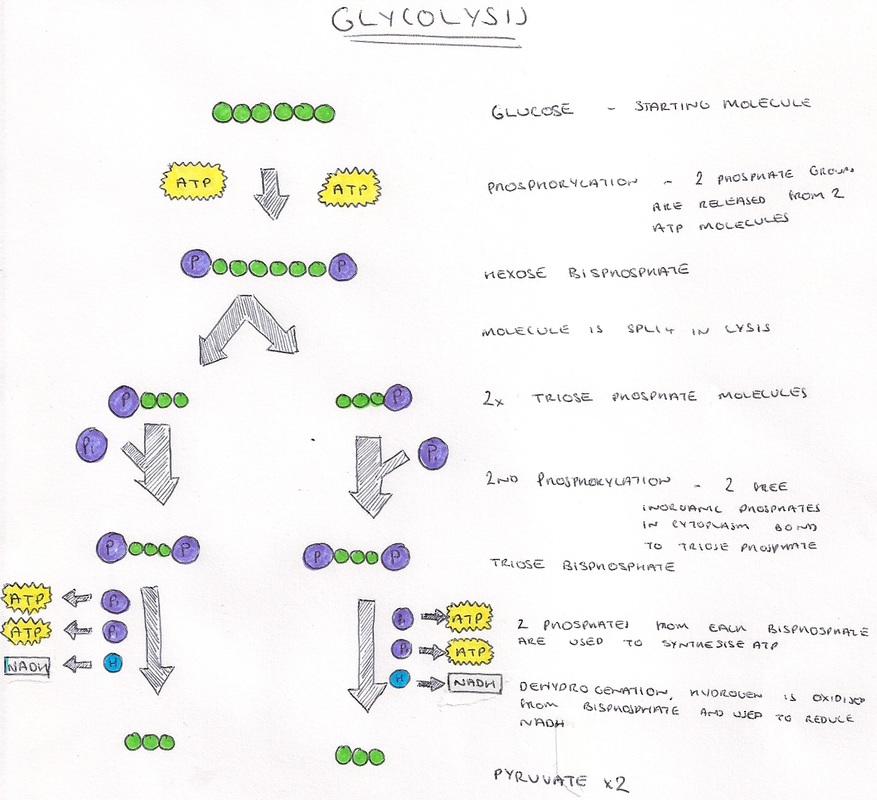
- The partial breakdown (oxidation) of a glucose molecule (a 6-C molecule) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3-C molecules).
- Uses 2 ATP's and makes 4 ATP's. So, there is a net gain of 2 ATP's
- M akes 2 NADH 2
/Glycolysis-58a468ce3df78c47584cd4d3.jpg)
How is ATP produced by glycolysis quizlet?
In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two 3-carbon molecules of pyruvate, and the potential energy released is used to phosphorylate ADP to form ATP.
How does glycolysis produce 8 ATP?
In the entire process of glycolysis, 2 NADPH molecules also formed. Each NADH produces 3ATP molecules that mean 6 ATP molecules in glycolysis are produced via NADPH. Therefore the total ATP molecules formed are 10ATP as 2ATPs used up in the initial steps, the net gain is 8 ATP molecules. So, the correct answer is '8'.
How does ATP get generated?
ATP is also formed from the process of cellular respiration in the mitochondria of a cell. This can be through aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. Aerobic respiration produces ATP (along with carbon dioxide and water) from glucose and oxygen.
Why does glycolysis produce 2 ATP?
Although four ATP molecules are produced in the second half, the net gain of glycolysis is only two ATP because two ATP molecules are used in the first half of glycolysis.
Why are 4 ATP produced in glycolysis?
ATP is produced when 1,3 bisphosphoglyceric acid (BPGA) is converted into 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) and when phosphoenolpyruvate is converted to pyruvic acid. These steps take place twice, once for each triose phosphate, so a total of 4 ATP molecules are produced.
Does glycolysis produce 2 or 4 ATP?
During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is split into two pyruvate molecules, using 2 ATP while producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
What are the 3 ways ATP is generated?
ATPs are generated during cellular respiration. ATP is generated in glycolysis in the cytoplasm and in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (ETS) in mitochondria.
What are the two ways to make ATP?
What Are the Four Major Methods of Producing ATP?Glycolysis. Glycolysis is one method of producing ATP and occurs in almost all cells. ... Oxidative Phosphorylation. ... Beta Oxidation. ... Aerobic Respiration.
When and where ATP is produced?
The majority of ATP synthesis occurs in cellular respiration within the mitochondrial matrix: generating approximately thirty-two ATP molecules per molecule of glucose that is oxidized.
Where is ATP produced in glycolysis?
Anaerobic glycolysis serves as a means of energy production in cells that cannot produce adequate energy through oxidative phosphorylation. In poorly oxygenated tissue, glycolysis produces 2 ATP by shunting pyruvate away from mitochondria and through the lactate dehydrogenase reaction.
