Terms in this set (55)
- In an atom, all of the positive and negative charges are randomly distributed.
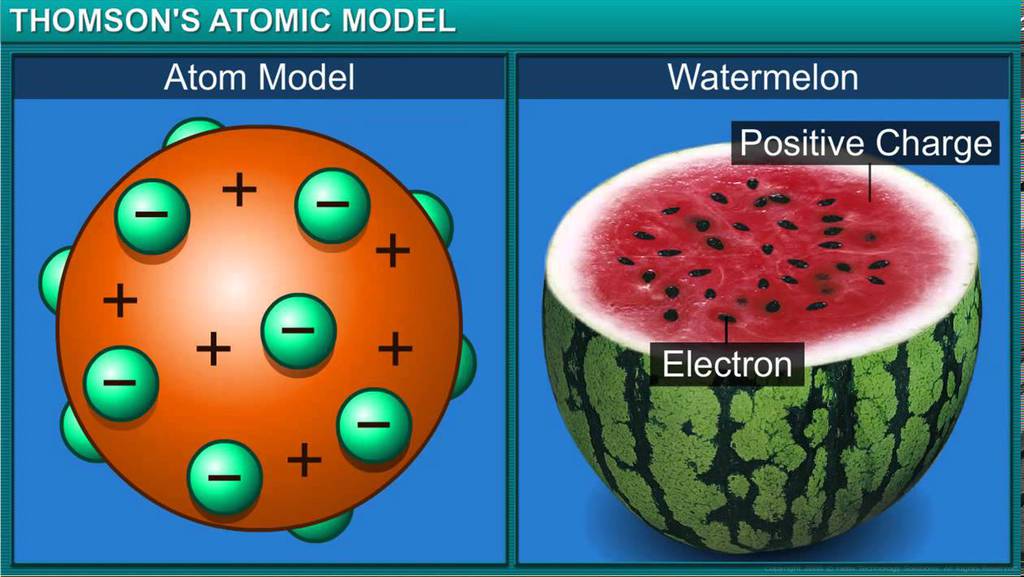
- In an atom, positively charged particles are dispersed in the space surrounding the negatively charged sphere.
- In an atom, the positive charges are located in a small core within the atom called the nucleus.
What is the distribution of charge in an atom?
The number of positively charged protons equals the number of negatively charged electrons, thus making the atom electrically neutral. So, the distribution of charge in an atom is thus one in which a positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons.
How is charge distributed over a conductor?
If the surface of the conductor is smooth and regular, like a sphere, the charges will push each other away until they all end up exactly the same distance from each other. Charge will be evenly distributed over the surface of a regularly shaped conductor.
Where is charge located in an atom?
There are 2 places where charge is located in the atom: the nucleus contains neutrons (zero charge) and protons (positive charge) Around the nucleus there are electrons located on electron shields and the charge of electrons is equal to the charge of protons in the nucleus, but have negative sign.
Does the charge distribution depend on the shape of the object?
Unlike conductors, the charge distribution on an insulator does NOT depend on the shape of the object. Charges stay wherever you put them, regardless of the shape or size of the object!
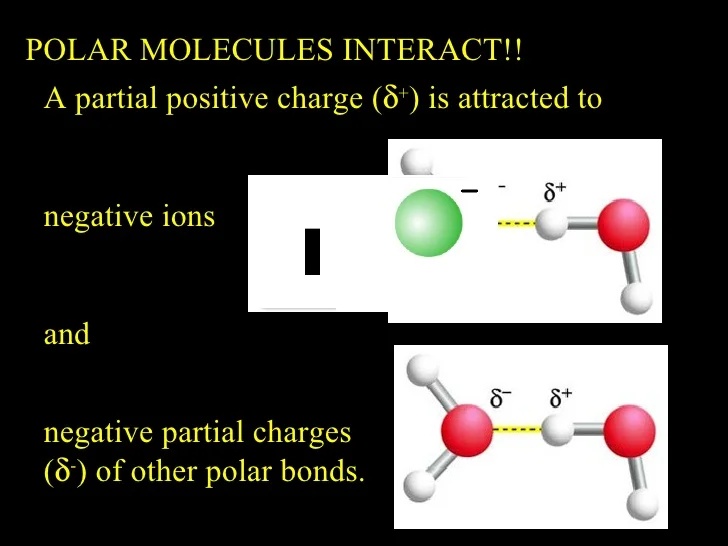
How is charge distributed in a molecule?
If a molecule has no net electrical charge, its negative charge is equal to its positive charge. The forces experienced by such molecules depend on how the positive and negative charges are arranged in space.
How is mass and charge distributed in an atom?
