
Active transport uses energy stored in ATP to fuel the transport. Active transport of small molecular-size material uses integral proteins in the cell membrane to move the material—these proteins are analogous to pumps. Some pumps, which carry out primary active transport, couple directly with ATP to drive their action.
Why does active transport require the use of ATP?
The utilization of energy by a cell is required in order to transport substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient. Active transport systems perform precisely this function, burning energy (typically in the form of ATP) in order to maintain the proper concentrations of ions and molecules in living organisms.
What is the role of ATP in the process of active transport?
During the process of active transport, a protein pump makes use of stored energy in the form of ATP, to move molecules The below diagram shows the process of active transport, which uses an external energy ATP for the movement of the molecules. Active Transport
Does active transport generate or require ATP?
Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell’s energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If a substance must move into the cell against its concentration gradient, that is, if the concentration of the substance inside the cell must be greater than its concentration in the extracellular fluid, the cell must use energy to move the substance.
What kind of active transport does not use ATP?
Secondary active transport, created by primary active transport, is the transport of a solute in the direction of its electrochemical gradient and does not directly require ATP. Carrier proteins such as uniporters, symporters, and antiporters perform primary active transport and facilitate the movement of solutes across the cell’s membrane.

What is the energy stored in ATP?
The energy stored in ATP then allows the channel to change shape, spitting the sodium ion out on the opposite side of the cell membrane. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called “primary” active transport. Another type of active transport is “secondary” active transport. In this type of active transport, ...
What is active transport?
Active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. In these cases, active transport is required. ...
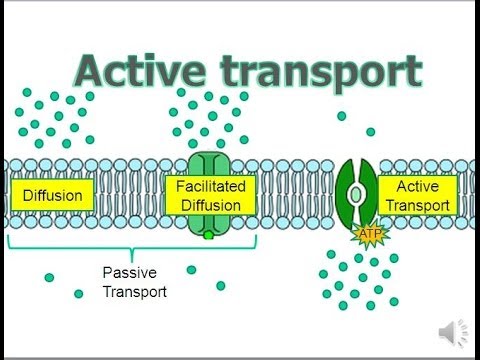
What is the Difference Between Active Transport and Passive Transport?
Active transport moves substances from a region of lower concentration to a higher concentration, i. e., against the concentration gradient. There is an energy requirement for this process, as it does not occur naturally in the absence of active forces.
How does folding of the cell membrane work?
The folding of the cell membrane is accomplished in a mechanism similar to the antiport transport of potassium and sodium ions. Molecules of ATP bind to proteins in the cell membrane, causing them to change their shape. The conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of the cell membrane until a vesicle is created.
What is the name of the channel that binds to the molecule it is supposed to transport?
For example, one type of active transport channel in the cell membrane will bind to the molecule it is supposed to transport – such as a sodium ion – and hold onto it until a molecule of ATP comes along and binds to the protein. The energy stored in ATP then allows the channel to change shape, spitting the sodium ion out on the opposite side of the cell membrane. This type of active transport directly uses ATP and is called “primary” active transport.
How does active transport occur?
In exocytosis, a cell moves something outside of itself in large quantities by wrapping it in a membrane called a vesicle and “spitting out” the vesicle. In endocytosis, a cell “eats” something by wrapping and re-forming its membrane around the substance or item.
Why are antiport pumps so efficient?
These pumps are extremely efficient because many of them can use one ATP molecule to fuel these two different tasks. One important type of antiport pump is the sodium-potassium pump, which is discussed in more detail under “Examples of Active Transport.”.
What are the functions of ATP?
Functions of ATP in cells. ATP finds use in several cellular processes. Some important functions of ATP in the cell are briefly discussed below: Active Transport. ATP plays a critical role in the transport of macromolecules such as proteins and lipids into and out of the cell. The hydrolysis of ATP provides the required energy for active transport ...
How does ATP help the cell?
ATP plays a very important role in preserving the structure of the cell by helping the assembly of the cytoskeletal elements. It also supplies energy to the flagella and chromosomes to maintain their appropriate functioning.
Why are high levels of dNTPs mutagenic?
Low concentrations of dNTPs inhibit DNA synthesis and repair whilst high levels are shown to be mutagenic because DNA polymerase tends to add the wrong dNTP during DNA synthesis. The adenosine from ATP is a building block of RNA and is directly added to RNA molecules during RNA synthesis by RNA polymerases.
What happens when you remove a phosphate from ATP?
The enzymatic removal of a phosphate group from ATP to form ADP releases a huge amount of energy which is used by the cell in several metabolic processes as well as in the synthesis of macromolecules such as proteins. The removal of a second phosphate group from ATP results in further energy release and the formation of adenosine monophosphate ...
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
ATP is critical for the contraction of muscles; it binds to myosin to provide energy and facilitate its binding to actin to form a cross-bridge. ADP and phosphate are then released and a new ATP molecule binds to myosin. This breaks the cross-bridge between myosin and actin filaments, thereby releasing myosin for the next contraction.
What is the role of adenosine in the central nervous system?
In the central nervous system, adenosine modulates neural development, the control of immune systems, and of neuron/glial signaling. ATP is also involved in signal transduction - its phosphate groups are used up by kinases in phosphate transfer reactions which activate a cascade of protein kinase reactions. Structural Maintenance.
