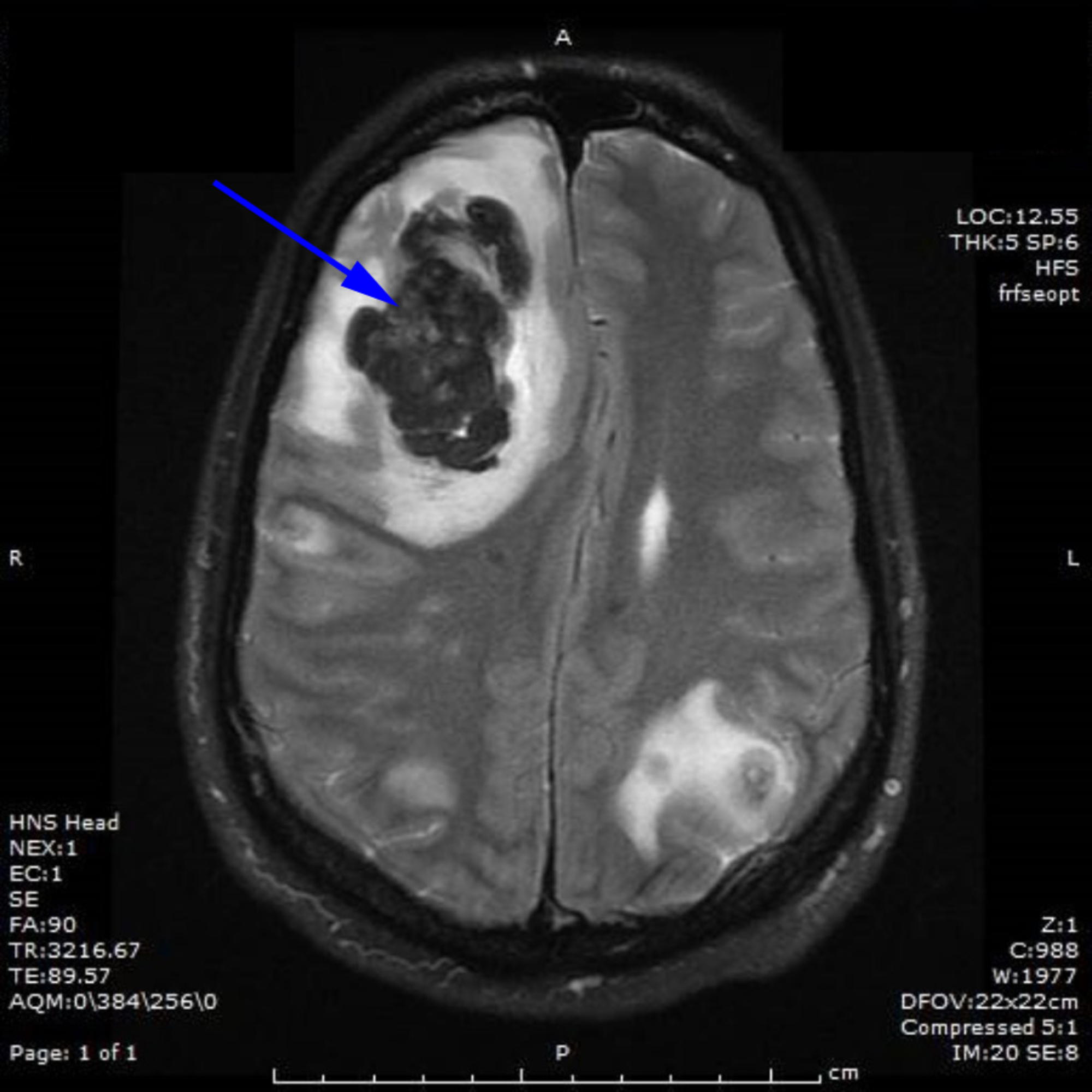
What are the treatment options for choriocarcinoma in women?
Chemotherapy of choriocarcinoma and related trophoblastic tumors in women. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Oct 18;168(7):845–854.