1:412:57(c) Describe the distribution of mass and charges within an atomYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe can see that majority of the mass is contained in a very very small region of space at the centerMoreWe can see that majority of the mass is contained in a very very small region of space at the center and the nucleus of the atom. So almost all the mass of the atom is contained in the nucleus.
How do you find the charge distribution?
2:207:40Understanding charge Distributions - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe cannot identify this charge a here or charge Q 1 here and Q 2 here no it's a continuum. OverMoreWe cannot identify this charge a here or charge Q 1 here and Q 2 here no it's a continuum. Over there and that's the whole idea behind continuous charge distribution.
What is charge distribution theory?
The charge distribution around a central ion produces an electric field with the local symmetry of the environment. This crystal field makes a contribution to the potential energy. V C r = ∫ e ρ R r − R d R ≈ e ∑ i q i r − R i.
How are the protons neutrons and electrons that make up an atom distributed?
Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, with electrons in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.
How does an atom become negative or positive?
The atom that has lost an electron becomes a positively charged ion (called a cation), while the atom that picks up the extra electron becomes a negatively charged ion (called an anion). Opposite charges attract one another while similar charges repel one another.
How does charge distribute itself across a conductor?
The distribution of charge is the result of electron movement. Since conductors allow for electrons to be transported from particle to particle, a charged object will always distribute its charge until the overall repulsive forces between excess electrons is minimized.
Do charges distribute evenly?
If the surface of the conductor is smooth and regular, like a sphere, the charges will push each other away until they all end up exactly the same distance from each other. Charge will be evenly distributed over the surface of a regularly shaped conductor.
Is charge always uniformly distributed?
Consider two conductors, one in the shape of a circle and one in the shape of a line. Charges are distributed uniformly along both conductors. With the circular shape, each charge has no net force on it, because there is the same amount of charge on either side of it and it is uniformly distributed.
What are the types of charge distribution?
Types of Charge DistributionType of charge distributionDenoted byUnitLine Chargeλ (Line charge density)C/mSurface Chargeσ (surface charge density)C/m2Volume Chargeρ (volume charge density)C/m3
How many types of charge distributions are there?
The generalization of Coulomb's force law allows for all four types of charge distribution (volume, surface, linear, and point): [1.22]
What is linear distribution of charge?
CHARGE DISTRIBUTIONS CHARGE DISTRIBUTIONS There are three types of charge distributions : a) Linear Charge Distribution. In this distribution the charge is distributed uniformly along a line.
How are electrons bound in conductors?
In conductors, some of the electrons are loosely bound to each atom so they can easily move around, allowing charge to flow and redistribute throughout the conductor. Lesson. Quiz. Course.
What happens when an object has excess charge?
When an object acquires some excess charge, what happens? Does the charge stay where you put it or does it move? Well, that depends on what type of material the object is made of. Certain materials, called conductors, allow electric charge to move pretty freely through them. Most metals are good conductors, so when a metal object is given some charge, it's free to move around. Other materials, like plastic and rubber, are called insulators because they don't allow electric charges to move through them.
Do charges move away from each other?
The charges aren't able to move away from each other no matter how much they repel. Unlike conductors, the charge distribution on an insulator does NOT depend on the shape of the object. Charges stay wherever you put them, regardless of the shape or size of the object!
Can an insulator be charged?
Since insulators don't contain mobile charge carriers like conductors, charges can't easily move through them in the same way. However, that doesn't mean that an insulator can't be charged! What it does mean is that, in an insulator, charges stay wherever they're initially placed.
What is the charge of a drop?
There can be many sources of this charge, typically charge separation by the differential motion of drops of different sizes, or the always-present electric current between ionosphere and the Earth's surface, which can charge up individual droplets at cloud boundaries. A net charge corresponds to an electrostatic energy on the drop which modifies the Gibbs free energy budget and therefore the saturated vapour pressure around the drop.
What happens if the charge does not move?
In electrostatics, we study the fields accompanying an immobile charge distribution. If the charge does not move, there is no current and no magnetic field. In such a situation, we need use only the following equations from the set (4.11 ):
What happens when an atom is charged?
A charged atom has either too many or too few electrons. In DS1, atoms are heated until they are very high energy and unstable. The are then hit by electrons that are discharged by a cathode ray in the thruster chamber. When the electrons hit the atoms in the chamber, they cause some of the electrons in the atoms to be stripped or knocked away.
What happens when electrons hit atoms?
When the electrons hit the atoms in the chamber, they cause some of the electrons in the atoms to be stripped or knocked away. The mass of superheated, charged atoms with disassociated electrons becomes a plasma. When one or more electrons is knocked off of an atom, it becomes positively charged. It is now an positive ion.