How are capillaries regulated in the body?
Capillary beds are regulated through something called autoregulation, so that if blood pressure would drop, flow through the capillaries will continue to provide oxygen and nutrients to the tissues of the body.
How does capillary blood flow affect the rate of oxygen usage?
the rate of oxygen usage by the tissue is great so that tissue oxygen concentration decreases below normal, the intermittent periods of capillary blood flow occur more often, and the duration of each period of flow lasts longer, thereby allowing the capillary blood to carry increased quantities of oxygen (as well as other nutrients) to the tissues.
How is blood flow regulated in the human body?
Blood flow through the body is regulated by the size of blood vessels, by the action of smooth muscle, by one-way valves, and by the fluid pressure of the blood itself. Figure 5. Blood pressure is related to the blood velocity in the arteries and arterioles.
What is the flow of blood in the capillaries?
Flow of Blood in the Capillaries Vasomotion. Blood usually does not flow continuously through the capillaries. Instead, it flows intermittently, turning on and off every few seconds or minutes.
How is blood flow regulated to the capillaries quizlet?
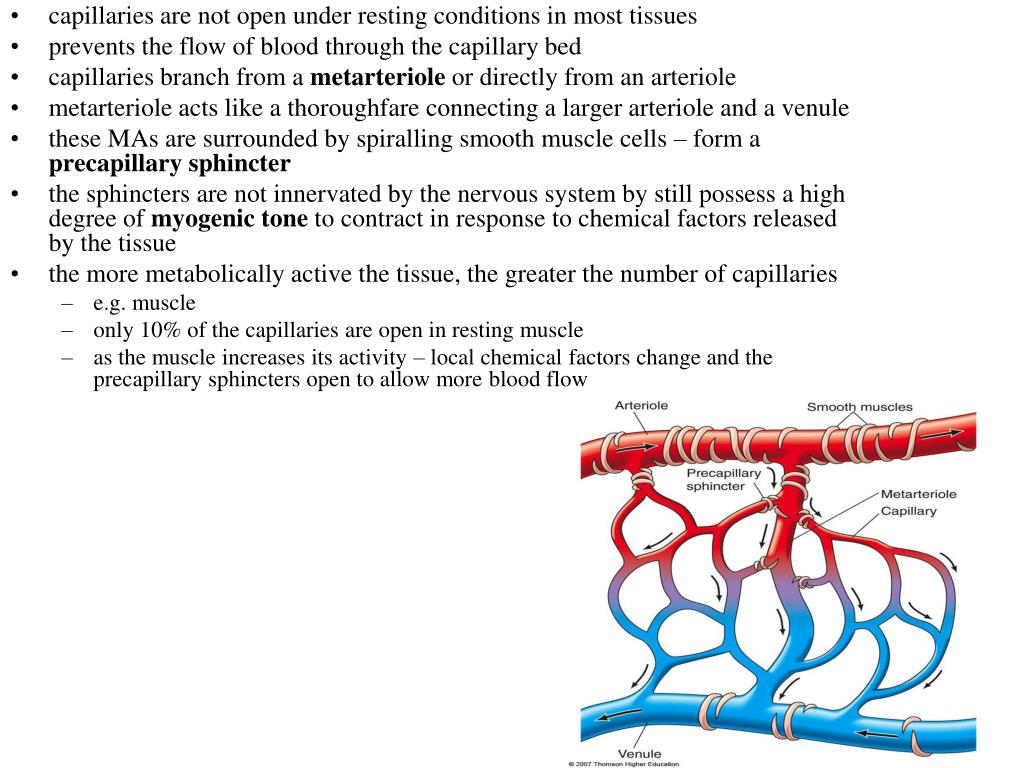
Blood flow into capillaries is controlled by smooth muscle tissue located at the arterial end of a capillary called a precapillary sphincter, which may close or open capillary, by contracting or relaxing. A precapillary sphincter responds to the demands of the cells the capillary supplies.
What regulates the flow of blood?
Blood flow through the body is regulated by the size of blood vessels, by the action of smooth muscle, by one-way valves, and by the fluid pressure of the blood itself. Figure 5. Blood pressure is related to the blood velocity in the arteries and arterioles.
How does capillaries affect blood flow?
Blood flow is slowest in the capillaries, which allows time for exchange of gases and nutrients. Resistance is a force that opposes the flow of a fluid. In blood vessels, most of the resistance is due to vessel diameter. As vessel diameter decreases, the resistance increases and blood flow decreases.
Which of the following regulates blood flow through most capillary beds?
Chapter 19 QuizesQuestionAnswerThe only vessels that provide direct access to nearly every cell in the body are the:capillaries.____________ regulates blood flow at the entrance to each true capillary?Precapillary sphincter44 more rows
Do capillaries have valves?
Veins use valves to transport blood towards the heart, but capillaries don't have valves. Capillaries diffuse blood and nutrients between veins and arteries through their thin walls.
How capillaries are adapted to their function?
Capillaries have walls only one endothelial cell thick, meaning their walls are very thin. This makes them well adapted for gas exchange, as substances only have to diffuse over a short distance. Additionally, there are many capillaries within a capillary bed.