Is choriocarcinoma curable?
Choriocarcinoma is a rare type of cancer. It usually develops from cells that remain inside the body after a pregnancy. In the vast majority of cases, choriocarcinoma is curable.
What are the treatment options for CNS metastases of choriocarcinoma?
^ Rustin GJ, Newlands ES, Begent RH, Dent J, Bagshawe KD (July 1989). "Weekly alternating etoposide, methotrexate, and actinomycin/vincristine and cyclophosphamide chemotherapy for the treatment of CNS metastases of choriocarcinoma".
What is choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma forms when cells that were part of the placenta in a normal pregnancy become cancerous. It can happen after a miscarriage, abortion, ectopic pregnancy, or molar pregnancy -- when an egg is fertilized, but the placenta develops into a mass of cysts instead of a fetus.

Can choriocarcinoma be cured?
If your tumor is low-risk, meaning it's small and hasn't spread, chemotherapy is the main treatment. You'll get it until there are no signs of cancer in your body based on hCG levels. If your cancer is high-risk, you may need surgery and chemo, or surgery, chemo, and radiation.
Can you survive choriocarcinoma?
Survival for persistent trophoblastic disease and choriocarcinoma is very high. Nearly all women are cured. The statistics here are intended as a general guide and can't tell you what is likely to happen in your individual case. Your doctor can give you more information about your own outlook (prognosis).
What chemotherapy is used for choriocarcinoma?
If you have high risk PTD or choriocarcinoma, you might have the drug methotrexate by drip into a vein (intravenous infusion). This is followed a week later by the drugs actinomycin and etoposide. Or you may have a combination of chemotherapy drugs called EMA-CO.
How long can you live with choriocarcinoma?
While 5-year overall survival and cure for this population is greater than 95%, choriocarcinoma is an aggressive subtype of this disease with far worse prognosis--5-year survival for choriocarcinoma is less than 80%.
How quickly does choriocarcinoma spread?
Choriocarcinoma can develop some months or even years after pregnancy and can be difficult to diagnose, because it is so unexpected. They can grow quickly and might cause symptoms within a short period of time. They can spread to other parts of the body but are very likely to be cured by chemotherapy treatment.
How long is the treatment for choriocarcinoma?
Treatment for choriocarcinoma usually takes 4-5 months to complete and the cure rate is over 95%.
Is methotrexate used in choriocarcinoma?
Conclusion: Methotrexate is routinely used in a parenteral intramuscular fashion for the treatment of gestational choriocarcinoma.
What are the signs and symptoms of choriocarcinoma?
The symptoms of gestational choriocarcinoma may include : bleeding from the vagina. infections that cause vaginal discharge, pelvic cramps, and fever. swelling around the stomach area....Signs that this may have happened include:coughing up blood.dry cough.chest pain.breathing difficulties.
Is methotrexate a chemo drug?
Methotrexate is one of a group of chemotherapy drugs called anti metabolites. These stop cells making and repairing DNA. Cancer cells need to make and repair DNA so that they can grow and multiply. Methotrexate stops the cells working properly.
Can Stage 4 choriocarcinoma be cured?
Fortunately, most women who are found to have choriocarcinoma can be cured; treatment with a combination of chemotherapy agents such as etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide and vincristine (EMA-CO) is found to be very effective at achieving remission.
What are the stages of choriocarcinoma?
Stage I: Disease is only in the uterus. Stage II: GTD extends outside the uterus but is limited to the genital structures. Stage III: GTD extends to the lungs and may or may not involve the genital tract. Stage IV: GTD has extended to other distant sites, called metastasis.
Is choriocarcinoma benign or malignant?
A choriocarcinoma is a malignant tumor that forms from trophoblast cells and spreads to the muscle layer of the uterus and nearby blood vessels.
How to diagnose choriocarcinoma?
If your doctor thinks you have choriocarcinoma, they’ll do some tests: 1 A pelvic exam to feel for lumps or unusual changes 2 A test to look for levels of a hormone called hCG. They’ll be high if you have a GTD. 3 Blood and urine tests 4 An exam to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body 5 Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, ultrasound, or X-ray
Can choriocarcinoma cause bleeding?
