How do you measure duration of contraction?
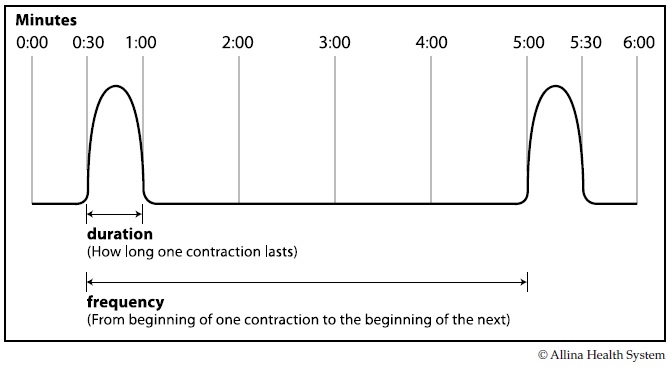
Duration is measured from the beginning of one contraction to the end of that contraction. Time the duration of a contraction by starting your timer when a contraction starts and stopping the timer when the contraction ends. Somewhere in the middle, you’ll feel a peak in intensity but wait until all sensation has stopped before you stop the timer.
How do you find the frequency of contractions?
Frequency of contractions – “How far apart are they?” Frequency is based on the time between the start of one contraction and the start of the next contraction. Time the frequency of contractions by noting the time when one contraction starts and the time when the next contraction starts.
What is duration and frequency of contractions?
You will need to know how long your contractions last (duration) and how close together they are (frequency). Duration is timed from when you first feel a contraction until it is over. This time is usually measured in seconds. Frequency is timed from the start of one contraction to the start of the next.
How do I time my contractions?
Here’s how to time your contractions: Make a note of the time when your first contraction starts (“time” on the table below) Then mark the length of time from the start of the contraction to the start of the next one (“frequency”)
How to tell how long a contraction lasts?
What is progressing contraction?
What information do you need to know when you call your health care provider?
Why is it important to keep a labor log?
How is frequency measured?
What does it mean when your contractions are not opening?
When are contractions considered regular?
See 4 more
About this website

How many mmHg is a strong contraction?
The intensity of Braxton Hicks contractions varies between approximately 5-25 mm Hg (a measure of pressure). For comparison, during true labor the intensity of a contraction is between 40-60 mm Hg in the beginning of the active phase.
How do you calculate contraction strength?
subtract the resting tone from the peak intensity of the contraction. add the 3 contractions together to get the MVUs. Montevideo units are calculated by obtaining the peak uterine pressure amplitude and subtracting the resting tone. Then adding up those numbers generated by each contraction within a 10-minute window.
How is contraction machine measured?
A nurse will wrap a belt around your waist and attach it to a machine called a tocodynamometer. The machine records the frequency and length of your contractions. Your doctor may also recommend monitoring your contractions at home.
What is normal contraction intensity?
During true labor, the intensity of a contraction is between 40-60 mmHg in the beginning of the active phase, which occurs when your cervix dilates from 6 to 10 centimeters, and your contractions become stronger, closer together and regular.
What is the 5 1 1 rule for contractions?
5-1-1- Rule: At term (actually after 36 weeks). When your contractions are 5 minutes apart, lasting 1 minute each for an hour consistently and increasing in strength/intensity.
What level is a strong contraction?
Active labor: The cervix will dilate from 4 cm to 7 cm and contractions will be stronger and last longer. Usually, they will last 45 to 60 seconds, with three minutes to five minutes between each one. This is the point where you should generally call your provider and/or head to the hospital or birth center.
What device is used to measure contractions?
A pressure-sensitive device called a tocodynamometer is placed on the mother's abdomen over the area of strongest contractions to measure the length, frequency, and strength of uterine contractions.
How many contractions should you have in 10 minutes?
Contact your midwifery team if: your contractions are regular and you're having about 3 in every 10-minute period.
What do strong contractions look like on monitor?
The red indicator on the bottom tracing shows the strength of a contraction, measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). 6 The higher the number, the stronger the contraction.
How many contractions per day is normal?
Your first contractions will start randomly, and you'll likely have three to four a day. Once a rhythm starts and you're having contractions every 10 minutes they should last for about 45 seconds.
How many contractions per hour are normal?
True Signs of Labor happen 4 times per hour or more, and get closer together (for example, they come every 15 minutes, and then every 10 or 5 minutes, etc.)
How many contractions is too many?
For most international obstetrical societies, 5 contractions per 10 min averaged over 30 min is considered as the upper limit of normal uterine activity. We hypothesize that it might be safer to adopt an upper limit of 4 contractions per 10 min.
What determines the strength of a mm contraction?
The higher the recruitment, the stronger the muscle contraction will be. The greater the cross-sectional area of the muscle, the more muscle fibres that can be activated simultaneously.
How is the contraction frequency calculated?
Contraction frequency is calculated from the start of one contraction to the start of the next one. For example, if the first contraction starts at 10 a.m. and the next contraction starts at 10:10 a.m., the contraction frequency is 10 minutes.
How do you calculate contraction intervals?
