- surgery to remove a tumor, blood clot, or abscess.
- ventriculostomy, a surgery that places a drain through a hole in the skull to get rid of fluids.
- osmotic therapy or diuretics, such as mannitol or hypertonic saline, to pull fluid out of the brain tissue.
- corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Which sign indicates impending herniation?
Which sign indicates impending herniation? Asymmetric pupillary response, unilateral or bilateral pupillary dilation, and abnormal motor posturing are signs of impending herniation from an uncontrolled increase in intracranial pressure
What are the symptoms of a brain herniation?
- Collection of pus and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection ( abscess)
- Bleeding in the brain (hemorrhage)
- Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling ( hydrocephalus)
- Strokes that cause brain swelling
- Swelling after radiation therapy
How to treat brain meningiomas?
Treatments for meningioma
- Observation. Observation means seeing a neurosurgeon and having imaging tests done periodically. ...
- Surgery. The most common type of surgery to remove a meningioma is called a craniotomy. ...
- Radiation therapy. ...
- Rehabilitation Therapy. ...
What are the treatments for brain swelling?
What are the treatment options?
- Medication. Depending on the severity of your condition and the underlying cause, doctors may prescribe you medication to help reduce swelling and prevent blood clots.
- Osmotherapy. When your brain swells, it accumulates excess fluid. ...
- Hyperventilation. ...
- Hypothermia. ...
- Ventriculostomy. ...
- Surgery. ...
Can you recover from a herniated brain?
People who have a brain herniation have a serious brain injury. They may already have a low chance of recovery due to the injury that caused the herniation. When herniation occurs, it further lowers the chance of recovery. The outlook varies, depending on where in the brain the herniation occurs.
Which brain herniation is the most life threatening?
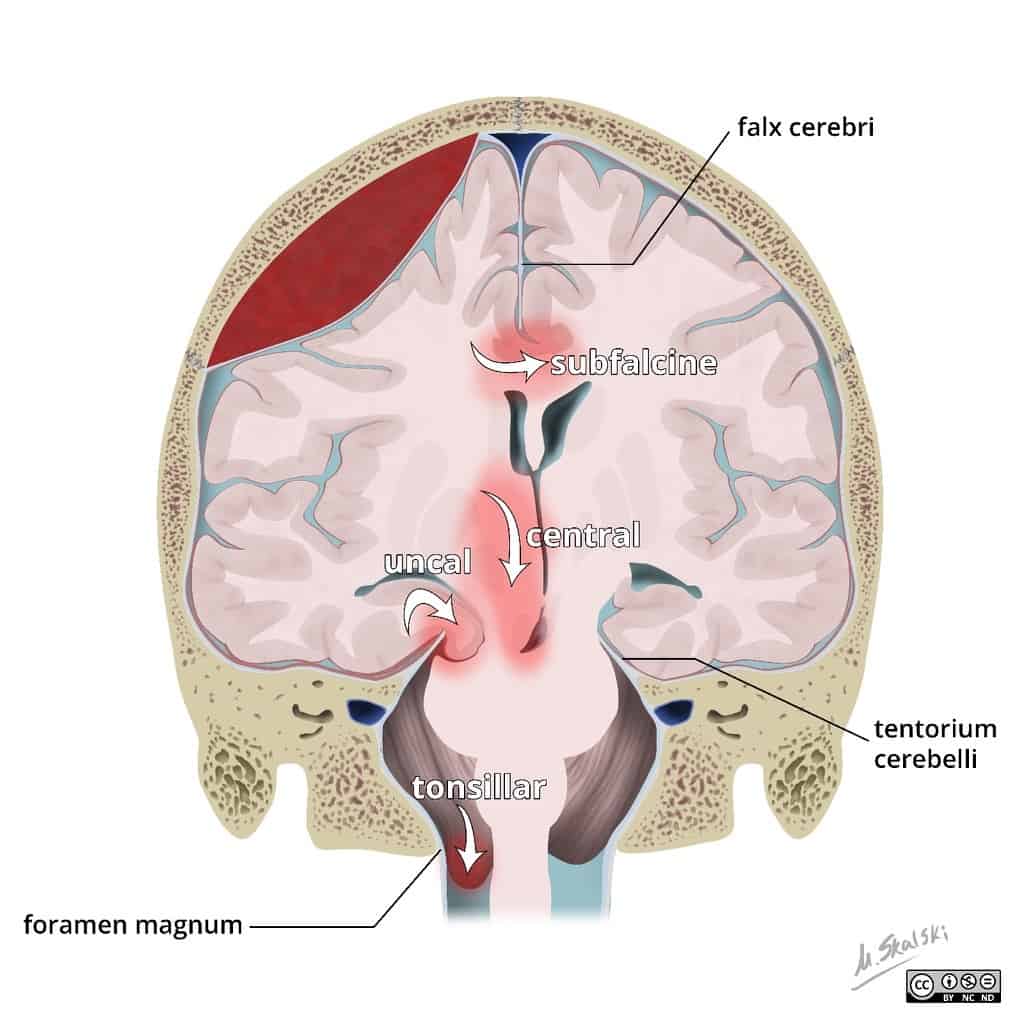
