How is chromatography
Chromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid called the mobile phase, which carries it through a structure holding another material called the stationary phase. The various constituents of th…
How is chromatography resolution calculated?
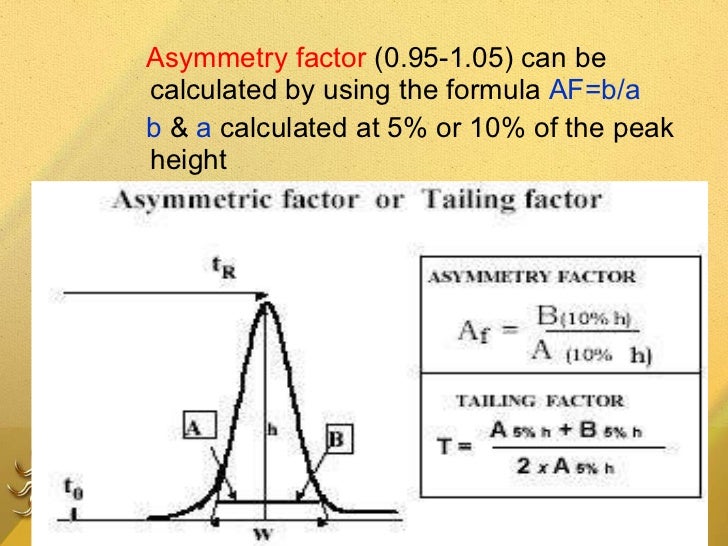
How is chromatography resolution calculated? Resolution is calculated using the separation of two peaks in terms of their average peak width at the base (tR2 > tR1). The width at the base of each peak is the segment of the peak base intercepted by the tangents drawn to the inflection points on either side of the peak as shown.
What is the equation for chromatography?
Using the theory of band broadening, the efficiency of chromatographic columns can be approximated by the van Deemter equation: (6) H = A + B u + C S u + C M u. where H is the plate height in centimeters and u is the linear velocity of the mobile phase in centimeters per second.
What are the steps in chromatography?
- Take a few leaves and crush them in a mortar.
- Spot a drop of the leaf extract on a strip of chromatographic paper ~ 0.5 cm above the edge of the paper. ...
- Place the strip of paper in a jar that contains a small volume of propanone (acetone). ...
- Let the solvent rise up the paper by capillary action. ...
What is resolution factor in chromatography?
Increase N (efficiency) by:
- Increasing column length
- Decreasing particle size
- Reducing peak tailing
- Increasing temperature
- Reducing system extra-column volume

How is chromatographic resolution calculated?
Equation (1) indicates that the resolution is the difference between peak retention times divided by the average peak width. In a peak with Gaussian distribution, the peak width is W = 4 σ (where σ is the standard deviation) and the peak FWHM is W0. 5h = 2.354σ.
What is the formula for calculating resolution?
In order to increase the resolution (d=λ/2 NA), the specimen must be viewed using either shorter wavelength (λ) light or through an imaging medium with a relatively high refractive index or with optical components which have a high NA (or, indeed, a combination of all of these factors).
What does chromatography resolution measure?
In chromatography, resolution is a measure of the separation of two peaks of different retention time t in a chromatogram.
How is TLC resolution calculated?
The resolution was calculated by dividing the distance between two spots by the sum of the two spot radii. The resolution (RS) varied from the lowest 1.3 for (RS)-Bpl to 2.6 for (RS)-Atl.
What is resolution in liquid chromatography?
Resolution is an important HPLC performance indicator usually assessed by how quickly and how completely target components in a sample separate as they pass through a column. Resolution is measured by dividing the difference in peak retention times by the average peak width.
What two factors determine resolution?
The primary factor in determining resolution is the objective numerical aperture, but resolution is also dependent upon the type of specimen, coherence of illumination, degree of aberration correction, and other factors such as contrast-enhancing methodology either in the optical system of the microscope or in the ...
How do you calculate retention factor k?
f) The retention factor (k) is the ratio of the amount of analyte in the stationary phase to the amount in the mobile phase. It is generally calculated by k' = (tR - tM)/tM = tR'/tM.
How is HPLC result calculated?
concentration of sample= Area of sample/ Area of standard x concentration of standard .
How do you calculate retention time in chromatography?
4:168:33Retention Time - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd the emergence of a given solute that retention time can be calculated directly from theMoreAnd the emergence of a given solute that retention time can be calculated directly from the parameters of our chromatogram. Really the linear distance on the time axis between the point of injection.
How do you calculate Rf value for TLC?
In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin).
What is the resolution factor?
Resolution factor shows the accuracy of the quantitative analysis and resolution factor should be greater than 1.5 or specified in the individual monograph. Resolution factor can be calculated by following formula: R = 2(t2-t1)
What is the resolution of chromatography?