Measure the duration of each contraction by timing when it begins and when it stops. True contractions last about 30 seconds at the onset and get progressively longer up to 75 seconds and stronger. False labour contractions vary in length and intensity.
The Stages of Labor and How Long Labor Lasts - What to Expect
For now, it’s difficult to predict exactly how your birth experience will go down. Just like the baby you’re about to bring into this world, every labor and delivery experience is unique.. That said, unless things are cut short by a C-section, all women go through three precise stages of labor and childbirth: labor itself (which includes early labor, active labor and transitional labor ...
What Are Contractions?
As labor begins, your cervix starts to dilate (open) and efface (thin out), and the muscles around your uterus contract to help your baby move down and through the birth canal.
What are the signs of Braxton Hicks contractions?
Other signs of labor include your water breaking and a clear or pinkish vaginal discharge called the mucus plug.
What are the benefits of timing contractions?
One benefit of timing contractions is that it can help you tell the difference between true and false labor contractions. With false labor contractions, the contractions will likely go away with movement, will feel weak and irregular, and won’t increase in frequency over time.
How long does a contraction last?
How long do contractions last? A contraction typically lasts for about 30 to 90 seconds.
How to tell if you are in labor?
Other signs of labor include your water breaking and a clear or pinkish vaginal discharge called the mucus plug.
How to pass time during contractions?
While you wait at home, you might like to try to pass the time by doing things like. breathing and relaxation exercises. going for a walk. lying down for a nap.
When to call your healthcare provider for labor?
Generally speaking, it’s a good idea to call your healthcare provider when you first notice the signs of labor such as your water breaking, the mucus plug discharge, or contractions.
How long should you be in labor for 5-1-1?
The 5-1-1 rule also takes into account the “How long have you been feeling them?” since contraction patterns should be recorded for at least one hour. This rule of thumb often comes from your care team and/or birth educator as a way to know when early labor becomes active labor. It may take many forms, you may hear 4-1-1 or 3-1-1, so talk with your care team about their specific recommendations.
How is duration measured?
Duration is measured from the beginning of one contraction to the end of that contraction.
What is frequency based on?
Frequency is based on the time between the start of one contraction and the start of the next contraction.
How to accurately time a contraction?
To time contractions, there are a few basics: note the start of one contraction, note the end of that contraction, and then note the start of the next contraction.
What happens when you have contractions in your abdomen?
The abdomen becomes very hard. The contractions tighten and thicken the upper part of the uterus (fundus) while stretching and relaxing the lower portion and cervix. These series of contractions help the baby pass through the birth canal.
What is contraction in labor?
Labor contractions are periodic tightening and relaxing of uterine muscles, which are stimulated by the oxytocin hormone released by the pituitary gland. They begin as cramps in the back and move along the abdomen in a wave-like manner. The abdomen becomes very hard.
What is a momjuction?
MomJunction provides the contraction timer, a tool that automatically records contractions for you. You can even download and print your count and share it with your doctor, friends, or family.
Why is a stopwatch important for labor?
A clock or stopwatch can keep track of the contractions frequency and duration , but it may not be precise. Therefore, a reliable tool is designed to assist moms-to-be to calculate their contractions.
Where do contractions begin?
True contractions begin atthe back and spread towards abdomen. Braxton Hicks are only in the belly and can cause hardening in a part of the belly. They are mostly not painful. You will get around four to five contractions at a time and then they disappear. True contractions, however, get stronger, closer, and more painful with time (4).
When do Braxton Hicks contractions begin?
These contractions are irregular and short, and are not very painful. The Braxton Hicks Contractions begin in the 5th or 7th month and go on until delivery. Q.
How far apart should contractions be?
If your contraction timing is three to four minutes apart and does not cease even after walking or lying on your left side, you could be in labor. It’s time for you to contact your gynecologist or get into the hospital. (5)
How to tell how long a contraction lasts?
You will need to know how long your contractions last (duration) and how close together they are (frequency). Duration is timed from when you first feel a contraction until it is over. This time is usually measured in seconds. Frequency is timed from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. It includes the contraction as well as the ...
What is progressing contraction?
Progressing contractions. Contractions that are lasting longer and getting closer together are considered to be progressing. Over the course of labor, contractions get longer, stronger and closer together. Non-progressing contractions. Contractions that are not getting longer, stronger and closer together.
What information do you need to know when you call your health care provider?
When you call your health care provider or hospital, you will need to give information about the duration and frequency of your contractions and about how long this has been the pattern.
Why is it important to keep a labor log?
Keeping a written labor log can help you see the pattern of your contractions. Partners and labor companions usually are the ones who time the contractions and keep the log. However, it is more important that you get the labor support you need than to have a complete labor log.
How is frequency measured?
Frequency is timed from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. It includes the contraction as well as the rest period until the next contraction begins. This time is measured in minutes.
What does it mean when your contractions are not opening?
This may mean that the contractions are not opening the cervix. It usually means that other work is being done, such as turning your baby to a different position, softening or thinning the cervix.
When are contractions considered regular?
Contractions are considered regular when the duration and frequency are stable over a period of time. An example is contractions lasting 60 seconds and coming five minutes apart for an hour. Irregular contractions. Contractions are irregular when there isn't a stable pattern.