Central herniation Downward herniation can stretch branches of the basilar artery (pontine arteries), causing them to tear and bleed, known as a Duret hemorrhage. The result is usually fatal.
What is the most common type of brain herniation?
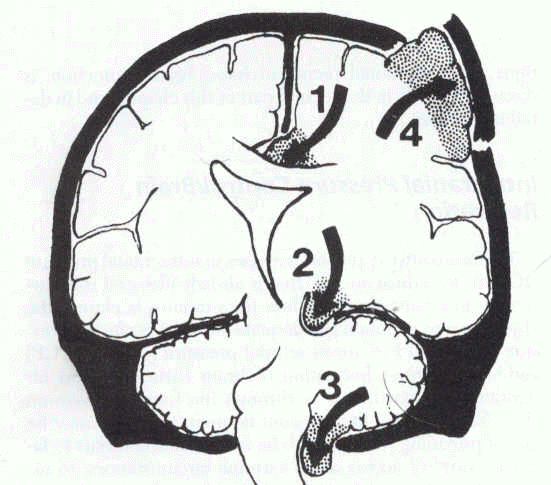
Subfalcine hernia, also known as midline shift or cingulate hernia, is the most common type of cerebral hernia. It is generally caused by unilateral frontal, parietal, or temporal lobe disease that creates a mass effect with medial direction, pushing the ipsilateral cingulate gyrus down and under the falx cerebri.
What are the stages of brain herniation?
Brain herniation can progress from a subtle finding of pupillary asymmetry (uncal herniation) to an altered level of consciousness (compression of the reticular activating system), then progressing to the moribund stage of abnormal posturing (compression of the diencephalon and the brainstem), and finally death ...
Where does your brain go when herniated?
During a central herniation, the temporal lobe gets pushed down to the tentorial notch, which is the closest part of the brain to the spine. Tonsillar herniations. These occur in the infratentorial area of the brain. The herniation pushes back brain tissue into the area that connects the skull to the spine.
Can brain herniation cause sudden death?
Understanding brain herniation The condition is usually caused by swelling from a head injury, stroke, bleeding, or brain tumor. A brain herniation is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention. It's often fatal if not treated right away.
What happens when your brain shifts?
Diffuse axonal injury is the shearing (tearing) of the brain's long connecting nerve fibers (axons) that happens when the brain is injured as it shifts and rotates inside the bony skull. DAI usually causes coma and injury to many different parts of the brain.
What causes brain to shift?
Brain shift is deformation of the brain that occurs during neurosurgery. It is caused by several factors indirectly related to surgery including gravity, head position, fluid drainage, use of hyperosmotic drugs, changes in intracranial pressure and swelling of brain tissue.