In general, resolution is the ability to separate two signals. In terms of chromatography, this is the ability to separate two peaks. Resolution, R, is given by where tr1 and tr2 and w1 and w2 are the times and widths, respectively, of the two immediately adjacent peaks. If the peaks are sufficiently close, which is the pertinent problem, w is nearly the same for both peaks and resolution may be expressed as
What is the second feature of chromatography?
The second feature important to efficiency and resolution is the width of the peak. Peaks in which the maxima are widely disengaged still may be so broad that the solutes are incompletely resolved. For this reason, peak width is of major concern in chromatography.
What determines the rate of migration of substances in chromatographic procedures?
The rates of migration of substances in chromatographic procedures depend on the relative affinity of the substances for the stationary and the mobile phases. Those solutes attracted more strongly to the stationary phase are held back relative to those solutes attracted more strongly to the mobile phase.
What is the concentration profile of a column?
There are two features of the concentration profile important in determining the efficiency of a column and its subsequent ability to separate or resolve solute zones. Peak maximum, the first, refers to the location of the maximum concentration of a peak. To achieve satisfactory resolution, the maxima of two adjacent peaks must be disengaged. Such disengagement depends on the identity of the solute and the selectivity of the stationary and mobile phases.
What is peak overlap in ultrafast chromatography?
One of the main problems in ultrafast chromatography is partial or complete peak overlap. As per Gidding’s statistical overlap theory, peak overlap cannot be avoided for a completely random sample for a column with a given peak capacity.
What is GC theory?
This chapter provides up-to-date theory of analytical gas chromatography (GC)—a technique of separation of components of mixtures ( samples) with the purpose of obtaining information about their molecular composition. The theory presented here is designed to address such issues as the effect of column dimensions, carrier gas type and flow rate, temperature programming, and other factors on duration of analysis, the number of peaks that can be resolved, detection limits, and the trade-offs between these performance factors. To get simple and insightful mathematical descriptions of these relations, simplicity of the basic models becomes more important than their accuracy. As a general trend, this chapter favors simplicity over unnecessary accuracy. The secondary factors complicating the models are typically ignored. The chapter starts with the review of relevant theoretical information regarding interaction of organic compounds with liquid polymers, properties of ideal gases, and flow of ideal gases. This information is then used as a basis for addressing such core issues of GC theory as formation of retention times and other parameters of eluting solutes; formation of peak spacing and factors affecting reversal of peak order; and formation of peak widths. This material is used then as the basis for the study of the column optimization—the optimal flow rate, optimal heating rate, and optimal trade-off between a column separation performance, analysis time, and detection limit. The study of the optimization is preceded by the review of the column performance metrics and by formulations of optimization goals.
Is resolution more accurate than most commonly employed resolution equations?
The concept of resolution in column chromatography is briefly reviewed. Two new resolution equations are compared with others previously introduced and are shown to be considerably more accurate than the most commonly employed resolution equations. The new equations are identical in form with the most commonly employed equations, a distinct advantage over previously introduced alternatives. For situations in which the plate counts of the peaks of interest differ by more than 20%, an accurate empirical resolution equation is proposed.
Credits
Soupayan banerjee has created this Calculator and 200+ more calculators!
Peak Resolution in Chromatography Solution
Retention Volume of Molecule 2 - Retention Volume of Molecule 2 is the volume that has passed through the column since the target molecule 2 was introduced onto the column. (Measured in Milliliter)
What is Column Chromatography?
Column chromatography separates substances based on differential adsorption of compounds to the adsorbent as the compounds move through the column at different rates which allow them to get separated in fractions. This technique can be used on a small scale as well as large scale to purify materials that can be used in future experiments.
How to Calculate Peak Resolution in Chromatography?
Peak Resolution in Chromatography calculator uses Peak Resolution = (Retention Volume of Molecule 2-Retention Volume of Molecule 1)/ ( (Width of Chromatographic Peak of Molecule 1+Widths of Chromatographic Peak of Molecule 2)/2) to calculate the Peak Resolution, The Peak Resolution in Chromatography formula is defined resolution is a measure of the separation of two peaks of different retention time in a chromatogram.
What is Multidimensional Chromatography?
Multidimensional chromatography uses a combination of several chromatography techniques, separation modes, and columns to separate multiple components. It achieves significantly higher separation than normal one-dimensional chromatography. Various separation modes and the corresponding mobile phases can be selected for HPLC, and the diverse permutations available suggest the possibility of achieving a degree of selectivity not possible using one-dimensional separation alone.
What is the resolution of a peak with Gaussian distribution?
In a peak with Gaussian distribution, the peak width is W = 4 σ (where σ is the standard deviation) and the peak FWHM is W0.5h = 2.354σ. Substituting these relationships into equation (1) gives results in equation (2).
What is the separation factor?
The separation factor is defined as the ratio of the retention factors ( k), as shown in equation (3).