If the choriocarcinoma is in your vagina, it could cause bleeding. If it has spread to your abdomen, you might also have pain or pressure there. If it has spread to other parts of your body like your lungs or brain, you may notice: Cough. Trouble breathing.
How often does choriocarcinoma occur?
Choriocarcinoma happens in about 1 in every 40,000 pregnancies. In rare cases, it can develop in males as a rare type of testicular cancer. The outlook for someone with choriocarcinoma who receives treatment is very positive. The most common treatment is chemotherapy.
What is the most common form of choriocarcinoma?
Gestational choriocarcinoma, which develops in the uterus, accounts for the majority of choriocarcinoma cases. It is a rare form of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD).
How does gestational choriocarcinoma work?
gestational choriocarcinoma with chemotherapy. It works by either killing the cancerous cells or stopping the tumor from growing. Some people might need more than one type of chemotherapy. If the tumor has spread, the person might also need radiation therapy and surgery. In many cases, surgeons will be able to remove.
What are the different types of tumors?
The tumors grow quickly and can spread through the blood to other parts of the body, including the: 1 lungs (most common) 2 liver 3 brain 4 kidney 5 bowel
Can choriocarcinoma be treated with chemotherapy?
Doctors can almost always cure gestational choriocarcinoma with chemotherapy. The survival rates range from about 90 to 100%, depending on a person’s risk factors.
How many pregnant women have choriocarcinoma?
In the United States, about 1 in 40,000 pregnant people will go on to develop choriocarcinoma.
Does choriocarcinoma cause symptoms?
According to the American Cancer Society, choriocarcinoma does not always cause symptoms.
What is the first line of treatment for choriocarcinoma?
In the United States and the United Kingdom, multi-agent chemotherapy with etoposide, actinomycin D, methotrexate, folinic acid, cyclophosphamide, and vincristine are utilized as first-line treatment for patients with high-risk choriocarcinoma. [1][12]
What should a healthcare professional do for choriocarcinoma?
The healthcare professional should conduct a thorough history and physical examination of any patient with suspected choriocarcinoma. In women, clinicians should pay particular attention to reproductive history because spontaneous abortions and molar pregnancies increase the risk for choriocarcinoma. One should consider post-menopausal bleeding suspicious. Choriocarcinoma tends to metastasize, and clinicians should note symptoms that arise from other organ systems, for example, hemoptysis or gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. [5]
What is the treatment for stage III choriocarcinoma?
In the United States, low-risk (cumulative score less than 7, refer to staging section below) and stage I to III choriocarcinoma is treated with either methotrexate or actinomycin D chemotherapy with survival rates approaching 100%.
When was choriocarcinoma first described?
Gestational trophoblastic diseases were first described in 400 BC by Hippocrates.[1] Choriocarcinoma, a subtype of gestational trophoblastic disease,[2] is a rare and aggressive neoplasm.[3] The 2 significant choriocarcinoma subtypes, namely: gestational and non-gestational, have very different biological activity and prognoses. Choriocarcinoma predominately occurs in women but can also occur in men, usually as part of a mixed germ cell tumor.
What percentage of ovarian neoplasms are choriocarcinoma?
Choriocarcinoma composes less than 0.1% of primary ovarian neoplasms in a pure form. [6]
Is choriocarcinoma a molar pregnancy?
Choriocarcinoma develops from an abnormal trophoblastic population undergoing hyperplasia and anaplasia, most frequently following a molar pregnancy.[3] There are 2 forms of choriocarcinoma, gestational and non-gestational . The former arises following a hydatidiform mole, normal pregnancy, or most commonly, spontaneous abortion, while non-gestational choriocarcinoma arises from pluripotent germ cells.[4] Non-gestational choriocarcinomas form in males or females, in the gonads, or midline structures with pluripotent germ cells. [4]
Is choriocarcinoma a neoplastic disease?