What is the main source of energy in a cell?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function in Cells. ATP is the main source of energy for most cellular processes. The building blocks of ATP are carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus. Because of the presence of unstable, high-energy bonds in ATP, it is readily hydrolyzed in reactions to release a large amount of energy.
What is the primary active transport protein?
A famous example of primary active transport is the Sodium-Potassium (Na/ K) Pump, which is shown in the figure below.
What is the most common source of energy for active transport?
The most common source of energy for active transport is ATP, or Adenosine Tri-Phosphate. Active transport can take place anywhere in the cell, for example:
What is the term for the movement of large molecules across a membrane?
Endocytosis and Exocytosis (also known as bulk transport) — Movement of very large molecules (e.g. proteins and carbohydrates) across a membrane using vesicles.
What is the purpose of a protons pump?
Protons pumps, which are also called H + -ATPases, are primary uniporters that use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to transport protons (H + ions) against their concentration gradient from low concentration to high concentration. These pumps are used throughout the cell to create high proton concentrations, which can then be used for secondary transport. These pumps can also create acidic environments in certain organelles, e.g. lysosomes.
Where do sodium ions bind to the active site of the transporter?
Three sodium ions bind to the active site of the transporter from the interior of the cell (the "intracellular space").
Which ions dissociate from the transporter?
The three sodium ions dissociate from the transporter, and two potassium ions from outside the cell bind in their place.
What are the two types of cellular transport?
There are two main types of cellular transport: active transport and passive transport. Both types of transport are necessary in every living organism.
What is the ADP/ATP carrier?
The ADP/ATP carrier is just one member of a large family of related transport proteins that bring different compounds in and out of mitochondria, and based on this discovery, the scientists believe that this mechanism is likely to work in a similar way for the whole family. There are many diseases associated with dysfunction ...
Which protein carries out the vital task of transporting ADP into mitochondria and ATP out?
The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier protein in the mitochondrial inner membrane, which carries out the vital task of transporting ADP into mitochondria and ATP out. Credit: MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit
What is the role of ADP in the cell?
For ADP to reach the enzyme, and for the product ATP to refuel the cell, each molecule has to cross an impermeable lipid membrane that surrounds the mitochondria. The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier is involved in the transport of ADP in and ATP out of mitochondria.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Cellular structures, called mitochondria, are the powerhouses of our cells. Every day, we humans need our own body weight in ATP to fuel all of the cellular activities. Nerve impulses, muscle contraction, DNA replication and protein synthesis are just some examples of essential processes that depend upon a supply of ATP. Since we only have a small amount of ATP in our body, we need to remake it from the spent product ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate using an enzyme complex, called ATP synthase, which is located in mitochondria. In this way, every molecule of ATP is recycled roughly 1300 times a day. For ADP to reach the enzyme, and for the product ATP to refuel the cell, each molecule has to cross an impermeable lipid membrane that surrounds the mitochondria. The mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier is involved in the transport of ADP in and ATP out of mitochondria.
What is the key transport protein?
Scientists at the MRC-MBU in Cambridge, U.K., have discovered how a key transport protein, called the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier, transports ad enosine triphosphate (ATP), the chemical fuel of the cell. This process is vital to keep us alive, every second of our lives, for all of our lives.
Where is ATP synthase located?
Since we only have a small amount of ATP in our body, we need to remake it from the spent product ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate using an enzyme complex, called ATP synthase, which is located in mitochondria. In this way, every molecule of ATP is recycled roughly 1300 times a day. For ADP to reach the enzyme, and for ...
Which state of the carrier is accessible for binding of ADP?
The carrier cycles between two states; in one state, the central binding site is accessible for binding of ADP, called the cytoplasmic-open state, and in another, the binding site is accessible for binding newly synthesized ATP, called the matrix-open state.
Definition
Process of Active Transport
- Active transport requires energy to move substances from a low concentration of that substance to a high concentration of that substance, in contrast with the process of osmosis. Active transport is most commonly accomplished by a transport protein that undergoes a change in shape when it binds with the cell’s “fuel,” a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). For ex…
Types of Active Transport
- Antiport Pumps
Antiport pumps are a type of transmembrane co-transporter protein. They pump one substance in one direction, while transporting another substance in the opposite direction. These pumps are extremely efficient because many of them can use one ATP molecule to fuel these two different … - Symport Pumps
Symport pumps take advantage of diffusion gradients to move substances. Diffusion gradients are differences in concentration that cause substances to naturally move from areas of high to low concentration. In the case of a symport pump, a substance that “wants” to move from an are…
Examples of Active Transport
- Sodium Potassium Pump
One of the most important active transport proteins in animals is the sodium-potassium pump. As animals, our nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells. It is this gradient that allows our nerve cells to fire, creatin… - Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein
A famous example of a symport pump is that of the sodium-glucose transport protein. This protein binds to two sodium ions, which “want” to move into the cell, and one glucose molecule, which “wants” to stay outside of the cell. It represents an important method of sugar transportin …
What Is The Difference Between Active Transport and Passive Transport?
- Active transport moves substances from a region of lower concentration to a higher concentration, i.e., against the concentration gradient. There is an energy requirement for this process, as it does not occur naturally in the absence of active forces. In contrast, passive transport occurs naturally, as substances move down a concentration gradient in the absence o…