
How is ATP transported out of the mitochondria? Transport systems of the mitochondrial inner membrane carry ADP and P into the matrix and allow the newly synthesized ATP to leave. The ATP -ADP translocase is an antiporter; the same protein moves ADP into the matrix and ATP out .
How do carrier proteins transport ADP and ATP in and out of mitochondria?
Mar 22, 2020 · How is ATP transported out of the mitochondria? Transport systems of the mitochondrial inner membrane carry ADP and P into the matrix and allow the newly synthesized ATP to leave. The ATP-ADP translocase is an antiporter; the same protein moves ADP into the matrix and ATP out. Click to see full answer.
How many times a day is ATP recycled from mitochondria?
When the dust settled, a picture emerged where ATP is exported across the inner membrane in a 1:1 exchange against ADP and where the selection of ATP versus ADP is controlled by the high membrane potential at the inner membrane, thus uplifting the free energy of ATP in the cytosol over the mitochondrial matrix.
How is ATP synthesized in the mitochondria?
Jan 24, 2019 · The archetypal member of the family, the ADP/ATP carrier, performs the vital role of transporting ADP into the mitochondrial matrix and ATP out of the mitochondrion to maintain high cytosolic ATP concentrations for energy-requiring reactions (Kunji et al., 2016). Every day, this carrier transports our own body weight in ADP and ATP, recycling each ATP molecule more …
What is the electron transport chain process in mitochondria?
How is ATP released from the mitochondria?
Most of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesized during glucose metabolism is produced in the mitochondria through oxidative phosphorylation. This is a complex reaction powered by the proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane, which is generated by mitochondrial respiration.
How does ATP get transported?
Free ADP is transported from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix, while ATP produced from oxidative phosphorylation is transported from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytoplasm, thus providing the cells with its main energy currency.
How is ATP transported across the mitochondrial membrane?
Mitochondrial ADP/ATP carriers import ADP and export ATP across the inner membrane. They function as monomers and do not associate with other proteins. They have a single substrate binding site and two salt bridge networks in the central cavity.
Does ATP go in or out of the mitochondria?
Some of the active transport processes driven by the electrochemical proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Pyruvate, inorganic phosphate (Pi), and ADP are moved into the matrix, while ATP is pumped out.
How does ATP move across the cell membrane?
Primary active transport directly uses a source of chemical energy (e.g., ATP) to move molecules across a membrane against their gradient.
What is ATP transport?
The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) is a major transport protein of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It exchanges mitochondrial ATP for cytosolic ADP and controls cellular production of ATP.Jul 24, 2019
How is ATP transported out of the mitochondria matrix and into the intermembrane space?
During electron transport, the participating protein complexes push protons from the matrix out to the intermembrane space. This creates a concentration gradient of protons that another protein complex, called ATP synthase, uses to power synthesis of the energy carrier molecule ATP (Figure 2).
Can ATP be transported from one cell to another?
The evidence presented by various investigators clearly indicates that ATP can cross the cell membrane and suggests that the release and uptake of ATP are physiological processes.
Is ATP an electron carrier?
ATP (Adenosine triphosphate): The major energy currency of the cell. ATP is a high-energy molecule that stores and transports energy within cells. NADH: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain.Jun 22, 2019
How is energy released from ATP?
When one phosphate group is removed by breaking a phosphoanhydride bond in a process called hydrolysis, energy is released, and ATP is converted to adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Likewise, energy is also released when a phosphate is removed from ADP to form adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
Why is the outward transport of ATP favored over the outward transport of ADP by the adenine nucleotide transporter?
The adenine nucleotide transporter. The charges on the substrates are such that ATP carries a net excess charge of -1 compared to ADP. The exchange reaction is therefore electrogenic, and driven by the electrical component (Dy) of the proton gradient, so that entry of ADP and exit of ATP are favored.
What is the process of ATP production?
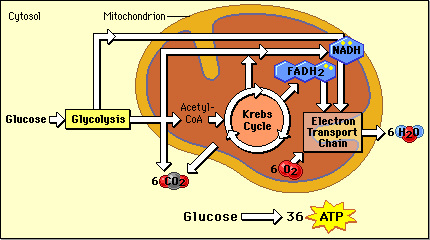
The production of ATP is called the process of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy in the form of glucose. Here are three steps before the ATP is created in the mitochondria. The first step is called Glycolysis.
How many ATP molecules does glycolysis produce?