What is the function of capillaries?
Capillaries: These tiny blood vessels have thin walls. Oxygen and nutrients from the blood can move through the walls and get into organs and tissues. The capillaries also take waste products away from your tissues. Capillaries are where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for carbon dioxide and waste.
How is blood pressure regulated?
In the short term, blood pressure is regulated by baroreceptors, which act via the brain to influence the nervous and the endocrine systems. Blood pressure that is too low is called hypotension, pressure that is consistently too high is called hypertension, and normal pressure is called normotension.
What is the function of pericytes?
Thus, pericytes are major regulators of cerebral blood flow and initiators of functional imaging signals. Prevention of pericyte constriction and death may reduce the long-lasting blood flow decrease that damages neurons after stroke.
Does ischaemia cause capillary constriction?
In pathology, ischaemia evokes capillary constriction by pericytes. We show that this is followed by pericyte death in rigor, which may irreversibly constrict capillaries and damage the blood-brain barrier. Thus, pericytes are major regulators of cerebral blood flow and initiators of functional imaging signals.
What is the role of capillaries in the body?
Only two layers of cells thick, the purpose of capillaries is to play the central role in the circulation , delivering oxygen in the blood to the tissues, and picking up carbon dioxide to be eliminated. They are also the place where nutrients are delivered to feed all of the cells of the body.
Why are capillaries in the lungs important?
Certainly, the lungs are packed with capillaries surrounding the alveoli to pick up oxygen and drop off carbon dioxide. Outside of the lungs, capillaries are more abundant in tissues that are more metabolically active. 2 .
How long does it take for a capillary refill to return?
If color returns within two seconds (the amount of time it takes to say capillary refill), circulation to the arm or leg is probably OK. If capillary refill takes more than two seconds, the circulation of the limb is probably compromised and considered an emergency.
What is the smallest blood vessel in the body?
Frequently Asked Questions. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body, connecting the smallest arteries to the smallest veins. These vessels are often referred to as the "microcirculation.".
What is the pressure of the capillary?
On the arterial side of the capillary, the hydrostatic pressure (the pressure that comes from the heart pumping blood and the elasticity of the arteries) is high. Since capillaries are "leaky" this pressure forces fluid and nutrients against the walls of the capillary and out into the interstitial space and tissues.
How many layers are there in the capillary?
Capillaries are very thin, approximately 5 micrometers in diameter, and are composed of only two layers of cells—an inner layer of endothelial cells and an outer layer of epithelial cells. They are so small that red blood cells need to flow through them single file.
What happens to the hydrostatic pressure of the veins?
On the vein side of the capillary, the hydrostatic pressure has dropped significantly. At this point, it is the osmotic pressure of the fluid within the capillary (due to the presence of salts and proteins in the blood) that draws fluids back into the capillary.
What are the sites of exchanges of materials between the blood and the tissue fluid surrounding cells?
Capillaries are the sites of exchanges of materials between the blood and the tissue fluid surrounding cells. Some of these substances move from the blood to tissue fluid, and others move from tissue fluid to the blood. The processes by which these substances are exchanged are illustrated in Fig. 13–2.
Why do precapillary sphincters dilate?
In an active tissue that requires more oxygen, such as exercising muscle, the precapillary sphincters dilate to increase blood flow.
What determines the rate of fluid movement at any point along a capillary?
The rate of fluid movement at any point along a capillary depends upon a balance of forces (Starling forces), Four primary forces determine whether fluid will move out of the capillary into the interstitial space or in the opposite direction:
What is the net fluid movement between the capillary and interstitial compartments?
Net shifts of the fluid between the capillary & interstitial compartments are important for many physiological functions including the maintenance of circulating blood volume, tissue fluid formation, interstitial fluid absorption, and urine production, Net fluid movement out of the capillaries is referred to as filtration, and fluid movement into capillaries is called reabsorption.
What is the osmotic pressure of a capillary?
Capillary colloid osmotic pressure: When a substance has a large molecule (e.g. plasma proteins), it is prevented from passing through the pores of the endothelial membrane. This substance creates an osmotic pressure inside the capillary. It is about 25 mm Hg caused mainly by albumin and to a lesser extent, globulin.
What is the smallest blood vessel in the body?
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body, they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. The capillaries contain only 5% of the circulatory blood, but this fraction is the most important part of the blood volume because the exchange across the capillary wall is essential for the survival of the tissues.
How does oxygen affect the metarterioles?
The concentration of oxygen in the tissues is the most important factor which affects the degree of opening & closing of the metarterioles and precapillary sphincters, When the rate of oxygen usage is great so that the tissue oxygen decreases , the intermittent periods of blood flow occur more often , and the duration of each period of flow lasts longer, allowing blood to carry increased quantities of oxygen (as well as other nutrients) to the tissues (metabolic autoregulation of blood flow ).
What is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
The diffusion is the passive movement of the molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Oxygen and glucose are in higher concentration in the bloodstream than in the interstitial fluid and diffuse into the interstitial fluid, whereas CO 2 diffuses in the opposite direction.