What is a clinical symptom of central herniation?
The clinical syndrome of central herniation classically manifests as a rostral to caudal progression of deficits attributed to brainstem dysfunction, including cranial nerve III (oculomotor nerve) palsy, diminished level of consciousness, decerebrate or decorticate posturing, rigidity or paralysis, abnormal respiratory ...
What patient presentation is indicative of the first stage of brain herniation?
A patient with impending uncal herniation will initially present with symptoms of increased intracranial pressure. These symptoms include headache, nausea, vomiting, and altered mental status.
What are 3 symptoms of a brain injury?
Physical symptomsLoss of consciousness from several minutes to hours.Persistent headache or headache that worsens.Repeated vomiting or nausea.Convulsions or seizures.Dilation of one or both pupils of the eyes.Clear fluids draining from the nose or ears.Inability to awaken from sleep.More items...•
How long can you live with brain trauma?
Despite initial hospitalization and inpatient rehabilitation services, about 50% of people with TBI will experience further decline in their daily lives or die within 5 years of their injury. Some of the health consequences of TBI can be prevented or reduced.
Which head injury is most serious?
Though it isn't as outwardly visible as other forms of brain injury, a diffuse axonal injury is one of the most dangerous types of head injuries. It can lead to permanent brain damage and even death.
How does uncal herniation cause death?
Uncal herniation occurs when rising intracranial pressure causes portions of the brain to move from one intracranial compartment to another. It is a life-threatening neurological emergency and indicates the failure of all adaptive mechanisms for intracranial compliance.
What is the most severe complication of traumatic brain injury?
Altered consciousness Moderate to severe traumatic brain injury can result in prolonged or permanent changes in a person's state of consciousness, awareness or responsiveness. Different states of consciousness include: Coma. A person in a coma is unconscious, unaware of anything and unable to respond to any stimulus.
Can you survive an uncal herniation?
Background: Uncal herniation (UH) caused by head trauma may become a fatal process if not treated rapidly.
Why is brain herniation important?
Brain herniation, also called brain code, requires early diagnosis and prompt management in order to prevent irreversible pathological cascades that eventually lead to respiratory arrest and subsequent death. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of brain herniation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and improving care for patients with this condition.
Why is brain herniation labeled as a brain code?
Brain herniation can be labeled as “brain code” to connate the emergent need to timely counteract such disastrous brain processes. [1]
What causes tonsillar herniation?
Central involves herniation of both temporal lobes through the tentorial notch. A tonsillar herniation is caused by an infratentorial mass, forcing the cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum. Upward herniation occurs when an infratentorial mass compressed the brainstem. Etiology.
What is the difference between anterior and posterior transalar herniation?
In the posterior (descending) variant of transalar herniation, there may be infarction within the middle cerebral artery territory resulting from its compression within the sphenoid ridge. In anterior (ascending) transalar herniation, compression of the supra-clinoid segment of the internal carotid artery against the anterior clinoid process leads to infarction within the territory of anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
Why do you need to be paralyzed when you have mechanical ventilation?
Most patients require mechanical ventilation and need to be paralyzed to avoid straining or agitation. Sedatives should be used to calm the patient.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Which part of the brain is pushed against the falx cerebri?
Subfalcine involves the cingulate gyrus, which is pushed against the falx cerebri.
How to reduce swelling in brain after herniation?
This may be done by the following: Placing a drain into the brain to help remove cerebrospinal fluid. Utilizing corticosteroids to try and reduce swelling. Diuretics which remove fluid from the body so as to reduce pressure from the brain.
What is the Prognosis of Brain Herniation?
Unfortunately, the prognosis of an individual with Brain Herniation is quite poor as the cause of the condition in itself decreases the life span of the patient such as a brain abscess or a brain tumor, which further decreases as a result of the swelling and increased pressure in the brain caused by Brain Herniation.
What Causes Brain Herniation and What are the Risk Factors?