Choriocarcinoma is a rare, aggressive neoplastic type of trophoblastic disease. The 2 major types of choriocarcinoma are gestational and non-gestational, and they have very different pathophysiology and prognosis. Choriocarcinoma predominantly occurs in women but can also occur in men, usually as part of a mixed germ cell tumor. This activity reviews the clinical evaluation of choriocarcinoma and the role of the interprofessional team in caring for patients with this disease.
Why do choriocarcinoma patients have poor prognosis?
Because of early spread and inherent resistance to anticancer drugs, patients have poor prognosis. Elements of choriocarcinoma in a mixed testicular tumor have no prognostic importance. Choriocarcinomas can also occur in the ovaries and other organs.
Where does choriocarcinoma occur?
Rarely, choriocarcinoma occurs in primary locations other than the placenta; very rarely, it occurs in testicles. Although trophoblastic components are common components of mixed germ cell tumors, pure choriocarcinoma of the adult testis is rare. Pure choriocarcinoma of the testis represents the most aggressive pathologic variant of germ cell tumors in adults, characteristically with early hematogenous and lymphatic metastatic spread. Because of early spread and inherent resistance to anticancer drugs, patients have poor prognosis. Elements of choriocarcinoma in a mixed testicular tumor have no prognostic importance.
Can choriocarcinoma occur in the testicles?
Choriocarcinoma of the placenta during pregnancy is preceded by: Rarely, choriocarcinoma occurs in primary locations other than the placenta; very rarely, it occurs in testicles. Although trophoblastic components are common components of mixed germ cell tumors, pure choriocarcinoma of the adult testis is rare.
Is choriocarcinoma rare?
Choriocarcinoma arising in the testicle is rare, malignant and highly resistant to chemotherapy. The same is true of choriocarcinoma arising in the ovary. Testicular choriocarcinoma has the worst prognosis of all germ-cell cancers. Stage I choriocarcinoma. Stage 2 choriocarcinoma. Stage 3 choriocarcinoma.
Is choriocarcinoma a hydatidiform mole?
Treatment. Since gestational choriocarcinoma (which arises from a hydatidiform mole) contains paternal DNA (and thus paternal antigens), it is exquisitely sensitive to chemotherapy. The cure rates, even for metastatic gestational choriocarcinoma, more than 90% when using chemotherapy for invasive mole and choriocarcinoma.
What is the treatment for choriocarcinoma?
Chemotherapy treatment. Chemotherapy can be used to treat persistent trophoblastic disease (PTD) and choriocarcinoma. PTD is a tumour that can form in the womb after an abnormal type of pregnancy called a molar pregnancy. Choriocarcinoma is a very rare tumour that can occur after a normal pregnancy, a molar pregnancy, ...
How to treat high risk choriocarcinoma?
If you have high risk PTD or choriocarcinoma, you might have the drug methotrexate by drip into a vein (intravenous infusion). This is followed a week later by the drugs actinomycin and etoposide.
What to do if your HCG is above a certain level?
If your hCG is above a certain level you will have one of the following treatments: EMA-CO – etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin one week , followed by cyclophosphamide and vincristine (oncovin) a week later. actinomycin and etoposide every day for 3 days, with a 1 week break before starting a new treatment cycle.
How does chemo work?
Chemotherapy uses anti cancer (cytotoxic) drugs to destroy tumour cells. They work by disrupting their growth. Chemotherapy circulates in the bloodstream around the body. Your doctors will look at various factors to find the stage of your disease.
What are the side effects of chemotherapy?
Common chemotherapy side effects include: Contact your doctor or nurse immediately if you have signs of infection, including a temperature above 37.5C or below 36C, or generally feeling unwell. Infections can make you very unwell very quickly. Tell your treatment team about any side effects that you have.
Can chemo help with choriocarcinoma?
Chemotherapy for persistent trophoblastic disease and choriocarcinoma can be difficult to cope with. Tell your doctor or nurse about any problems or side effects that you have. The nurse will give you telephone numbers to call if you have any problems at home.