For the glycolysis to work, it needs two ATP molecules and then in the end it generates four ATP molecules, so two it gains two more ATP molecules. It also produces two pyruvate molecules and two NADH, the pyruvate molecules are molecules that are rich in carbon and the NADH is a high energy molecule used to produce more ATP. ...
How does pyruvate work?
How it works is at first one of the pyruvate molecules are oxygenated and then there is two pyruvates left. This then causes the two pyruvate molecules to create two more NADH for further ATP production. Lastly, there is the Electron Transport Chain process.
What is the first step in cellular respiration?
The first step is called Glycolysis. Then there is The Krebs Cycle and last there is the Electron Transport Chain before ATP is created. Glycolysis. This part of the process of cellular respiration is where all the glucose is broken down and turned into two, three carbon molecules called pyruvate molecules. This takes place in the cytoplasm.
Where does the electron transport chain take place?
The Electron Transport Chain takes place in the inter membrane space of the mitochondria. This process can only function if there is oxygen available. The simplest way to understand this, is that it basically moves the electrons from high energy to low energy.
What is the process of fermentation?
The process of fermentation is when there is no oxygen in the cell and it needs NADH for the glycolysis to keep working. This is the next part of the production of ATP! In this process of The Krebs Cycle, it finally completes the breakdown of glucose, which was originally started by the process of Glycolysis.
Which organelle is responsible for ATP synthesis?
As discussed in Chapter 14, mitochondria and chloroplasts are double-membrane-enclosed organelles. They specialize in the synthesis of ATP, using energy derived from electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria and from photosynthesis in chloroplasts . Although both organelles contain their own DNA, ribosomes, ...
What is the role of TIM23 in the inner membrane?
The TIM23 complex then transports some of these proteins into the matrix space, while helping to insert transmembrane proteins into the inner membrane . The TIM22 complex mediates the insertion of a subclass of inner membrane proteins, including the carrier proteinthat transports ADP, ATP, and phosphate.
Where is cytochrome oxidase located?
Cytochrome oxidase is a large multiprotein complex located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it functions as the terminal enzyme in the electron-transport chain (discussed in Chapter 14). (A) (more...)
What is the function of HSP70?
Thus, a hand-over-hand binding of multiple hsp70 proteins translocates the polypeptide chain into the matrix.
What is the ADP/ATP carrier?
The ADP/ATP carrier is just one member of a large family of related transport proteins that bring different compounds in and out of mitochondria, and based on this discovery, the scientists believe that this mechanism is likely to work in a similar way for the whole family. There are many diseases associated with dysfunction ...
Where is ATP synthase located?
Since we only have a small amount of ATP in our body, we need to remake it from the spent product ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate using an enzyme complex, called ATP synthase, which is located in mitochondria. In this way, every molecule of ATP is recycled roughly 1300 times a day. For ADP to reach the enzyme, and for ...
What is the role of ADP in the cell?
For ADP to reach the enzyme, and for the product ATP to refuel the cell, each molecule has to cross an impermeable lipid membrane that surrounds the mitochondria. The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier is involved in the transport of ADP in and ATP out of mitochondria.
Why is mitochondria important?
This process is vital to keep us alive, every second of our lives, for all of our lives. This work will help us understand how mutations can affect the function of these proteins, resulting in a range of neuromuscular, metabolic and developmental diseases. Cellular structures, called mitochondria, are the powerhouses of our cells.
What is a nanobody?
Nanobodies are fragments of llama antibodies, which bind specifically to the matrix-open state, and the structure of carrier-nanobody complex with bound bongkrekic acid was determined by X-ray crystallography. Together with earlier structures of the cytoplasmic-open state, this discovery reveals how the carrier works at the atomic scale.
Where is ATP synthase located?
As ATP synthase generates ATP, it deposits this molecule in the innermost region of the mitochondria ( called the matrix or the lumen).
What are the functions of mitochondria?
Mitochondria serve cells in a number of ways, including: 1 Calcium storage 2 Calcium signaling 3 Signaling with reactive oxygen species 4 Regulation of cellular metabolism 5 Heat production 6 Apoptosis
What is the endosymbiotic origin of mitochondria?
Much of the evidence for the endosymbiotic origin of mitochondria centers around the similarity between mitochondria and bacteria. These organelles are about the same size and shape as typical bacteria and have a double membrane structure like gram-negative cells. These organelles also divide in a way that is reminiscent of bacterial cells.