The main cause of Brain Herniation is anything which increases pressure within the brain causing the brain to move from its position. Head injury, brain tumor, brain abscess, or strokes are the main causes that result in swelling and increased pressure in the brain causing Brain Herniation. A Brain Herniation can occur due to the following:
What is the tissue that supports the brain?
Anatomically speaking, the brain is supported within the skull by an extremely tough tissue called tentorium. This tissue has an opening in it which connects the brainstem to the brain.
What are the symptoms of a herniated brain?
What are the Symptoms of Brain Herniation? 1 Coma 2 Headache 3 Lethargy 4 Loss of all brainstem reflexes 5 Loss of consciousness 6 Respiratory arrest 7 Dilated pupils.
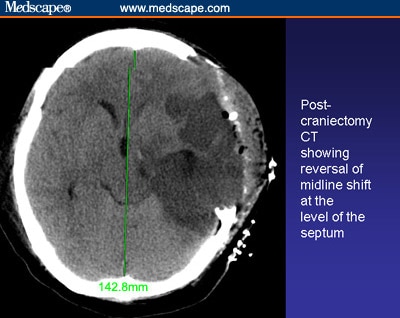
Can a CT scan show a brain herniation?
It should be noted that the location where the Brain Herniation occurs and the actions that the area controls in the body will be severely affected. Advanced imaging studies like CT and MRI scan of the brain will clearly show a change in the anatomical position of the brain and pinpoint the diagnosis of Brain Herniation.
Which structure is herniated in the brain?
Brain herniation is classified based on the structure through which tissue is herniated: Transtentorial (uncal) herniation: The medial temporal lobe is squeezed by a unilateral mass across and under the tentlike tentorium that supports the temporal lobe.
What nerves are involved in herniation?
As herniation progresses, the ipsilateral cerebral peduncle. In about 5% of patients, the contralateral 3rd cranial nerve and cerebral peduncle. Eventually, the upper brain stem and the area in or around the thalamus.
What is an upward transtentorial herniation?
Upward transtentorial herniation can occur when an infratentorial mass (eg, tumor in the posterior fossa, cerebellar hemorrhage) compresses the brain stem, kinking it and causing patchy brain stem ischemia. The posterior 3rd ventricle becomes compressed.
Why does the skull have a cushing reflex?
Because the skull is rigid after infancy, intracranial masses or swelling may increase intracranial pressure, sometimes causing protrusion (herniation) of brain tissue through one of the rigid intracranial barriers (tentorial notch, falx cerebri, foramen magnum). When intracranial pressure is increased sufficiently, regardless of the cause, Cushing reflex and other autonomic abnormalities can occur. Cushing reflex includes systolic hypertension with increased pulse pressure, irregular respirations, and bradycardia.
Why do temporal lobes herniate?
Central herniation: Both temporal lobes herniate through the tentorial notch because of bilateral mass effects or diffuse brain edema.
What are the symptoms of a compressed hernia?
Specific symptoms vary based on which structures are compressed; patients also have impaired consciousness and other neurologic deficits caused by the disorder causing herniation.
How to maximize venous outflow from the head?
Position: Positioning the patient to maximize venous outflow from the head can help minimize increases in ICP. The head of the bed can be elevated to 30° (with the head above the heart) as long as cerebral perfusion pressure remains at the desired range. The patient’s head should be kept in a midline position, and neck rotation and flexion should be minimized. Tracheal suctioning, which can increase ICP, should be limited.
What is the cause of brain herniation?
Brain herniation occurs when pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure) is increased, causing the brain to be pushed sideways and downward through small natural openings in the relatively rigid sheets of tissue that divide the brain into compartments. Brain herniation is a medical emergency.
What causes a herniated brain?
Brain herniation may occur when a brain tumor, bleeding in the brain, another mass, or a disorder (such as liver or kidney failure) greatly increases pressure within the skull.
Why do people with brain herniation need a ventilator?