How does glucose become ATP?
Glucose is converted into ATP by cellular respiration. Glucose is completely oxidised to CO2 and water producing energy, which is stored as ATP. One molecule of glucose produces 38 ATP molecules by aerobic respiration.
Why is ATP required for glycolysis?
Why is ATP required for glycolysis? ATP makes it easier to break apart glucose into two three-carbon molecules.
How many ATP are in glycolysis?
The total number of ATP produced in glycolysis is 4 from one glucose molecule. 2 molecules of ATP are utilised in the first half of glycolysis so there is a net gain of 2 ATP molecules in glycolysis.
How is 38 ATP formed?
Our body produces a large amount of ATP during respiration. If glucose is the respiratory substrate, then we get the net gain of 38 ATP molecules in aerobic respiration from one glucose molecule.
How many ATP are invested in glycolysis?
two ATP moleculesReview: The energy investment phase of glycolysis involves the investment of two ATP molecules and results in the formation of two molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate.
Where is ATP produced in glycolysis?
Anaerobic glycolysis serves as a means of energy production in cells that cannot produce adequate energy through oxidative phosphorylation. In poorly oxygenated tissue, glycolysis produces 2 ATP by shunting pyruvate away from mitochondria and through the lactate dehydrogenase reaction.
How many ATP molecules are produced from each triose phosphate molecule?
In glycolysis, 2 ATP molecules are produced from each triose phosphate molecule ... I don't understand how this would be the case, as each triose phosphate only has one phosphate group
How is acetone phosphate converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate?
Similarly Dihydroxy acetone phosphate the other triose is first converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by an isomerisation reaction catalysed by triosephosphate isomerase. This glyceraldehyde-3-PO 4 formed undergoes phosphorylation to form a two phosphoryl group containing compound.
What is a biology stack exchange?
Biology Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for biology researchers, academics, and students. It only takes a minute to sign up.
Is phosphate added to glycoldehyde?
Yes the Phosphate group added to Glyceraldehyde-3-PO$_4$ is derived from orthophosphate (HPO43−).
Is glyceraldehyde phosphorylated?
You can see that out of the two trioses Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is phosphorylated into a compound (1,3-bisphosphoglycerate) that has two phosphoryl groups. Similarly Dihydroxy acetone phosphate the other triose is first converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by an isomerisation reaction catalysed by triosephosphate isomerase. This glyceraldehyde-3-PO$_4$ formed undergoes phosphorylation to form a two phosphoryl group containing compound.
What is the function of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (?
First, it dehydrogenates GAP by transferring one of its hydrogen (H⁺) molecules to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) to form NADH + H⁺.
What happens to the phosphoglycerokinase in BPG?
The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a phosphate from BPG to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens to each molecule of BPG. This reaction yields two 3-phosphoglycerate (3 PGA) molecules and two ATP molecules.
How many molecules does glycolysis produce?
Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
How many ATP molecules does pyruvate kinase produce?
This happens for each molecule of PEP. This reaction yields two molecules of pyruvate and two ATP molecules.
How many ATP molecules are produced in glycolysis?
A net of two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis (two are used during the process and four are produced.) Learn more about the 10 steps of glycolysis below.
How many ATP molecules are in a multistep process?
This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water.
What is the isomer of G6P?
The enzyme phosphoglucomutase isomerizes G6P into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate or F6P. Isomers have the same molecular formula as each other but different atomic arrangements.
How many ATP molecules does glycolysis produce?
For the glycolysis to work, it needs two ATP molecules and then in the end it generates four ATP molecules, so two it gains two more ATP molecules. It also produces two pyruvate molecules and two NADH, the pyruvate molecules are molecules that are rich in carbon and the NADH is a high energy molecule used to produce more ATP. ...
What is the first step in cellular respiration?
The first step is called Glycolysis. Then there is The Krebs Cycle and last there is the Electron Transport Chain before ATP is created. Glycolysis. This part of the process of cellular respiration is where all the glucose is broken down and turned into two, three carbon molecules called pyruvate molecules. This takes place in the cytoplasm.
How does pyruvate work?
How it works is at first one of the pyruvate molecules are oxygenated and then there is two pyruvates left. This then causes the two pyruvate molecules to create two more NADH for further ATP production. Lastly, there is the Electron Transport Chain process.
What is the process of ATP production?
The production of ATP is called the process of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy in the form of glucose. Here are three steps before the ATP is created in the mitochondria. The first step is called Glycolysis.
Does cellular respiration need oxygen?
The process of cellular respiration needs oxygen for it to work but, not in all the phases. The process of fermentation is when there is no oxygen in the cell and it needs NADH for the glycolysis to keep working. This is the next part of the production of ATP!
Where does the electron transport chain take place?
The Electron Transport Chain takes place in the inter membrane space of the mitochondria. This process can only function if there is oxygen available. The simplest way to understand this, is that it basically moves the electrons from high energy to low energy.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.