If doctors suspect that the pressure within the skull is increased, a breathing tube is inserted through the mouth so that mechanical ventilation can be used to make sure that enough carbon dioxide is exhaled and to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood. Most people with brain herniation need a mechanical ventilator to breathe for them. Mechanical ventilation is also used to quickly decrease the increased pressure within the skull.
How does mechanical ventilation help with herniation?
As a result, blood vessels in the undamaged part of the brain narrow, and less blood reaches the brain. This measure quickly but temporarily lowers pressure within the skull and temporarily stops herniation . The beneficial effect of hyperventilation lasts about 30 minutes. Doctors use this time to start treatments that can stop herniation, such as drugs and surgical procedures, which take more time.
What happens if the brain is pushed?
As a result, brain tissue may be damaged. If pressure is put on the areas of the brain that control consciousness, stupor or coma results. If the pressure is high enough, the brain may be forced through small openings in these dividers. This life-threatening disorder is called brain herniation. Herniation can further damage brain tissue, making an already dire condition worse.
What is the mass in the brain called?
Masses in the brain, such as brain tumors, areas of swelling (edema), an accumulation of blood ( hematoma ), or a pocket of pus ( abscess)
Can a brain herniation cause symptoms?
People with brain herniation may have symptoms of the disorder causing the problem. They may also have various symptoms depending on which part of the brain is being compressed. These symptoms include
Why is herniated brain tissue surgically reduced?
The herniated brain tissue requires surgical reduction as it is at risk of ischemia and venous infarction from occluded cortical veins.
What is the most common brain herniation?
Subfalcine herniation or cingulate herniation, the most common brain herniation pattern, is characterized by displacement of the brain (typically the cingulate gyrus) beneath the free edge of the falx cerebri due to raised intracranial pressure.
What happens if a herniated primary lesion is large enough?
If the primary lesion becomes large enough, uncal or central herniation may develop. As the lesion grows and herniation becomes prominent, symptoms progress and patients may develop anisocoria, a decreased level of consciousness, changes in respiratory pattern, changes in muscle tone and posturing.
Why is uncal herniation bad?
Uncal herniation carries a bad prognosis due to the direct compression of the vital midbrain centers. They often require emergency neurosurgical decompression.
Why is my subfalcine hernia missed?
Subfalcine herniation may present with very subtle clinical symptoms. The hernia may be missed because the symptoms don’t warrant neural imaging.
What is the term for the extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cereb?
The tentorium is an extension of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum. There are two major classes of herniation: supratentorial and infratentorial. Supratentorial refers to herniation of structures normally found above the tentorial notch, and infratentorial refers to structures normally found below it.
What is the name of the condition where the brain is displaced?
Brain herniation is also called cerebral herniation, acquired intracranial herniation or brain herniation syndrome, is a condition in which a portion of the brain, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood vessels is displaced because of increased pressure inside the skull. Increase in pressure results in progressive damage to brain tissue that may include life-threatening damage to the brainstem.
What is the term for a herniated brain?
A cerebral herniation or brain herniation is a serious medical condition that happens when brain tissues move from one part of the brain to another adjacent part of the brain. It is usually caused when another condition causes swelling or pressure inside the brain. Cerebral herniations are severe and need immediate treatment.
What causes cerebral herniation?
Strokes. Both ischemic strokes (caused by blocked arteries) and hemorrhagic strokes (caused by excess bleeding) can lead to cerebral herniations. Strokes cause stress and damage to brain cells, leading to cerebral herniations.
Where do subfalcine herniations occur?
Subfalcine herniations. These take place in a part of the brain called the cingulate gyrus. The cingulate gyrus is a part of the brain just behind the frontal lobe. During these herniations, the cingulate gyrus is pushed into another part of the brain that is much deeper and farther back into the skull.
Does radiation make your brain swell?
Radiation therapy. Radiation treatments often make the brain swell. This is usually a short-term swelling, but you should pay attention if you begin to experience severe headaches, sickness, or seizures after your radiation treatment.